- The EUR/JPY shoots as the feeling of risk reinforces the strength of the euro.
- Concerns about tariffs eclipsan the hard line comments of the Bank of Japan (BOJ).
- The EUR/JPY is directed around 170.00, pushing Momentum indicators to overcompra territory.
The euro (EUR) is strengthening in front of the Japanese Yen (JPY) in the trading session on Wednesday, with a feeling of improved risk that reduces demand by Yen, considered safe refuge.
With the EUR/JPY quoting above the key psychological level of 169.00, a resurgence of the bullish momentum could provide the potential for a new 170.00 test.
As tensions in the Middle East continue to decrease, attention has focused again on monetary policy and growth prospects for global markets.
For Japan, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) opinions on Wednesday offered temporary relief for YEN, since some policy managers adopted a hard line tone. However, the majority of those responsible expressed concerns about the possible threats that tariffs represent for the Japanese economy.
While Boj’s person in charge of the Boj, Naoki Tamura, hinted at the prospects for a possible increase in rates “as soon as in July” in response to the growing inflation, the BOJ’s ability to increase rates seems to depend on the perspectives of a commercial agreement with the United States.
EUR/JPY Technical Analysis: Can Alcistas push prices at 170.00?
The EUR/JPY is being quoted at 169.25, just below the key level of 170.00 key psychological resistance. The next level of resistance is observed at the Fibonacci recoil level of 78.6% of the July-August, located in 170.93.
EUR/JPY DAILY GRAPH
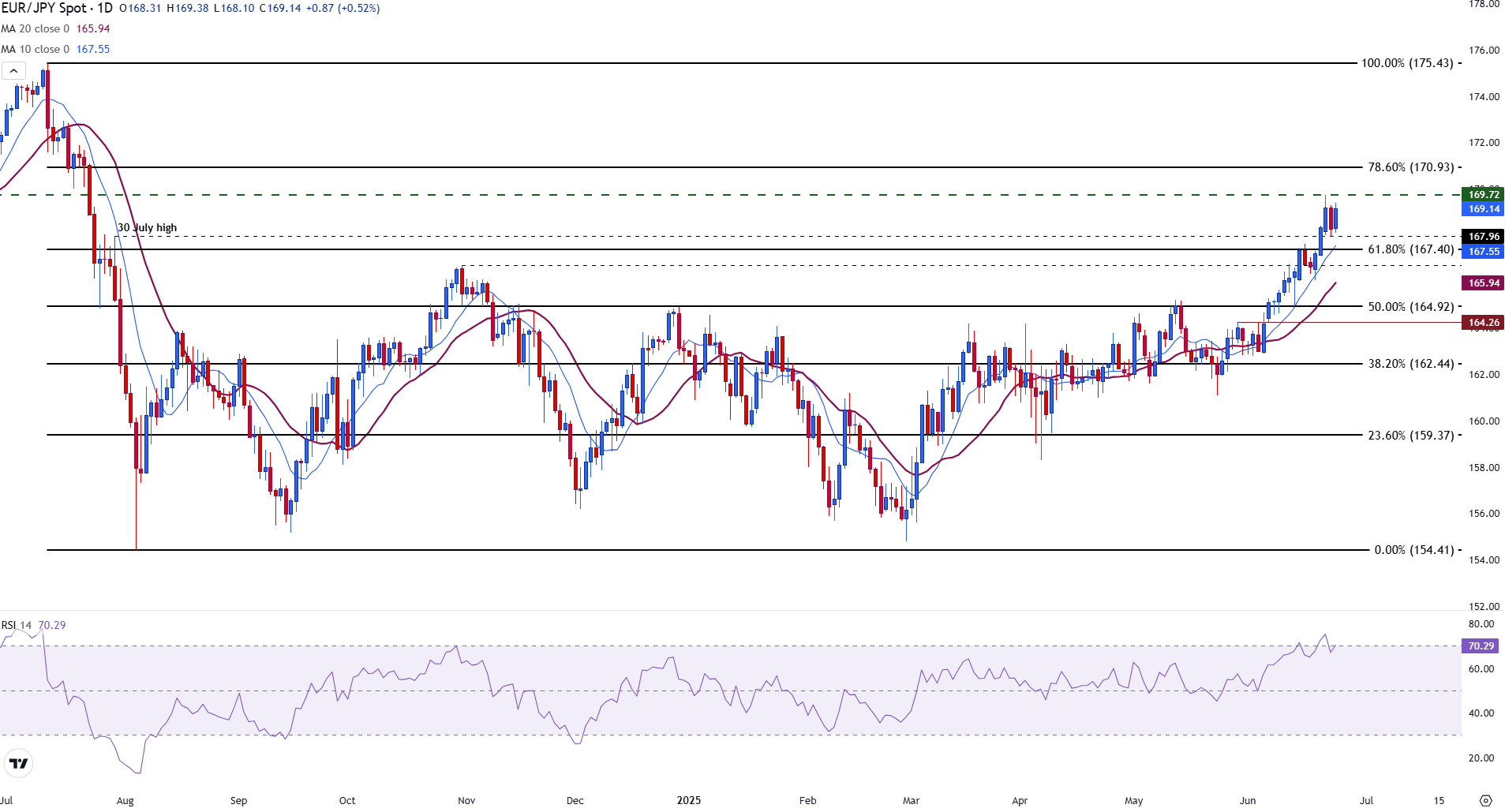
The ascending momentum of the PAR remains strong, supported by the wide divergence of policies between the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Boj.
Technically, the EUR/JPY remains in overcompra territory, with the relative force index (RSI) above 70, suggesting extended conditions; However, purchases in the falls continue to support the pair.
The price is well above the simple mobile socks (SMA) of 10 days (167.56) and 20 days (165.95), reinforcing the upward trend.
However, operators are now observing exhaustion signs or a break above 171 to test the level of 175.43, which marks the 100% setback from the July peak of 2024.
US interest rates
Financial institutions charge interest rates on loans to borrowers and pay them as interest to savers and depositors. They influence the basic types of interest, which are set by central banks based on the evolution of the economy. Normally, central banks have the mandate to guarantee the stability of prices, which in most cases means setting as an objective an underlying inflation rate around 2%.
If inflation falls below the objective, the Central Bank can cut the basic types of interest, in order to stimulate credit and boost the economy. If inflation increases substantially above 2%, the Central Bank usually rises the interest rates of basic loans to try to reduce inflation.
In general, higher interest rates contribute to reinforce the currency of a country, since they make it a more attractive place for world investors to park their money.
The highest interest rates influence the price of gold because they increase the opportunity cost of maintaining gold instead of investing in an asset that accrues interest or depositing effective in the bank.
If interest rates are high, the price of the US dollar (USD) usually rises and, as gold quotes in dollars, the price of low gold.
The federal funds rate is the type to a day that US banks lend each other. It is the official interest rate that the Federal Reserve usually sets at its FOMC meetings. It is set at a fork, for example 4.75%-5.00%, although the upper limit (in this case 5.00%) is the aforementioned figure.
Market expectations on the interest rate of the Federal Reserve funds are followed by the Fedwatch of the CME tool, which determines the behavior of many financial markets in the forecast of future monetary policy decisions of the Federal Reserve.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







