- The USD/CHF corrects about 0.8400 while the US dollar faces pressure due to US CPI data for April, which were lower than expected.
- Market expectations so that the FED maintains stable interest rates in April were firm despite the slowdown in inflation in the US.
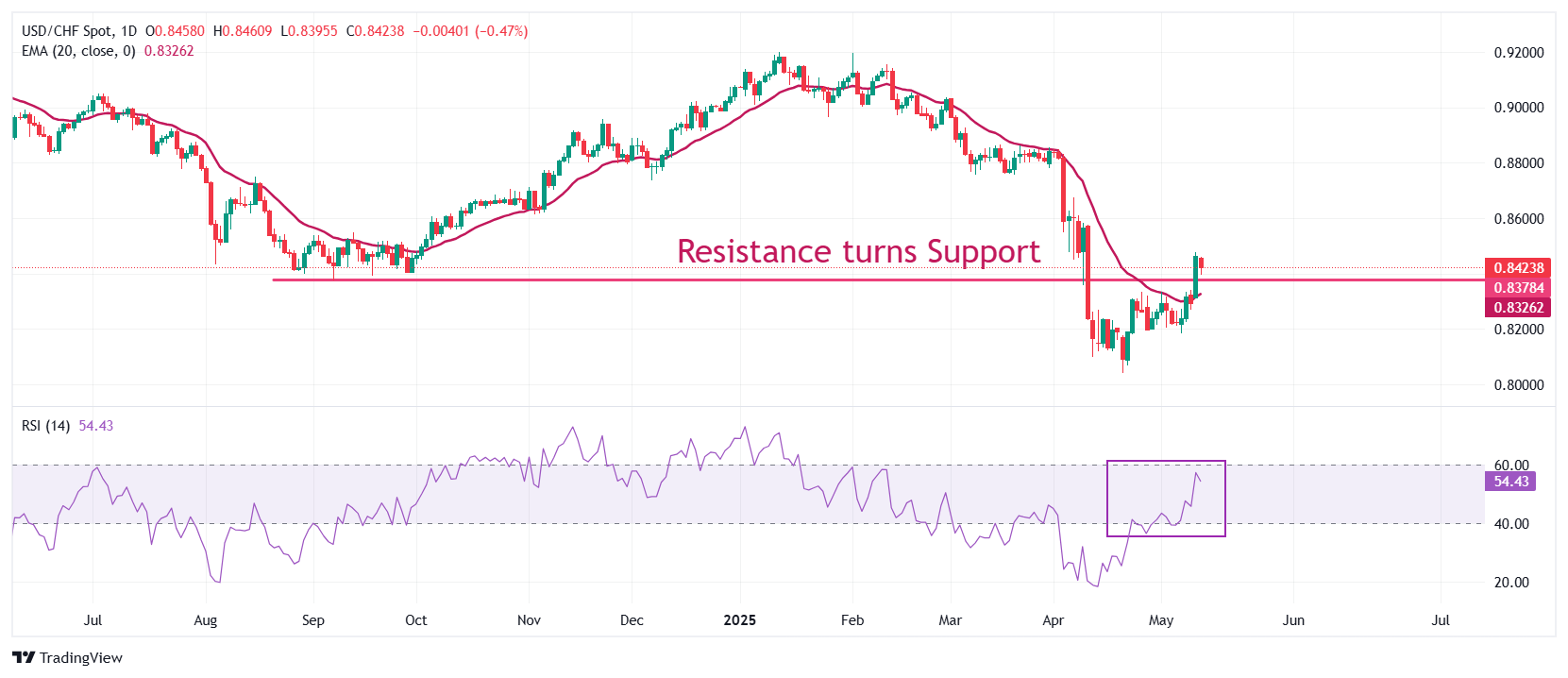
- The Swiss Franco pair breaks above the 20 -day ema, suggesting a strong upward trend.
