The history of the universe began about 14 billion years ago. After the Big Bang, which turned out to be the moment of its birth, outer space began a sudden violent expansion, and this process continues to this day. With the help of modern telescopes aimed towards space, it is possible to fix the early glow of the elements of the Universe and, in fact, take a picture of it from the deep past. The more successfully such a “device” is located and the more powerful it has, the more years it will be possible to look back. However, the study of the history of the development of space is far from one question, the answer to which can be the most modern (by today’s standards, of course) James Webb telescope.
To the point:
- Not an observatory, but the hope of mankind: 10 space facts about the Webb telescope.
- Humanity hopes for the Webb telescope – perhaps in vain. 8 problems he may face.
James Webb will help find life in the solar system
While scientists can not explore the satellites of the giant planets
In the 90s, the Galileo spacecraft, named after Galileo, who discovered Jupiter’s moon Europa, analyzed the surface of this celestial body. It was possible to find out that under the massive “crust” of ice encircling the entire satellite, there is an ocean. The availability of water is usually one of the key factors in the search for the potential origin of life. It is likely that in the future NASA or similar organization will send a probe to Europa for detailed study, but for now, scientists will be able to observe it using the James Webb telescope (Hubble was not powerful enough for this). It will also help in the study of another satellite of Jupiter – Titan. It also contains liquid water, which may indicate the presence of some kind of life. It is likely that “James Webb” will help determine the advisability of a more detailed study of these celestial bodies in the future. The main thing is that this is not enough time for him.
New telescope to help search for Earth-like planets
It will make it possible to look into space much further.
In recent years, space exploration has steadily gained momentum. Until about ten years ago, scientists did not know about the planets located outside the solar system, in fact, nothing. But seven Earth-sized planets are already known today, and three of them may well be in the habitable zone. The big leap forward was the Kepler telescope, with which it was possible to detect about five thousand planets. However, it does not provide an opportunity to study in detail the many planets that resemble the Earth in size. They may well have an atmosphere and even life, but only the James Webb telescope will help to recognize them. Scientists will be able to use the built-in infrared spectrometers to help detect possible life on planets from the potentially habitable zone of nearby star systems.
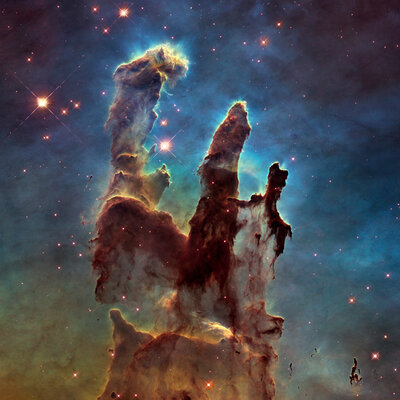
How new stars are born in our Milky Way
Hubble can’t see what’s behind the clouds
Hubble is able to take quite interesting pictures in both visible light and infrared. However, it is known that stars are born in massive clouds of dust and gas, which are called nebulae. This telescope may well see what they look like from the outside, but their inside remains insufficiently detailed even in the infrared spectrum. The James Webb Telescope is more efficient in this particular frequency range, so it should help to get even more detailed images of such nebulae. It is likely that scientists will be able to personally observe the birth and initial period in the life of stars and young planets.
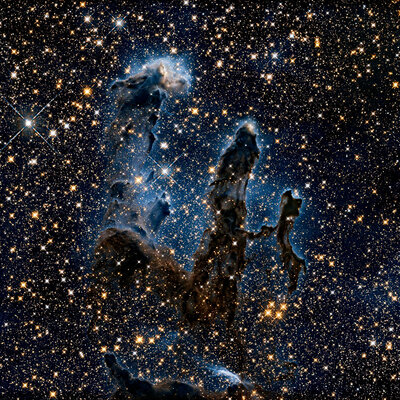


