- EUR/USD cuts profits after reaching 1,1420 by tariff relief; Thin vacation markets keep the dollar under pressure.
- Trump postpone the threat of tariffs of 50% to the EU until July 9, relieving commercial tensions in the short term.
- BCE lagarde hints that the euro could rival the dollar if the block strengthens its financial unit.
- Kashkari of the Fed indicates risks of tariff stings; The path of September policy is still uncertain.
The EUR/USD begins the week with good foot but cuts some of its previous profits after reaching a maximum of four weeks of 1,1420, sponsored by the reversal of US President Donald Trump about his decision to impose tariffs on the European Union (EU) on June 1. At the time of writing, the main currency is quoted at 1,1380, with an increase of 0.20%.
Last week, late on Friday, Trump threatened to impose 50% tariffs on EU goods on June 1, since negotiations with the block do not advance as expected. This caused an increase in the EUR/USD, which ended in a maximum of two days of 1,1375. However, a call among the president of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, and Trump on Sunday bought some time for both parties to reach an agreement with a deadline on July 9.
The decline of the dollar has favored the euro, which, according to the president of the European Central Bank (ECB), Christine Lagarde, could become a viable alternative to the US dollar (USD) as a world reserve currency. However, she said that this could happen if governments strengthen the financial and security architecture of the block.
The US dollar index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the American currency compared to six other currencies, has dropped 0.10%. Even so, it remains stable in 99.00 due to moderate negotiation conditions of the Fallen Day Holiday in the US.
The president of the Federal Reserve of Minneapolis (Fed), Neel Kashkari, said the uncertainty is in the mind of the FED and US companies. He said that the September meeting is open to “anything”, adding that the American central bank is in waiting and observation mode. He added that the impact of tariffs is stagning.
Euro price today
The lower table shows the percentage of euro change (EUR) compared to the main currencies today. Euro was the strongest currency in front of the Japanese yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | Aud | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.14% | -0.27% | 0.19% | 0.03% | 0.10% | -0.22% | -0.03% | |
| EUR | 0.14% | -0.12% | 0.36% | 0.17% | 0.24% | -0.08% | 0.12% | |
| GBP | 0.27% | 0.12% | 0.15% | 0.29% | 0.36% | 0.04% | 0.26% | |
| JPY | -0.19% | -0.36% | -0.15% | -0.15% | -0.09% | -0.46% | -0.21% | |
| CAD | -0.03% | -0.17% | -0.29% | 0.15% | 0.08% | -0.25% | -0.03% | |
| Aud | -0.10% | -0.24% | -0.36% | 0.09% | -0.08% | -0.36% | -0.10% | |
| NZD | 0.22% | 0.08% | -0.04% | 0.46% | 0.25% | 0.36% | 0.22% | |
| CHF | 0.03% | -0.12% | -0.26% | 0.21% | 0.03% | 0.10% | -0.22% |
The heat map shows the percentage changes of the main currencies. The base currency is selected from the left column, while the contribution currency is selected in the upper row. For example, if you choose the euro of the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US dollar, the percentage change shown in the box will represent the EUR (base)/USD (quotation).
EUR/USD daily market movements: sustained by a large fiscal deficit from the US, strong EU data
- Recent data in the EU support a greater increase in the EUR/USD, since Germany’s economy grew faster than expected. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the first quarter of 2025 was 0.4%, compared to 0.2%.
- The US dollar remains at a disadvantage, pressed for the approval of Trump’s fiscal bill in the House of Representatives, which is on their way to the Senate. If approved, the proposal would add about 4 billion dollars to the US debt limit in a decade, according to the Congress Budget Office (CBO).
- EUR/USD will continue to be promoted by economic data. The EU’s economic agenda will include the confidence of the GFK consumer of Germany, employment and retail sales data in the EU. Inflation will be informed in Germany, France, Italy, Spain and the EU.
