- The EUR/USD falls about 1,0860 while the president of the ECB, Lagarde, hopes that the commercial war led by US President Donald Trump can decelerate the economic growth of the eurozone.
- The Fed maintained stable interest rates and adhered to its forecasts of two features in 2025 on Wednesday.
- The Fed expects Trump’s policies to weigh on the economic growth of the US and accelerate pressures on prices.
The EUR/USD decreases to about 1,0860 during Thursday’s European negotiation hours. The main currency pair falls as the euro (EUR) faces pressure after the president of the European Central Bank (ECB), Christine Lagarde warned about the economic risks of the Eurozone due to possible tariffs by the United States (USA).
Lagarde testified to the Committee on Economic and Monetary Affairs of the European Parliament during Thursday’s European negotiation hours. He said that American tariffs of 25% of imports from Europe, as the US president Donald Trump threatened, would reduce “the growth of the euro zone by approximately 0.3% in the first year,” according to an analysis of the ECB. The study also shows that Europe’s retaliation tariffs would increase this to approximately 0.5%.
The fears of weak economic growth in the Eurozone would decrease the appeal of the euro (EUR) as they would force the ECB to further reduce interest rates. However, the end of Germany of more than a decade of fiscal conservatism, with the aim of promoting domestic consumption and defense spending, would compensate for the impact of the commercial war.
On the inflation prospects, Christine Lagarde predicted that the reprisal measures of the European Union (EU) and a weaker euro exchange rate could raise inflation in about 0.5%. However, the president of the ECB expects this to be temporary, since the effect would be softened in the medium term due to “lower economic activity that would cushion inflationary pressures.”
What moves the market today: the Eur/usd falls while the US dollar wins
- The EUR/USD slides below 1,0900 while the US dollar (USD) is strengthened, while investors digest the confusing economic perspective of the United States under the leadership of President Donald Trump, anticipated by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The dollar index (DXY), which follows the value of the green ticket compared to six main currencies, rose to about 103.65.
- On Wednesday, the Fed left the key interest rates without changes in the range of 4.25%-4.50%, as expected, for the second time consecutive and adhered to its guide of two interest rate cuts this year, as projected at the December policy meeting. The Fed did not expressed a hurry for adjustments in monetary policy in the midst of “unusually high” uncertainty about the president’s policies. “We are not going to be in a hurry to move in feat cuts,” said Fed President Jerome Powell, at the press conference, since “tariffs tend to reduce growth and increase inflation.”
- The Fed reviewed its forecast for the Personal Consumption Expenditure Index (PCE) for this year to 2.8%, from 2.5% projected at the December meeting. The Central Bank reviewed the growth of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of this year to 1.7% from its previous 2.1% forecast, despite maintaining confidence that labor market conditions are solid.
- Contrary to the “approach to wait and see” of the Fed, US President Trump said the Central Bank should have trimmed interest rates since the impact of tariffs is traveling towards the economy. “The Fed would be much better by cutting up as well as US tariffs begin to travel (relieve!) In the economy.
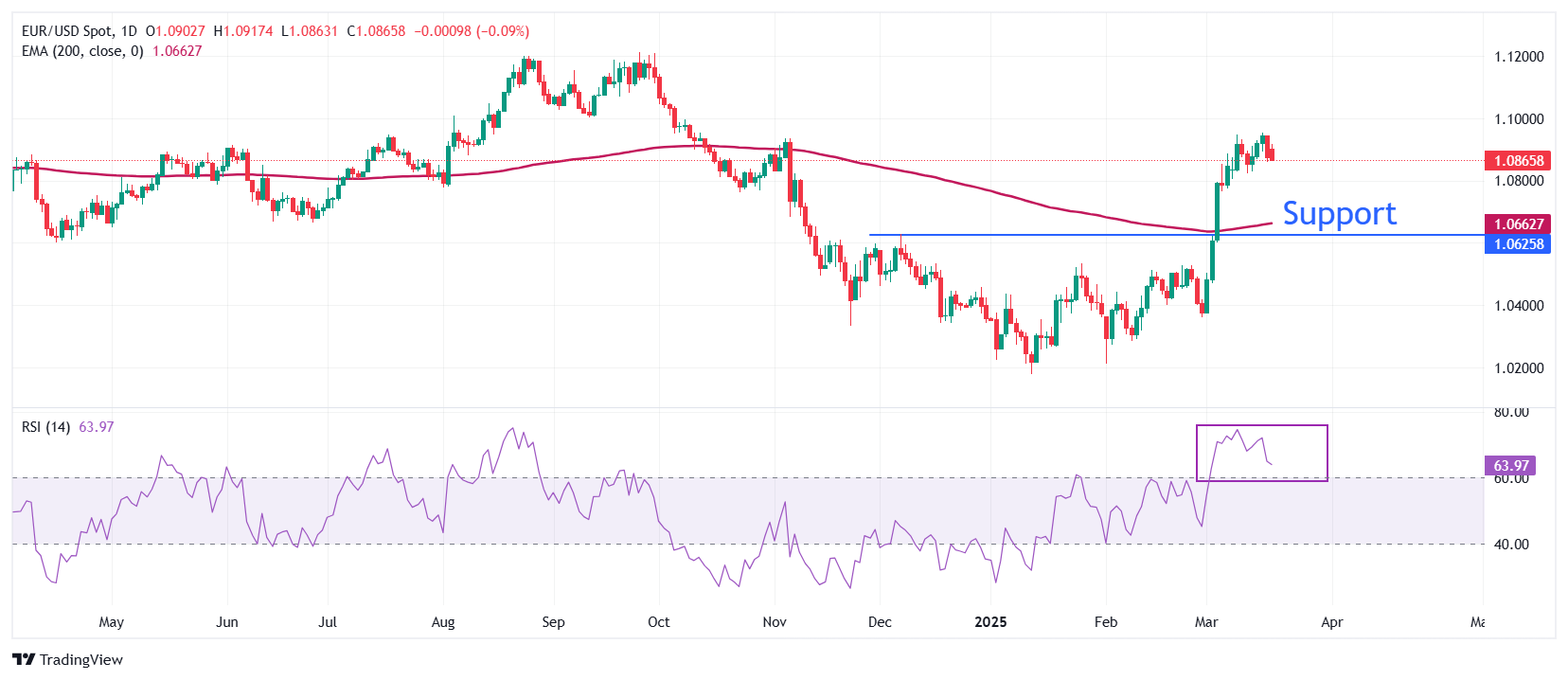
