- The euro doubts while the markets are prepared for an ECB interest rate cut.
- The weak growth of the eurozone and the soft inflation figures point to greater relief this year.
- The US dollar fights after negative services of services in the USA.
EUR/USD He went down in a quiet Asian session on Thursday and quotes just above the level of 1,1400 at the time of writing. The US dollar (USD) was beaten by US negative macroeconomic data on Wednesday before stopping at 1,1435, and the approach has moved to the monetary policy decision of the European Central Bank (ECB) that will be announced later in the day.
It is widely expected that the BCE Cut the interest rates for the eighth consecutive time, and it is very likely to indicate a pause in July. The Bank President, Christine LagardeIt will try to convey a neutral message, but the weak economic growth of the Eurozone and the moderation of inflation point to greater relief in the future.
The US dollar, on the other hand, is still fragile, since the negative data of the US have revived the fears of an economic recession, amid uncertainty about tariffs and imminent concerns about US debt.
The activity of the US services sector was contracted against expectations in May, according to the PMI publication of the ISM. This is the first contraction in almost a year and continues to another decrease in manufacturing activity and poor factory orders observed earlier this week, which has revived concerns about an economic recession.
Beyond that, US ADP figures revealed an increase in the shortest employment than expected, which decreased enthusiasm on optimistic employment offers seen Tuesday and generated doubts about the non -agricultural payroll report on Friday. Wednesday data bitter the feeling of the market and caused a significant reversal in the US dollar index (DXY).
Euro price this week
The lower table shows the percentage of euro change (EUR) compared to the main currencies this week. Euro was the strongest currency against the US dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | Aud | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.55% | -0.73% | -0.36% | -0.51% | -0.98% | -1.15% | -0.30% | |
| EUR | 0.55% | -0.19% | 0.20% | 0.03% | -0.44% | -0.62% | 0.25% | |
| GBP | 0.73% | 0.19% | 0.41% | 0.23% | -0.24% | -0.45% | 0.44% | |
| JPY | 0.36% | -0.20% | -0.41% | -0.15% | -0.63% | -0.82% | -0.03% | |
| CAD | 0.51% | -0.03% | -0.23% | 0.15% | -0.46% | -0.67% | 0.22% | |
| Aud | 0.98% | 0.44% | 0.24% | 0.63% | 0.46% | -0.14% | 0.76% | |
| NZD | 1.15% | 0.62% | 0.45% | 0.82% | 0.67% | 0.14% | 0.89% | |
| CHF | 0.30% | -0.25% | -0.44% | 0.03% | -0.22% | -0.76% | -0.89% |
The heat map shows the percentage changes of the main currencies. The base currency is selected from the left column, while the contribution currency is selected in the upper row. For example, if you choose the euro of the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US dollar, the percentage change shown in the box will represent the EUR (base)/USD (quotation).
What moves the market today: the euro doubts before the ECB Decision
- The euro is moving laterally, just above the level of 1,1400, driven by a US dollar. However, investors are cautious when making great bets in the euro, waiting for the ECB monetary policy decision and more information about the next steps.
- The ECB, most likely, will cut interest rates in 25 basic points to a level of 2%. The main attraction of the event will be the press conference of President Lagarde, from which markets are expected to obtain new clues about the plans of the Central Bank.
- Lagarde will remain in the “meeting by meeting” line, but the recent eurozone data have shown weak economic growth and inflationary pressures in cooling, which suggests that the ECB could cut the rates even more further later this year to support economic activity.
- In the US, the ISM services PMI fell against expectations and bitter the feeling of the market. The May PMI decreased to 49.9 from April 51.6, against market expectations of a level of 52.00. The paid prices increased, and the employment subscript expanded after having contracted in the previous months.
- The negative impact of the PMI was aggravated by an Adp negative employment change report, which showed a 37K increase in the private payrolls of May, well below the increase of 115K anticipated by the market consensus.
- Beyond that, commercial uncertainty remains high. 50% tariffs from US President Donald Trump on steel and aluminum entered into force on Wednesday in the midst of lack of progress in any significant commercial agreement. He complained that it is “extremely difficult to reach an agreement” with the Chinese president Xi Jinping, confirming that the world’s main economies are far from solving their commercial problems.
