How can astronomy be of interest to the layman? Of course, an endless stream of unusual questions, the answers to which have yet to be discovered! There are so many unresolved dilemmas in the universe that it makes your hair stand on end. It would seem that mankind has been studying space for a very long time, but this does not make it any less secrets. Even in the solar system, there are a lot of inconsistencies that the most authoritative scientists from different parts of the world cannot explain. It makes sense to pay special attention to the most unusual of them.
- To the point: Why are billions spent on space exploration when there are still problems on Earth
Is there life in the solar system somewhere other than Earth?
The most important question that still remains unanswered is that it is a priority for NASA researchers. It is quite possible that the new James Webb space observatory will help in his search – however, we still have to make sure of this. The discovery of life beyond the Earth would be the greatest discovery in the history of mankind – it is a pity that it has not yet happened. It is important to understand that scientists have not yet been able to answer the question of the potential existence of what we call life anywhere in the solar system, even in the distant past. Indirect signs for this are regularly discussed, but no one has come to anything concrete.
Mars is potentially habitable. Experts suggest that this is primarily due to the possible location of a huge ocean on its surface, which has long disappeared, as well as a similar temperature regime in the past. In 2018, the Curiosity research “SUV” found complex chemical compounds on the surface of Mars, but they did not become the final proof of the presence of life on the planet.
Life could be on Europa or Titan. The satellites of the giant planets are another logical place to look for it in the solar system. This applies to Europa – one of the moons of Jupiter, as well as Titan, which “obeys” Saturn. Under the ice crust of the first is potentially salt water, which is suitable for the origin of life. The second one has its own atmosphere – this is the only satellite in the solar system with such a feature. Atmospheric pressure here is close to Earth’s, there is also an ocean – however, it consists of methane.
How exactly was formed the only satellite of the Earth – the Moon
Another confirmation that our knowledge of the solar system in particular and the universe as a whole is very limited is the absence of a single approved version of the formation of the moon. At the moment, most experts agree that during the formation of the nearest outer space, a celestial body the size of Mars (or so) collided with the Earth. After this incident, a lot of debris remained in space, which eventually fell into the gravitational field of our planet and bonded together, forming the Moon. Despite the widespread use of this particular theory, a natural question arises: why, after such an incident, the Earth did not deorbit? Also, what happened to the second planet?
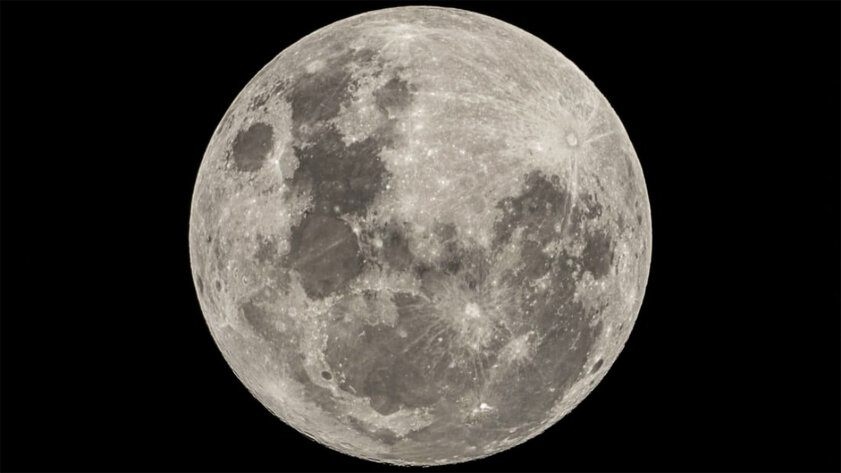

- To the point: Humanity does not know where the moon came from. But there are realistic guesses
Could water-filled oceans exist on Mars?
Apparently, humanity is close to getting an answer to this question. For years, astrologers have found evidence of erosion of the Martian soil, as well as channels and canyons on the surface of the Red Planet. It is likely that they owe their appearance to the behavior of the liquid – about a third of the area of Mars could be covered with water. Moreover, one should not discount the fact that water can be under the surface of this celestial body even today. As the planet is explored, the location of water on its plane is already less and less doubtful. However, a new question arises: what could happen to Mars that all the water on it evaporated?

