- EUR/USD falls near 1.0830 as weak Eurozone flash PMI weighs on the Euro.
- The ECB is expected to cut interest rates twice more before the end of the year.
- Investors are looking to US core PCE inflation for further guidance on interest rates.
EUR/USD weakened near 1.0830 in the European session on Wednesday as the Hamburg Commercial Bank (HCOB) preliminary Eurozone Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) report for July showed that the composite numbers unexpectedly softened due to a slowdown in activities in both the manufacturing and services sectors.
The HCOB Composite PMI declined to 50.1, just above the 50 threshold that separates expansion from contraction. Investors had expected the Composite PMI to have expanded at a faster pace to 51.1 from the previous release of 50.9. The HCOB Manufacturing PMI contracted to 45.6, while the Services PMI expanded at a slower pace of 51.9.
Comments by Dr. Cyrus de la Rubia, Chief Economist at Hamburg Commercial Bank, on the flash PMI indicated that weak demand in the Eurozone’s largest economy has weighed heavily on the manufacturing sector. De la Rubia said, “French service providers increased their business activity in July due to preparation for the Olympic Games. In contrast, demand in the German manufacturing sector appears to have dragged down overall private sector output.”
Weak economic activity in the Eurozone is expected to raise expectations for further rate cuts by the European Central Bank (ECB). However, price data did not offer any relief to ECB policymakers. According to the preliminary PMI report, input prices in the services sector rose at a faster pace, and sales prices rose at a similar pace to the previous survey period.
Traders currently see the ECB making two more rate cuts this year. Moreover, some ECB officials view market expectations for two more rate cuts as appropriate.
Market Movers and Daily Moves: EUR/USD Falls as US Dollar Advances
- EUR/USD faces intense sell-off and extends its decline near 1.0830 as the US Dollar (USD) advances. The US Dollar is rising amid risk aversion of Donald Trump emerging victorious in the United States (US) presidential election in November and uncertainty ahead of the Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index data for June due on Friday.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the value of the greenback against six major currencies, is posting a fresh weekly high around 104.50. Expectations of Trump’s return to power have risen following an assassination attempt against him. Meanwhile, Democrats have nominated Vice President Kamala Harris as a leader to fight the Republicans.
- On the economic front, investors will focus on the US core PCE inflation data as it would provide fresh clues as to when the Federal Reserve (Fed) will start cutting interest rates. The report is expected to show that core PCE inflation, the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, slowed to 2.5% from May’s figure of 2.6%, with the monthly figure growing steadily by 0.1%.
- A scenario in which price pressures ease as expected or at a faster pace would increase expectations for early rate cuts by the Fed. On the contrary, persistent figures would weaken bets on rate cuts. According to the CME FedWatch tool, 30-day federal funds futures show that the central bank will start to reduce its key interest rates from their current levels at the September meeting.
- In Wednesday’s session, the US Dollar will be boosted by the preliminary S&P Global PMI data for July, due out at 13:45 GMT. Economists expect the manufacturing PMI to have expanded at a nominal pace of 51.7 from June’s reading of 51.6. The services PMI, a measure of activities in the service sector, is estimated to have expanded at a slower pace of 54.4 from the previous release of 55.3.
