- The AUD/USD is directed towards psychological resistance as concerns about commercial uncertainty intensify.
- The FED acts solidify the expectations of a rate cut in September amid concerns about increasing inflation due to tariffs.
- The US dollar faces a renewed pressure for political and commercial uncertainty, which supports the Australian dollar.
The Australian dollar (AUD) is negotiating in a well -defined range against its counterpart in the US dollar (USD) on Wednesday, while the markets digest the last minutes of the Fed and the new holders related to tariffs.
Although tariffs will take effect in August, persistent commercial uncertainty continues to weigh on the dollar. The last round of tariff cards was sent to countries such as Libya, Iraq and the Philippines on Wednesday.
At the time of writing, the AUD/USD is negotiating around 0.6540, with firm resistance at 0.6550.
The minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) of June revealed that the majority of monetary policy are still cautious about the premature reduction of interest rates. However, many also recognized the potential that tariffs exacerbate inflation pressure.
On Tuesday, President Trump requested the immediate resignation of the president of the FED, Powell, urging his replacement for someone more inclined to cut rates. Speaking at the White House on Wednesday, Trump reiterated his position, stating that the US should have “the lowest interest rates in the world.”
Despite political rhetoric, the CME Fedwatch tool continues to reflect expectations of a rate cut in September. With these projections largely discounted, the AUD/USD has shown little reaction to the Fed report.
The expansive wedge pattern maintains the AUD/USD price action under control
The AUD/USD is being negotiated about 0.6540, with firm resistance at 0.6550, a level that aligns with the 61.8% of the fall from September to April.
The price action currently remains within an expansive and ascending wedge formation. This is a pattern, characterized by a series of higher maximum and minimum, which widens towards the top.
The torque is currently consolidating just below the upper limit of the wedge, with layers in layers near the 50 -day exponential mobile average (EMA) in 0.6476 and the 200 -day EMA in 0.6437.
A recent golden cross, where the 50 -day EMA moved above the 200 -day EMA, supports a medium -term bullish perspective.
Meanwhile, the relative force index (RSI) about 54 indicates a slight bullish inclination above the neutral zone at level 50.
Aud/USD Daily Graph
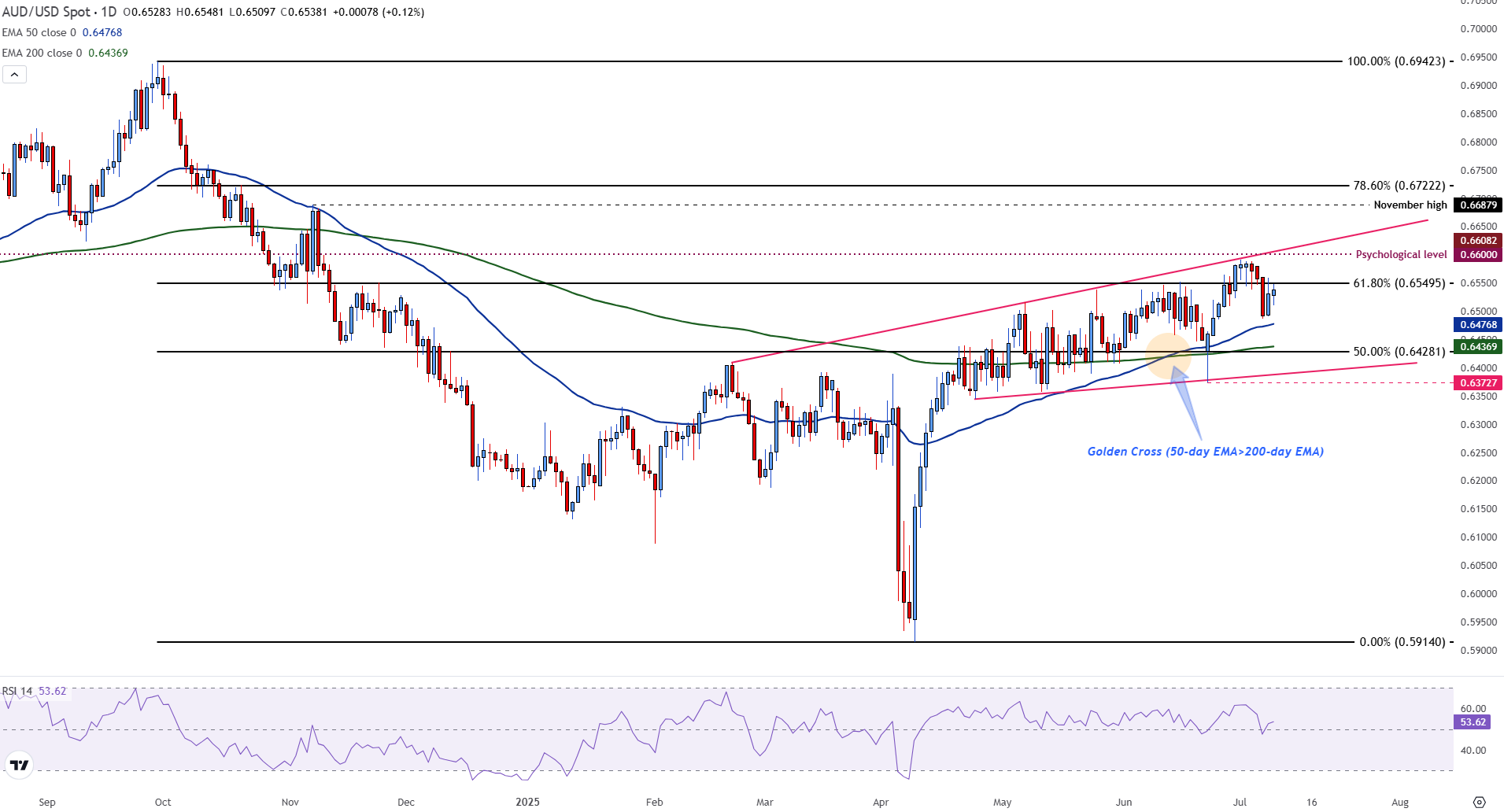
A sustained breakout above 0.6550 would confirm the bullish impulse and will probably attract an additional purchase interest. In this case, the following object objects is at the psychological level of 0.6600, followed by a possible advance towards the maximum of November 0.6688.
On the contrary, a break below 0.6470 would indicate a weakening of the bullish pressure and suggest a possible downward reversion within the wedge structure. This would expose a deeper support at 0.6428, near the 50%Fibonacci level, with a higher downward risk towards the 200 -day EMA at 0.6437.
Fed – Frequently Questions
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve prices stability and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the objective of 2% set by the Federal Reserve, it rises interest rates, increasing the costs of loans throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US dollar (USD), since it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to foster indebtedness, which weighs on the green ticket.
The Federal Reserve (FED) celebrates eight meetings per year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is made up of twelve officials of the Federal Reserve: the seven members of the Council of Governors, the president of the Bank of the Federal Reserve of New York and four of the eleven presidents of the regional banks of the Reserve, who exercise their positions for a year in a rotary form.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non -standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy high quality bonds of financial institutions. The one usually weakens the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the inverse process to the QE, for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the bonds that it has in portfolio that they expire, to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







