- EUR/USD goes back to 1,1695 after reaching an annual maximum above 1,1750.
- The underlying inflation of the PCE in the US increases above expectations; The feeling of the consumer improves, pressing the euro.
- The Knot of the ECB provides one more cut in 2025; Inflation in France cools, the IAPC of Spain exceeds 2%.
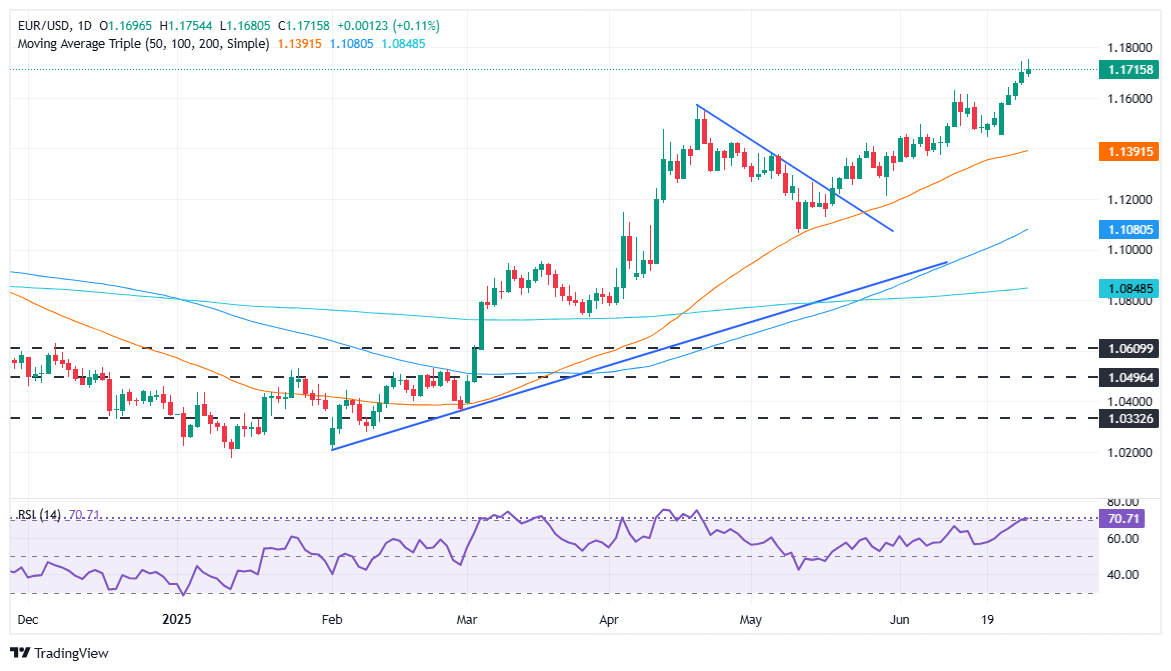
The EUR/USD retires from the annual maximums above 1,1750, falling below 1,1700 despite the fact that market participants are convinced that the Federal Reserve (FED) will cut rates at the September meeting. A mixed inflation report in the United States (USA) and optimism among American consumers exerted downward pressure. At this time, the pair is negotiated at 1,1695, practically unchanged.
Economic data occupy the center of the stage on Friday, after the de -escalation of the conflict in the Middle East and the news that China and the US have reached a commercial agreement. The US Economic Analysis Office reported that the PCE General was in line with the estimates and figures of April. At the same time, the underlying PCE, which the Federal Reserve seeks as its preferred inflation indicator, increased above expectations, indicating that prices are modestly rising.
On the other side of the Atlantic, the Klas Knot of the European Central Bank (ECB) commented that at least one more cut of interest rates of 25 basic points towards the end of 2025 is anticipated. The Vice President of the ECB, Luis de Guindos, said that inflation is about to reach the objective of 2%.
The Eurozone agenda revealed that inflation in France fell, while the harmonized consumer prices index (IAPC) in Spain exceeded the objective of the ECB.