Technical Analysis: The EUR/USD corrects about 1,0860
The EUR/USD falls to about 1,0860 after not being able to maintain the key level of 1,0900 on Thursday. However, the long -term perspective of the main currency pair remains bullish since it remains above the 200 -day exponential (EMA) mobile average, which is negotiated around 1,0660.
The pair was strengthened after a decisive breakdown above the maximum of December 6, 1,0630 on March 5.
The 14 -day relative force index (RSI) cools after around 75.00, suggesting that the bullish impulse has been moderated, but the upward inclination remains intact.
Looking down, the maximum of December 6, 1,0630 will act as the main support zone for the torque. On the contrary, the psychological level of 1.1000 will be the key barrier to the euros of the euro.
Euro Faqs
The euro is the currency of the 19 countries of the European Union that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most negotiated currency in the world, behind the US dollar. In 2022, it represented 31 % of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily business volume of more than 2.2 billion dollars a day. The EUR/USD is the most negotiated currency pair in the world, with an estimate of 30 %of all transactions, followed by the EUR/JPY (4 %), the EUR/GBP (3 %) and the EUR/AU (2 %).
The European Central Bank (ECB), based in Frankfurt (Germany), is the Eurozone reserve bank. The ECB establishes interest rates and manages monetary policy. The main mandate of the ECB is to maintain price stability, which means controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its main tool is the rise or decrease in interest rates. Relatively high interest rates (or the expectation of higher types) usually benefit the euro and vice versa. The GOVERNMENT BOOK of the ECB makes decisions about monetary policy in meetings that are held eight times a year. The decisions are made by the directors of the National Banks of the Eurozone and six permanent members, including the president of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the harmonized consumer prices index (IPCA), are an important economic indicator for the euro. If inflation increases more than expected, especially if it exceeds 2% of the ECB, it forces the ECB to rise interest rates to control it again. Relatively high interest rates compared to their counterparts usually benefit the euro, since they make the region more attractive as a place for global investors to deposit their money.
Published data measure the health of the economy and can have an impact on the euro. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, employment and consumer trust surveys can influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the euro. Not only attracts more foreign investment, but it can encourage the ECB to raise interest rates, which will directly strengthen the euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the euro is likely to fall. The economic data of the four largest economies in the euro zone (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, since they represent 75% of the economy of the euro area.
Another important fact that is published on the euro is the commercial balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns with its exports and what you spend on imports during a given period. If a country produces highly demanded export products, its currency will gain value simply by the additional demand created by foreign buyers seeking to buy those goods. Therefore, a positive net commercial balance strengthens a currency and vice versa in the case of a negative balance
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.