- The Dow Jones remained near 42,000 points to start the new week.
- Investors are awaiting key US labor market data due on Friday.
- Despite a quiet Monday, the Dow Jones is coming off a winning month.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) was hampered at the start of a new trading week. The main stock index eased slightly on Monday, but remained near the 42,000 level. Stock traders are watching data risks and rates markets are grappling with the odds of a further cut by the Federal Reserve (Fed) in November.
The market’s focus will slowly shift to Friday’s US nonfarm payrolls report as investors look for more data on the state of the US economy. Rate traders continue to mull over the Fed’s November rate decision, with odds tilted slightly in favor of a modest 25bp cut. However, many market participants still expect an additional double 50bp cut when the Fed meets again for another rate decision on November 7.
A looming port strike along the East and Gulf coasts is weighing on investor expectations for near-term economic activity, reducing investor demand and cooling stock gains. Adding downward pressure on stocks, Fed officials drew a line at the Fed’s rate cuts, noting that further deterioration in the US labor market would be needed to prompt additional major moves by the Fed. Fed. This proposal weighs negatively on market participants hungry for rate cuts, as further declines in employment data would signal a higher risk of an imminent US recession.
Dow Jones News
The Dow Jones is generally weaker on Monday, with more than two-thirds of the stock index testing in the red at the start of the new trading week. However, firm gains in major components are helping to contain broader losses in the DJIA.
Boeing (BA) is being affected by its own ongoing strike, which has now been going on for two weeks. The aerospace company fell 2.45% on Monday, falling from $125.50 per share. On the bright side, Apple (AAPL) rose 1.6% to over $231 per share despite the company announcing it was pulling out of a capital raising round for a planned investment in OpenAI. Apple’s withdrawal of an investment in a major AI project has raised some eyebrows, showing warning signs that OpenAI’s recent pivot toward seeking profitability may have some bumps in the road.
Dow Jones Price Forecast
Despite a tepid Monday, the Dow Jones is poised to post a stellar performance in September. The main stock index reached a new record last week of 42,636 points, adding more than 1.5% for the month. The Dow Jones is on track to close its fifth consecutive month in the green, rising more than 13.5% bottom-up from April lows near 37,550 points.
Dow Jones Daily Chart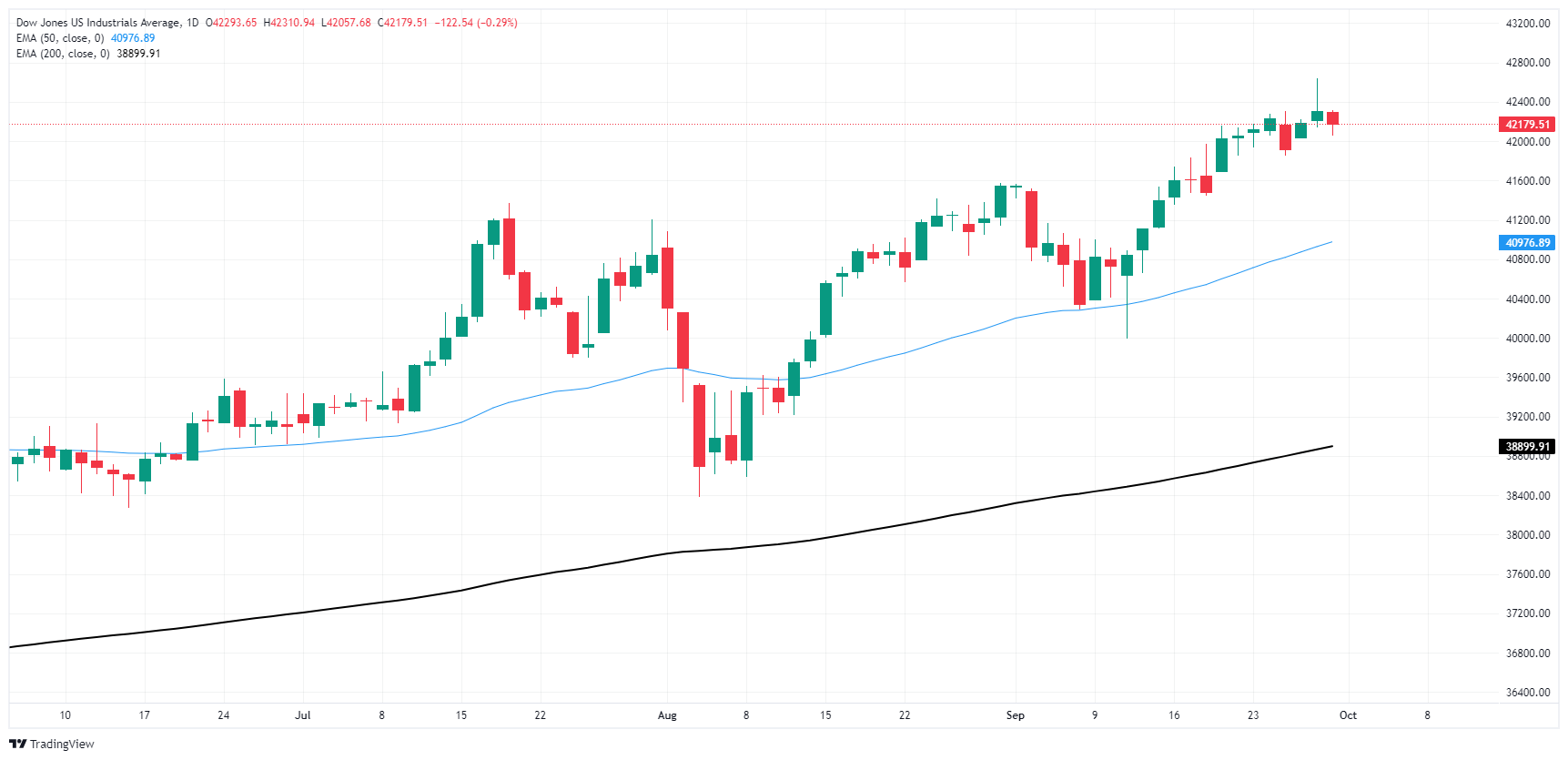
The Fed
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: achieving price stability and promoting full employment. Your main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the Federal Reserve’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, raising borrowing costs throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US Dollar (USD), as it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight meetings a year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is made up of twelve Federal Reserve officials: the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the eleven presidents of the regional Reserve banks, who serve for one year on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit into a clogged financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy high-quality bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the capital of the maturing bonds it has in its portfolio to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