What moves the market today: the rise in the expectations of an Fed cut in July promotes the EUR/USD
- The dollar recovery limited the progress of the EUR/USD to 1,1800. The US dollar index (DXY), which tracks the value of the dollar value against a rivals basket, rises 0.03% to 97.37 after reaching a minimum of three and a half years of 96.99.
- The US PCE revealed by the BEA increased a 2.3% year -on -year, without changes compared to April, and as expected by the median. The underlying PCE, which excludes volatile elements such as food and energy, expanded 2.7% year -on -year, above estimates and 2.6% of the previous month.
- The feeling of the consumer in the US in June improved, according to the University of Michigan (UOM). The index improved from 60.5 to 60.7, and inflation expectations are expected to be lower. For 1 year, American households see prices reaching 5%, lowering 5.1%. For 5 years, inflation is projected to fall from 4.1% to 4%.
- The president of the Fed of Minneapolis, Neel Kashkari, declared that although a possible increase in inflation could be on the horizon, current data suggests continuous progress towards the objective of underlying inflation of 2% of the Fed. He added that more time is needed to assess whether the effects of the commercial war are simply delayed or less severe than initially anticipated.
- The Wall Street Journal reported that the EU is considering reducing tariffs on US imports as an effort to win the favor of President Trump. In addition, the US Secretary of Commerce, Howard Lutnick, said the EU had a slow beginning but is now going well, adding that there is optimism about an agreement with Europe.
- The president of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, said that the EU is prepared for both an agreement and for a result without agreement, stating that all options are still on the table.
- Monetary markets suggest that operators are discounting 59 basic relief points towards the end of the year, according to Prime Market Terminal data.
EURO TECHNICAL PERSPECTIVE: EUR/USD is ready to test 1,1800 in the short term
The upward trend remains intact after printing a successive series of higher and higher minimums, indicating that buyers are still in control. Although the relative force index (RSI) has reached overcompra conditions, opening the door to a setback, it is likely that the EUR/USD experiences a fall, providing a purchase opportunity to push the exchange rate towards 1,1800. A rupture of this last will expose 1,1900 and 1,2000.
On the contrary, if the EUR/USD falls below 1,1700, the first support would be the minimum daily of June 26, 1,1653. Once surpassed, the following support would be 1,1600, before the 50 -day SMA in 1,1515.
Euro Faqs
The euro is the currency of the 19 countries of the European Union that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most negotiated currency in the world, behind the US dollar. In 2022, it represented 31 % of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily business volume of more than 2.2 billion dollars a day. The EUR/USD is the most negotiated currency pair in the world, with an estimate of 30 %of all transactions, followed by the EUR/JPY (4 %), the EUR/GBP (3 %) and the EUR/AU (2 %).
The European Central Bank (ECB), based in Frankfurt (Germany), is the Eurozone reserve bank. The ECB establishes interest rates and manages monetary policy. The main mandate of the ECB is to maintain price stability, which means controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its main tool is the rise or decrease in interest rates. Relatively high interest rates (or the expectation of higher types) usually benefit the euro and vice versa. The GOVERNMENT BOOK of the ECB makes decisions about monetary policy in meetings that are held eight times a year. The decisions are made by the directors of the National Banks of the Eurozone and six permanent members, including the president of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the harmonized consumer prices index (IPCA), are an important economic indicator for the euro. If inflation increases more than expected, especially if it exceeds 2% of the ECB, it forces the ECB to rise interest rates to control it again. Relatively high interest rates compared to their counterparts usually benefit the euro, since they make the region more attractive as a place for global investors to deposit their money.
Published data measure the health of the economy and can have an impact on the euro. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, employment and consumer trust surveys can influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the euro. Not only attracts more foreign investment, but it can encourage the ECB to raise interest rates, which will directly strengthen the euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the euro is likely to fall. The economic data of the four largest economies in the euro zone (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, since they represent 75% of the economy of the euro area.
Another important fact that is published on the euro is the commercial balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns with its exports and what you spend on imports during a given period. If a country produces highly demanded export products, its currency will gain value simply by the additional demand created by foreign buyers seeking to buy those goods. Therefore, a positive net trade balance strengthens a currency and vice versa in the case of a negative balance
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