How did Saturn get its famous rings
The rings of Saturn are the calling card of the solar system. And no one dares to argue with this. It is known that they are composed of millions of tiny pieces of stone, as well as ice and dust. But how exactly they were formed is a question that still has no answer. There are a couple of key theories: firstly, the rings may represent the remains of a satellite of Saturn, which was destroyed after a collision with a random celestial body; secondly, the rings around the planet could have formed even during the initial formation – these are its remnants.
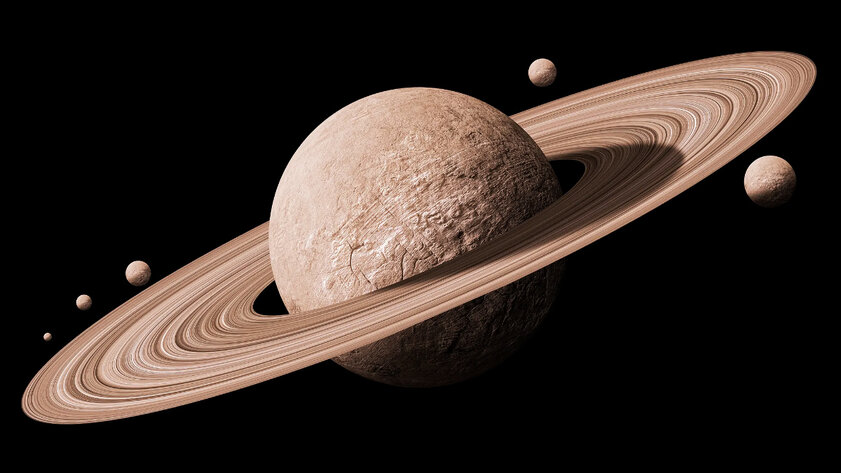
It is important to understand that when discussing the rings of Saturn, it is necessary to take into account the issue of the specific time of their formation. Space specialists still do not know exactly when they appeared – either relatively recently, or at the time of the formation of the solar system. It is likely that the answer to this question will be a natural solution to the previous problem. Recent data from the Cassini probe give reason to think that the rings of Saturn may be quite young – they were supposedly formed when dinosaurs walked the Earth. But this information is yet to be confirmed.
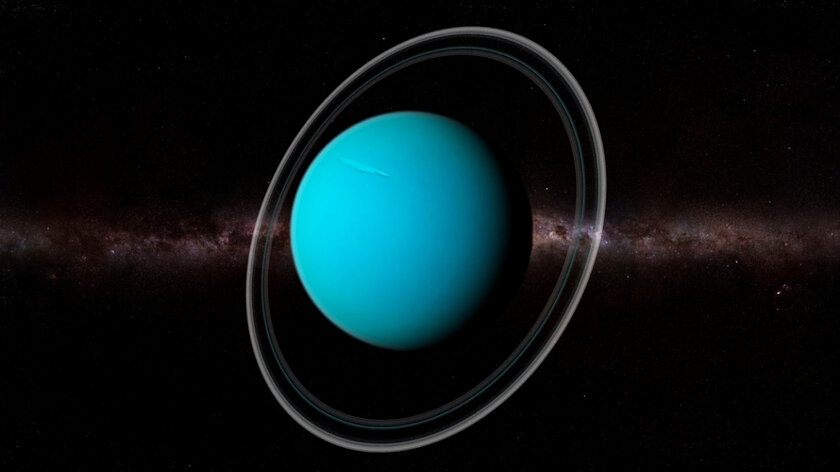
Why is Uranus’ axis of rotation comparatively tilted sideways?
When Uranus rotates on its axis, it feels like it is lying on its side – at least when compared with the rest of the planets in the solar system. The other axes are perpendicular to the central star – Uranus’ axis points directly to the Sun. It is likely that the planet tilted after a collision with a massive cosmic body – the same incident could cause the emergence of almost three dozen satellites orbiting Uranus.
What causes Venus to spin backwards
All planets in the solar system rotate in the same direction. Well, like everyone else, all but one. Unlike “brothers”, Venus prefers to “walk” clockwise, they are against it. Scientists involved in the study of space have only a “classical” explanation for the incident – once the planet collided with a massive celestial body, so it changed the direction of its rotation. However, there is another curious assumption about the direction of Venus’s motion. The planet is too close to the Sun, and its atmosphere is so dense that the gravitational attraction of our star created a system of tides, which, in fact, turned the planet’s axis of rotation by 180º.
Where does Neptune get its extra heat for radiation?
When Pluto was no longer considered a planet, Neptune was the most distant such object in the solar system. It is very cold on the surface of this celestial body – the temperature of the upper atmosphere averages -221.3 ° C. However, winds and hurricanes continuously rage on its surface, which can only be explained by the presence of an internal source of thermal energy. The ice giant also radiates 2.6 times more heat than it receives from the sun’s rays, and this surprises space explorers on Earth. It is quite possible that radioactive processes are taking place in the bowels of the planet, or unaccounted for gravitational waves affect Neptune. But, if for sure, it will be possible to find out only after a close study of Neptune.
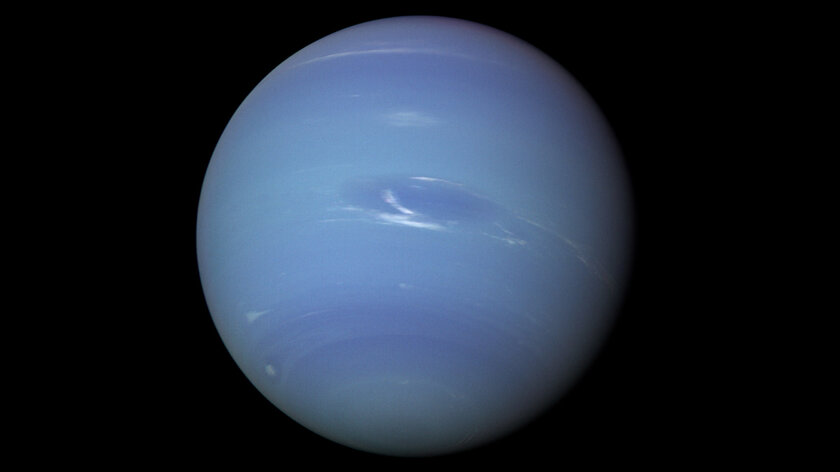

- To the point: The coldest planet in the solar system. What about the temperature on Uranus
Why are the planets in the solar system so different in composition?
Many researchers of the Universe, when discussing the origin of the solar system, agree in one opinion. They believe that initially a ring of cosmic rock formed around the Sun, which systematically collided, forming planets. However, this theory breaks down into one stubborn argument – if they were all formed from the same material, why then do the planets of the solar system have such a different form factor ?! Some differences, of course, can be associated with the distance from the Sun – this, for example, concerns the permanent state of the liquid. The size can be explained by the different duration of growth. But all this does not solve the dilemma of differences in composition.
Source: Trash Box
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.