- The US economic agenda will include the requests for lasting goods in April, the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee Meeting (FOMC), the second estimate of the GDP of the first quarter of 2025 and the publication of the Personal Consumption Price Index (PCE), the Fed’s preferred inflation indicator.
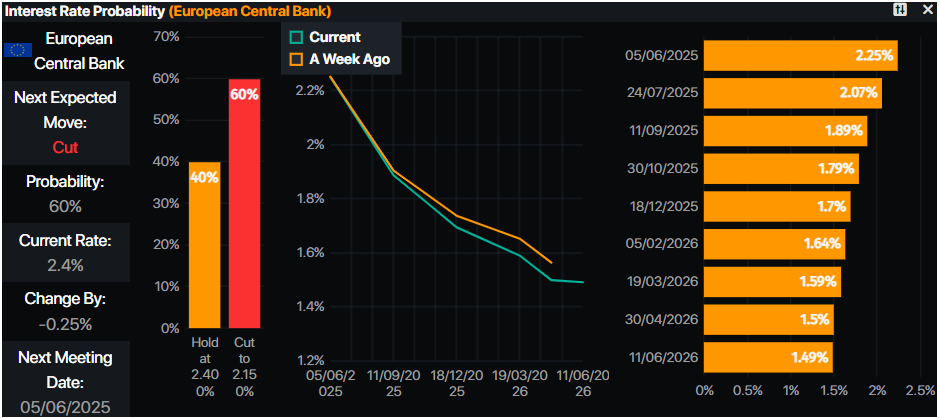
- The European Central Bank (ECB) is expected to lower interest rates in the next meeting. On Friday, Rehn and Stournaras of the ECB supported a rate cut in June, being the latter favorable to a pause after that meeting.
Fountain: Prime Market Terminal
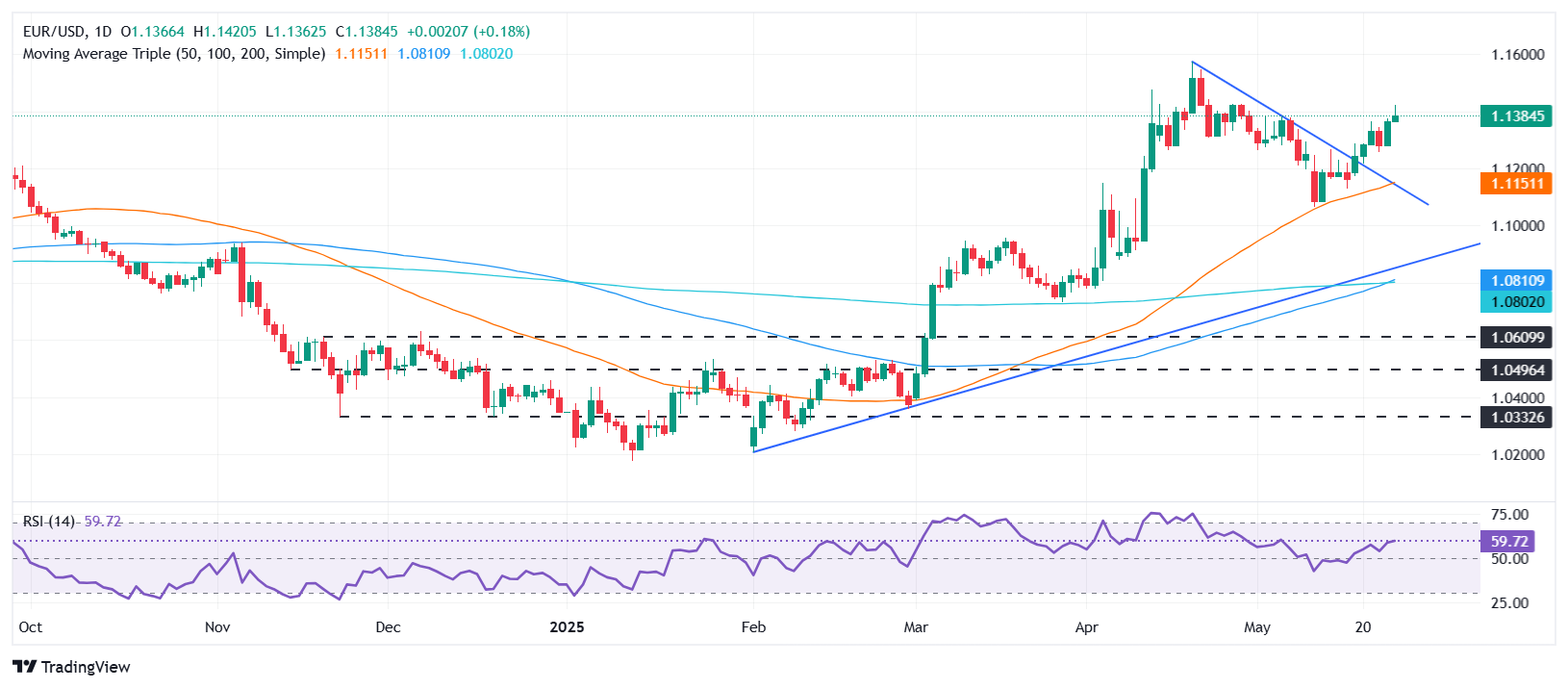
EUR/USD technical perspective: Ready to challenge 1,1400 in the short term
The EUR/USD maintains an upward trend despite forming an ‘inverted hammer’, indicating that sellers are surpassing buyers due to the large upper shadow in today’s price action. However, greater confirmation is needed, and the torque must fall below 1,1300 so that sellers can try lower prices.
The next key support level would be the simple mobile average (SMA) of 20 days in 1,1270, followed by the 1200 mark.
On the positive side, if the EUR/USD remains above 1,1375, the following resistance would be the maximum of May 26, 1,1418, followed by 1,1450 and 1,1500.
Euro Faqs
The euro is the currency of the 19 countries of the European Union that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most negotiated currency in the world, behind the US dollar. In 2022, it represented 31 % of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily business volume of more than 2.2 billion dollars a day. The EUR/USD is the most negotiated currency pair in the world, with an estimate of 30 %of all transactions, followed by the EUR/JPY (4 %), the EUR/GBP (3 %) and the EUR/AU (2 %).
