The visit of a young boy to a municipal fountain in Texas as he was infected by a rare amoeba that eats him brain. According to NBC 5, the boy died at Cook Children’s Medical Center on September 11, after contracting a disease called primary amoebic meningoencephalitis, a rare and often fatal infection caused by the amoeba Naegleria Fowleri.
An investigation by the city health authorities and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the presence of the Naegleria Fowleri amoeba in water samples in the Don Misenhimer Park, where the swimming pool was located.
Water samples were taken on September 10 and 14 from the fountains of Don Misenhimer Park. However, reports indicate that the chlorine level was normal two days before the boy’s arrival. One day later, the levels were recorded as low. City officials say records from two of the four fountains – at Don Misenhimer Park and the Beacon Recreation Center – showed that officials did not consistently record, or in some cases did, conduct water quality tests required prior to daily opening of the premises.
Officials did not record the details correctly
“The review identified gaps in the day-to-day inspection program,” said Lemuel Randolph, the city’s deputy director. “These gaps have resulted in non-compliance with maintenance standards.”
City officials said examining inspection records in Don Misenhimer found that the water chlorination measurements had not been documented on two of the three dates the child was there, in late August and early September.
Workers reportedly added chlorine to the fountain the day after the boy’s visit, according to the Fort Worth Star-Telegram, but did not make continuous follow-up measurements after the pool was disinfected.
The city has since closed all four fountains for the rest of the year.
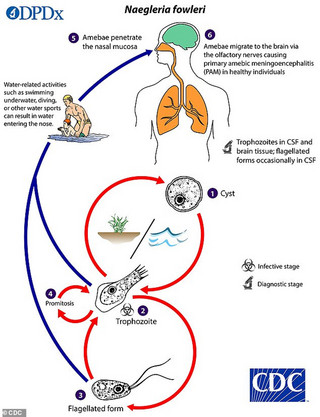
The CDC says Naegleria fowleri infections are rare, with only 34 reported in the US from 2010 to 2019. Infection from this amoeba occurs when water containing this microorganism enters the human body through the nose, usually during swimming.
CDC chart of how the amoeba works in the brain
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.







