- The Dow Jones fell 150 points on Wednesday after US employment numbers fell short of expectations.
- ADP hiring data slowed more than expected, and wage growth slowed to a two-year low.
- Investors await the latest minutes from the Fed’s meeting on evaluating the December rate cut.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) fell again on Wednesday. The index retreated 150 points after stocks cooled due to an error in preliminary employment data ahead of this week’s key Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report.
The ADP employment change showed a slower-than-expected pace of hiring in December, declining to 122K from the expected 140K and 146K in November. ADP wage data also slowed, reaching its slowest pace since mid-2021.
The key data on Wednesday will be the latest minutes from the Federal Reserve (Fed) meeting on the December rate decision. The Fed last cut interest rates by 25 basis points to close out 2024, but now looks set to hold off on further rate cuts until mid-2025 as the U.S. economy chugs along. Political concerns about incoming President Donald Trump weigh on policymakers, although they insist they do not.
US markets will close early on Thursday, so traders should expect an adjustment in market volumes during the US trading window. US operations are winding down in observance of the passing of former US president Jimmy Carter, who died in late December at age 100.
Dow Jones News
Stocks listed on the Dow Jones split roughly in half on Wednesday, but concentrated losses in key stocks are dragging the average toward the downside. Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) fell to a new yearly low despite achieving ‘Fast Track’ status with the Food and Drug Administration for several of its new pharmaceutical offerings. JNJ is now down around 3% on the day and sits below $142 per share.
Dow Jones Price Forecast
The downward trend in the Dow Jones, which began in late November, continues to weigh on the main stock index. The DJIA is on track to close in the red for the sixth consecutive week and is still down almost 6% from its all-time peak of 45,071 in November. Of the last 19 consecutive trading days, the Dow Jones has closed flat or in the red on all but three of them, including a record streak of 11 consecutive bearish sessions.
Despite a short-term bearish turn, bearish momentum still faces significant headwinds. The DJIA continues to trade north of the 200-day EMA near 41,200, and bidders are still trying to find their footing and push the price action above the 50-day EMA near 43,150.
Dow Jones Daily Chart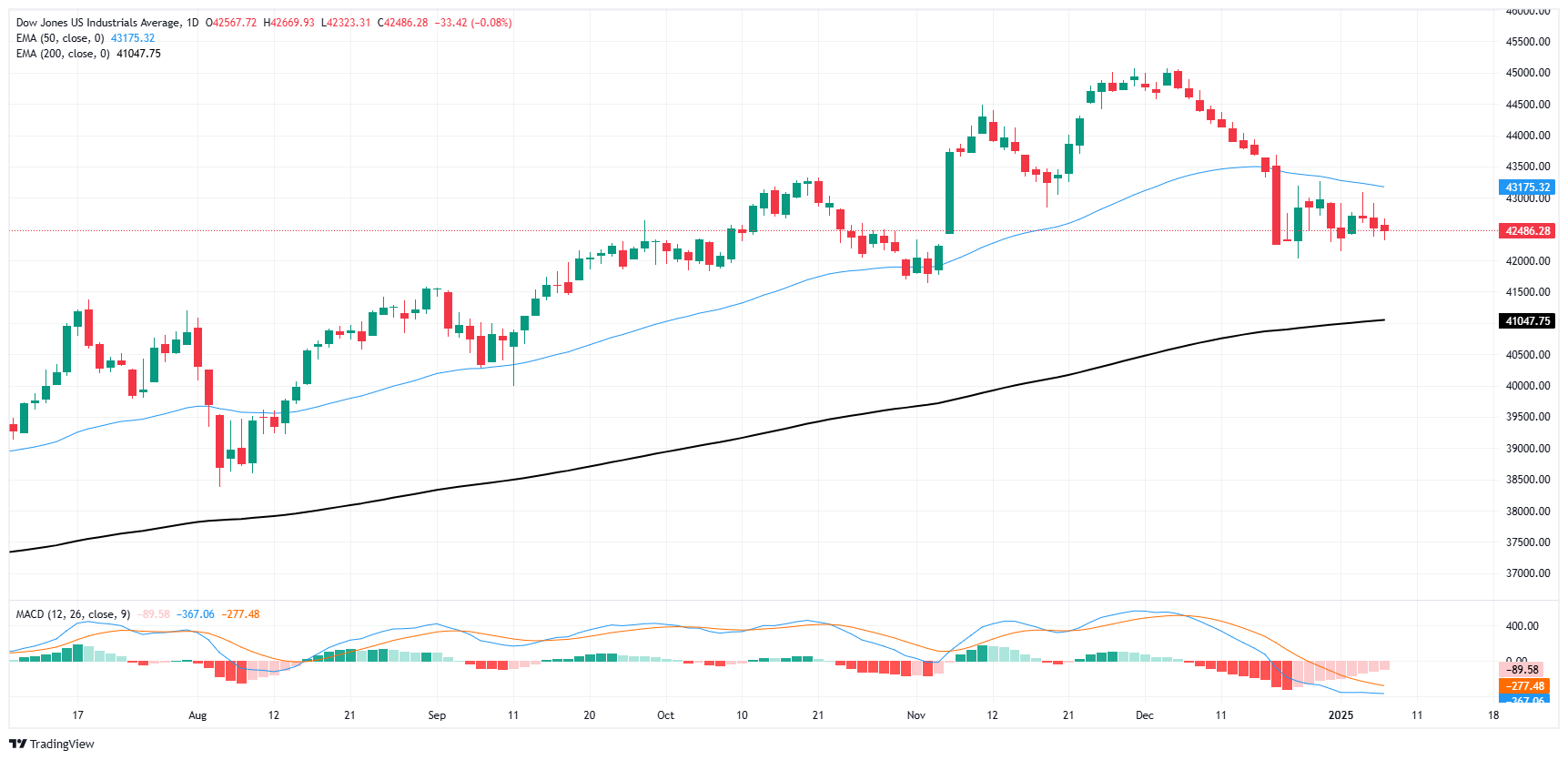
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the world’s oldest stock indices, is made up of the 30 most traded securities in the United States. The index is weighted by price rather than capitalization. It is calculated by adding the prices of the securities that comprise it and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, also founder of the Wall Street Journal. In recent years it has been criticized for not being sufficiently representative, since it only follows 30 companies, unlike broader indices such as the S& P 500.
There are many factors that drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The main one is the aggregate performance of its component companies, revealed in quarterly corporate earnings reports. US and global macroeconomic data also contribute, influencing investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA, as it affects the cost of credit, on which many companies largely depend. Therefore, inflation can be a determining factor, as well as other parameters that influence the decisions of the Federal Reserve.
The Dow Theory is a method for identifying the main trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where they are both moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmation criterion. The theory uses elements of maximum and minimum analysis. The Dow theory proposes three phases of the trend: accumulation, when the smart money begins to buy or sell; public participation, when the general public joins the trend; and distribution, when the smart money abandons the trend.
There are several ways to trade the DJIA. One of them is to use ETFs that allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, instead of having to buy shares of the 30 companies that comprise it. A prominent example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). Futures contracts on the DJIA allow traders to speculate on the future value of the index, and options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds allow investors to purchase a portion of a diversified portfolio of DJIA securities, providing exposure to the global index.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







