- The Dow Jones remains stable below 39,900, awaiting significant data.
- Despite the words of some members of the Federal Reserve, investors continue to expect an interest rate cut.
- Home sales, PMI and durable goods orders will be released this week.
The Dow Jones Index (DJIA) remains stable above 39,800 on Tuesday, as Federal Reserve (Fed) officials try to put downward pressure on rate cut expectations in the market. Fed officials signaled Tuesday that the Fed is not likely to cut rates until it has more data pointing to a steady decline in inflation to the Fed's annual target of 2%. Despite the easing of inflation data for April, central planners remain scared after inflation data for the first quarter as a whole did not show that disinflation has definitively taken hold.
USD economic data remains sparse in the first half of the week, but investors will be keeping an eye on US home sales figures due mid-week. The Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) will also be published on Thursday and durable goods orders on Friday.
Dow Jones News
The Dow Jones is trading mixed on Tuesday, with about half of its stocks rising. 3M Co. (MMM) fell -1.9% to $103.25 per share, while International Business Machines Corp. (IBM) rose more than 2% to trade at $173.44 per share.
Dow Jones Technical Outlook
The Dow Jones set a new all-time high of 40,070.82 on Monday, and the index is taking water just below 39,900.00 on Tuesday. DJIA traders failed to push the index back above 39,880.00 as bullish momentum remains weak, but selling pressure remains low and a technical bottom is quoted near 39,780.00.
Dow Jones five minute chart
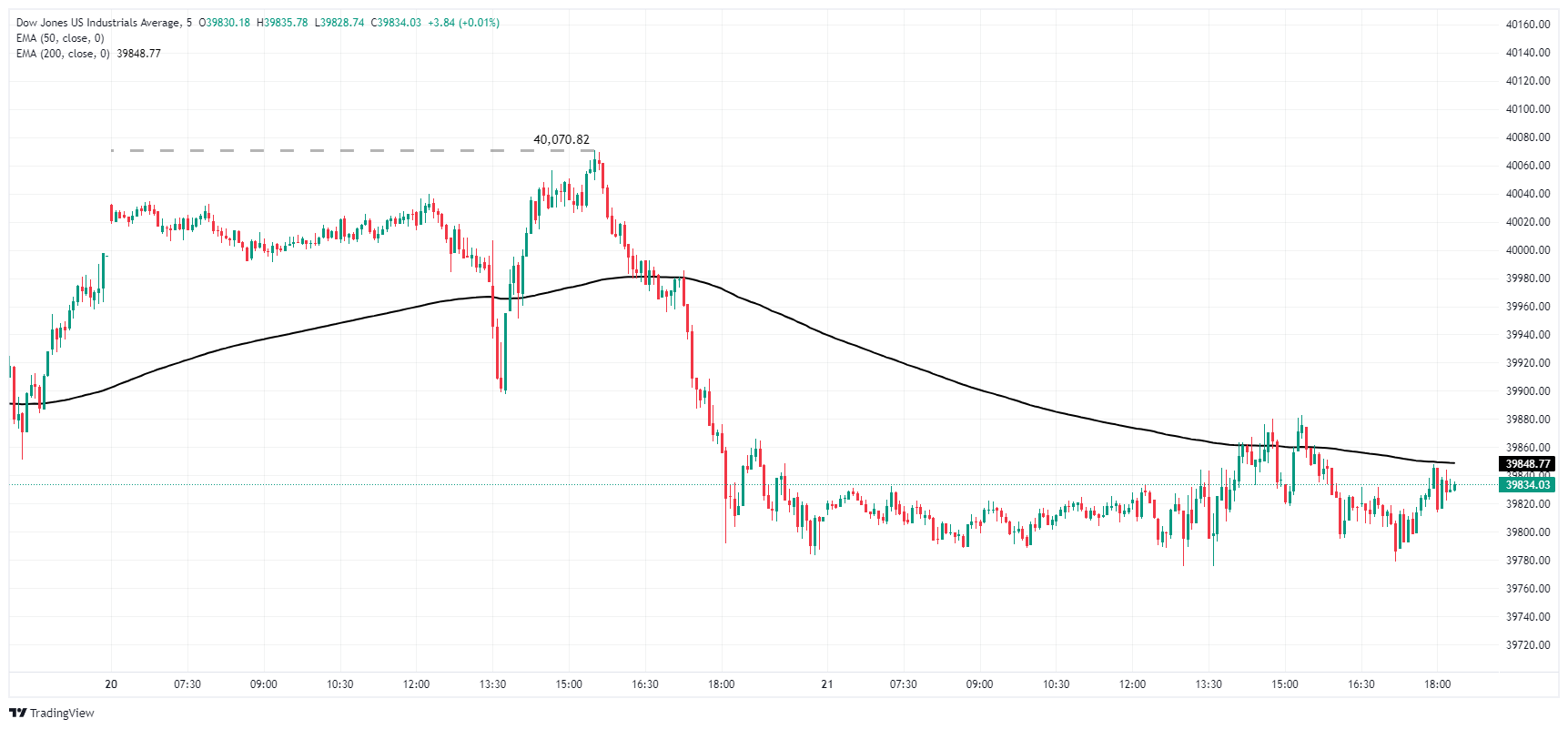
Dow Jones Daily Chart
The Fed FAQs
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: achieving price stability and promoting full employment. Your main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the Federal Reserve's 2% target, it raises interest rates, raising borrowing costs throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US Dollar (USD), as it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight meetings a year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is made up of twelve Federal Reserve officials: the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the eleven presidents of the regional Reserve banks, who serve for one year on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit into a clogged financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed's weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy high-quality bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the capital of the maturing bonds it has in its portfolio to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