The European Central Bank (ECB), based in Frankfurt (Germany), is the Eurozone reserve bank. The ECB establishes interest rates and manages monetary policy. The main mandate of the ECB is to maintain price stability, which means controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its main tool is the rise or decrease in interest rates. Relatively high interest rates (or the expectation of higher types) usually benefit the euro and vice versa. The GOVERNMENT BOOK of the ECB makes decisions about monetary policy in meetings that are held eight times a year. The decisions are made by the directors of the National Banks of the Eurozone and six permanent members, including the president of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the harmonized consumer prices index (IPCA), are an important economic indicator for the euro. If inflation increases more than expected, especially if it exceeds 2% of the ECB, it forces the ECB to rise interest rates to control it again. Relatively high interest rates compared to their counterparts usually benefit the euro, since they make the region more attractive as a place for global investors to deposit their money.
Published data measure the health of the economy and can have an impact on the euro. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, employment and consumer trust surveys can influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the euro. Not only attracts more foreign investment, but it can encourage the ECB to raise interest rates, which will directly strengthen the euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the euro is likely to fall. The economic data of the four largest economies in the euro zone (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, since they represent 75% of the economy of the euro area.
Another important fact that is published on the euro is the commercial balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns with its exports and what you spend on imports during a given period. If a country produces highly demanded export products, its currency will gain value simply by the additional demand created by foreign buyers seeking to buy those goods. Therefore, a positive net trade balance strengthens a currency and vice versa in the case of a negative balance
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.


.jpg)