Technical analysis: EUR/USD oscillates around 1,1400, lacking a clear trend
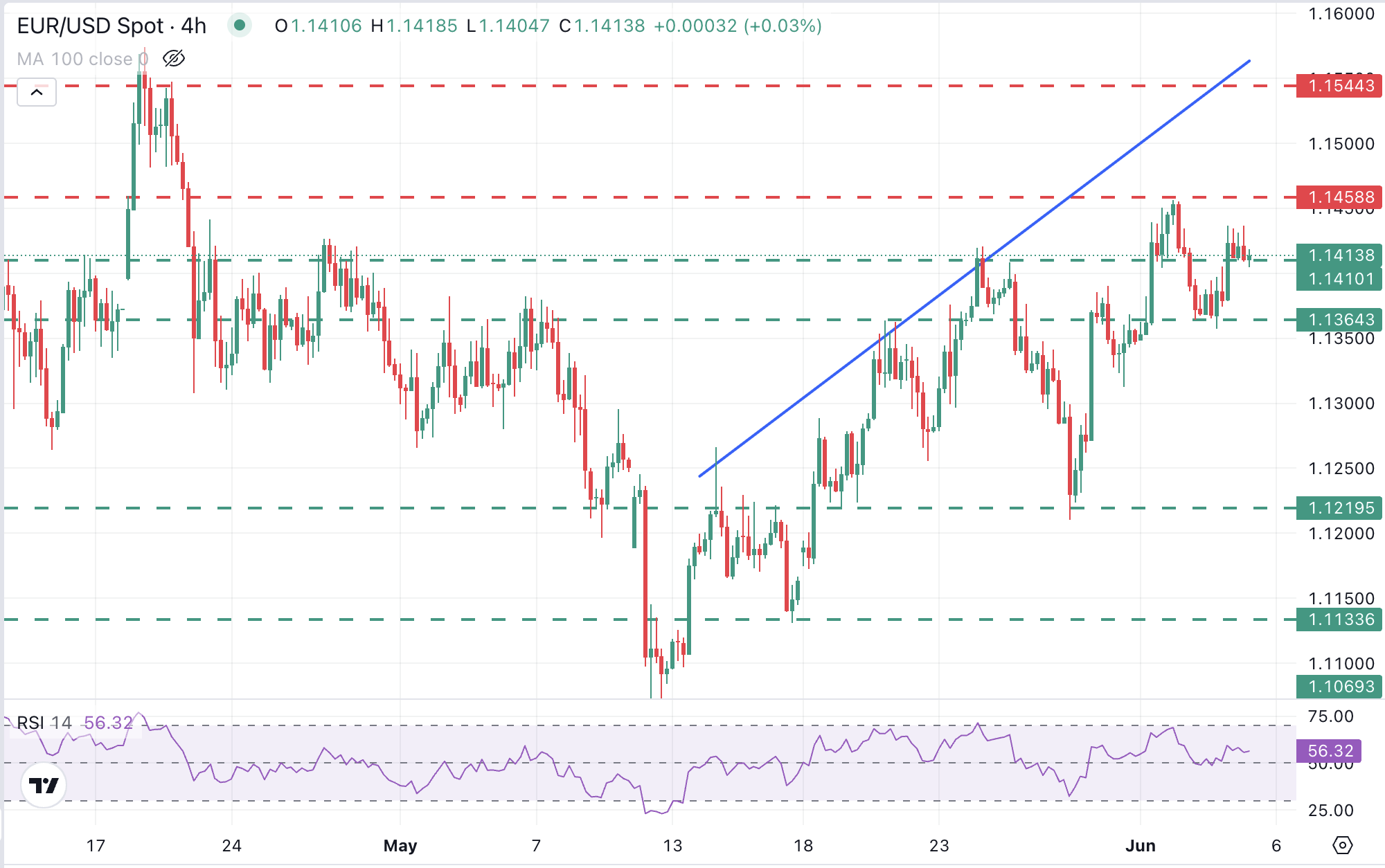
The reversal of the EUR/USD from the maximum of six weeks reached on Tuesday has contained in the middle part of the 1,1300, but the torque has lost impulse above 1,1400 with investors observing from the lateral line, a few hours before the ECB monetary policy decision.
The RSI of the four -hour graph is maintaining plane near level 50, suggesting that the torque impulse is decreasing. The lowest maximum on Wednesday, despite the weak US data, is a negative signal.
The pair would need to break 1,1460 to confirm the upward trend and point to 1,1545, where the maximum of April 22 and the resistance of the trend line are located.
BCE FAQS
The European Central Bank (ECB), based in Frankfurt (Germany), is the euro zone reserve bank. The ECB sets interest rates and manages the monetary policy of the region.
The main mandate of the ECB is to maintain prices stability, which means maintaining inflation around 2%. Its main tool to achieve this is to raise or lower interest rates. Relatively high interest rates often translate into a stronger euro, and vice versa.
The BCE Governing Council adopts monetary policy decisions in meetings that are held eight times a year. The decisions are adopted by the directors of the national banks of the euro zone and six permanent members, including the president of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can launch a political tool called Quantitative Easing (quantitative relaxation). The QE is the process by which the ECB prints euros and uses them to buy assets (normally state or business bonds) to banks and other financial institutions. The result is usually a weaker euro ..
The QE is a last resort when it is unlikely that a simple decrease in interest rates achieves the price stability objective. The ECB used it during the great financial crisis of 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the Coronavirus pandemic.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the reverse of the QE. It is carried out after the QE, when economic recovery is underway and inflation begins to increase. While in the QE the European Central Bank (ECB) buys state and business bonds from financial institutions to provide liquidity, in the QT the ECB stops buying more bonds and stops reinvesting the main one that overcomes the bonds it already has. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the euro.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.