Why are massive black holes at the center of galaxies?
Most likely, “James Webb” will help deal with this.
It is curious that at the center of every galaxy known to mankind is a supermassive black hole, the mass of which can be millions and even billions of times larger than our Sun. In 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope took the first picture of the extreme part of an incredibly large black hole from the galaxy M87, around which specific gases accumulate. Such images shed light on the structure of such cosmic phenomena, but they are far from being fully explained. It is likely that giant black holes evolved from small ones, and those were the result of the usual life cycle of stars. To verify this, you need to connect the James Webb telescope. It will help to track the formation of massive black holes and, at least in theory, prepare for the dangers they may hide.
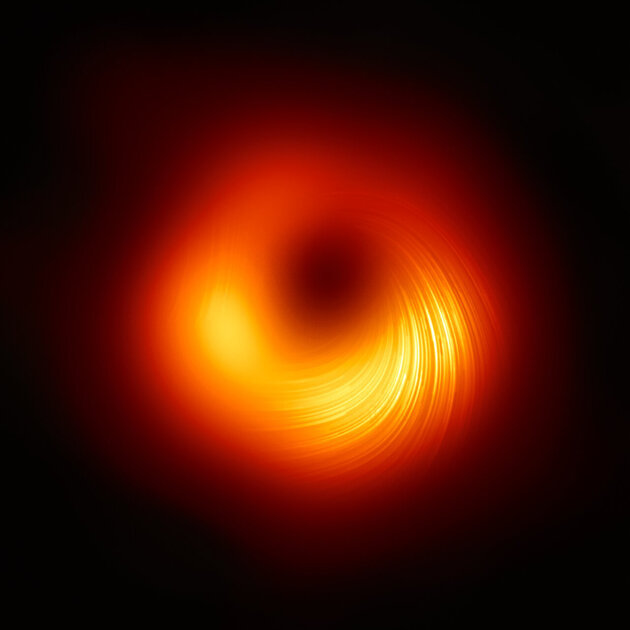

James Webb will help to look into the depths of the history of space
It has high power and position at the point without interference
With the help of Hubble (as well as earlier space observatories like COBE – Cosmic Background Explorer), scientists were able to look at really ancient galaxies that existed between 400 and 800 million years after the Big Bang. Scientists suggest that before that, the Universe was an extremely hot fog, consisting of energy and seething plasma, through which light could not penetrate. This time period is called the “dark ages” of space. It is known that as the Universe expanded and cooled, the earliest stars, transforming the plasma around them, pumped out hydrogen and helium. In theory, they were very different from modern ones, but so far no one knows exactly how. It is likely that James Webb will help to look into this time, fixing not light, but other types of radiation from celestial bodies. You can talk about a gap up to 100 million years after the birth of the universe.
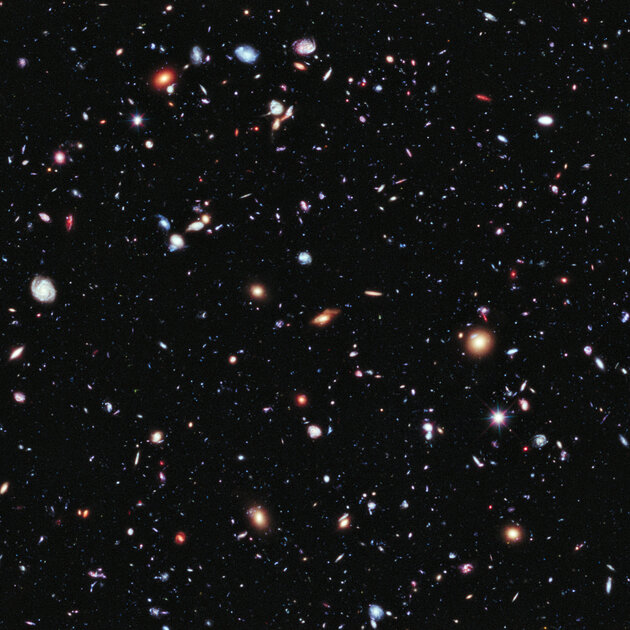

Source: Trash Box
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.