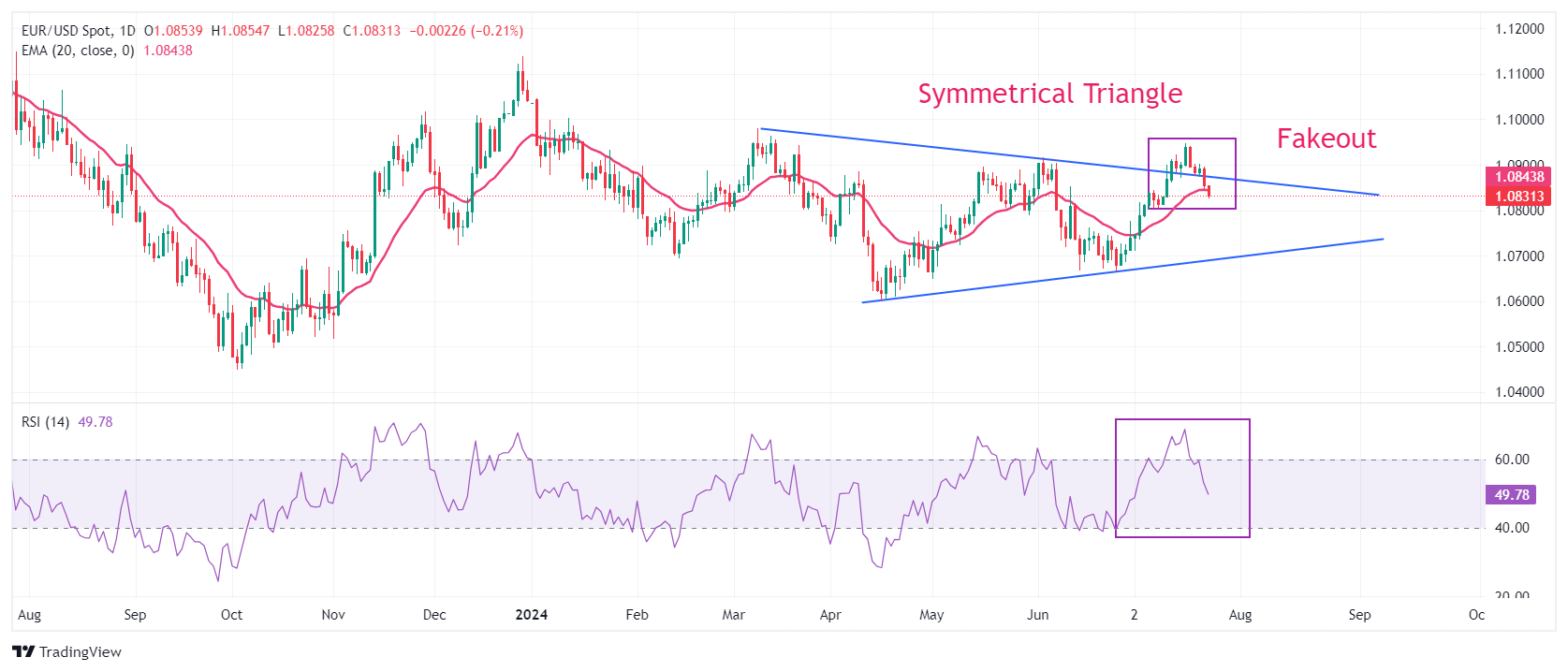
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD Fails to Hold Triangle Breakout
EUR/USD is back inside the Symmetrical Triangle formation on a daily time frame after failing to sustain the breakout. The major currency pair is extending its decline below the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which is trading around 1.0840. The shared currency pair could slide further towards the round-level supports near 1.0800 and 1.0700.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is back within the 40.00-60.00 range, suggesting that the bullish momentum has faded.
On the upside, the round-level resistance at 1.0900 will be a key barrier for Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency of the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most traded currency in the world, behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily volume of over $2.2 trillion per day. EUR/USD is the most traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% of all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB), based in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank of the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s main mandate is to maintain price stability, which means controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its main instrument is to raise or lower interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – generally benefit the Euro and vice versa. The Governing Council of the ECB takes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are taken by the heads of the national banks of the Eurozone and six permanent members, including ECB President Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, as measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric data point for the euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if it exceeds the ECB’s 2% target, the ECB is forced to raise interest rates to bring inflation back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to their peers usually benefit the euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases measure the health of the economy and can influence the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, employment and consumer sentiment surveys can influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment, but it can encourage the ECB to raise interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Conversely, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data from the four largest Eurozone economies (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone economy.
Another important output for the euro is the trade balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports during a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after export products, its currency will appreciate due to the additional demand created by foreign buyers who wish to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net trade balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.