The USD/CHF pair goes back to the round level support of 0.8400 during the North American negotiation hours on Tuesday. The Swiss frank torque corrects while the US dollar faces sales pressure after the publication of the US consumer price index (CPI) for April, which showed that price pressures increased at a moderate rate.
The US dollar index (DXY), which measures the value of the dollar against six main currencies, corrects about 101.30 from the monthly maximum of around 102.00 registered on Monday.
According to the IPC report, general inflation increased at a slower pace of 2.3% year -on -year, compared to estimates and the previous 2.4% publication. In the same period, the underlying IPC – which excludes volatile food and energy prices – constantly grew by 2.8%, as expected.
Inflationary pressures in cooling have not impacted market expectations on the monetary policy perspective of the Federal Reserve (FED). According to the CME Fedwatch tool, the probability that the Fed maintain stable interest rates in the current range of 4.25%-4.50%in July remained firm at 61.4%. On Monday, the operators reduced the Fed Dovish bets for the July policy meeting after the US and China agreed to reduce tariffs by 115% for 90 days.
Meanwhile, the Swiss Franco (CHF) is negotiated in front of his peers, except the antipodals, on Tuesday.
Franco Swiss price today
The lower table shows the rate of change of the Swiss Franco (CHF) compared to the main coins today. Franco Swiss was the strongest currency against the Canadian dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | Aud | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.48% | -0.40% | -0.37% | 0.16% | -0.90% | -0.95% | -0.39% | |
| EUR | 0.48% | 0.09% | 0.12% | 0.64% | -0.42% | -0.45% | 0.12% | |
| GBP | 0.40% | -0.09% | 0.04% | 0.55% | -0.50% | -0.56% | 0.04% | |
| JPY | 0.37% | -0.12% | -0.04% | 0.54% | -0.53% | -0.60% | 0.03% | |
| CAD | -0.16% | -0.64% | -0.55% | -0.54% | -1.14% | -1.11% | -0.53% | |
| Aud | 0.90% | 0.42% | 0.50% | 0.53% | 1.14% | -0.04% | 0.54% | |
| NZD | 0.95% | 0.45% | 0.56% | 0.60% | 1.11% | 0.04% | 0.58% | |
| CHF | 0.39% | -0.12% | -0.04% | -0.03% | 0.53% | -0.54% | -0.58% |
The heat map shows the percentage changes of the main currencies. The base currency is selected from the left column, while the contribution currency is selected in the upper row. For example, if you choose the Swiss Franco from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US dollar, the percentage change shown in the picture will represent the ChF (base)/USD (quotation).
The USD/CHF finds support near the horizontal support set from the minimum of September 6, 0.8375, which used to be an important resistance for the torque. The asset has risen above the 20 -day exponential (EMA) mobile average, which is negotiated around 0.8326, indicating a strong upward trend.
The 14 -day relative force index (RSI) jumps to about 60.00. A new bullish impulse will take effect if the RSI breaks above the level of 60.00.
A new upward movement towards the maximum of April 10, 0.8580 and the maximum of April 8, 0.8611 would appear if it breaks above the psychological level of 0.8500.
On the other hand, a downward movement below the minimum of May 7, 0.8186 would drag the asset towards the minimum of April 11, 0.8100, followed by the minimum of April 21, 0.8040.
USD/CHF daily graphics
US dollar FAQS
The US dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation along with local tickets. According to data from 2022, it is the most negotiated currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency change operations, which is equivalent to an average of 6.6 billion dollars in daily transactions. After World War II, the USD took over the pound sterling as a world reserve currency.
The most important individual factor that influences the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% objective set by the Fed, it rises the types, which favors the price of the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and promulgate quantitative flexibility (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure that is used when the credit has been exhausted because banks do not lend each other (for fear of the default of the counterparts). It is the last resort when it is unlikely that a simple decrease in interest rates will achieve the necessary result. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed to combat the contraction of the credit that occurred during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy bonds of the US government, mainly of financial institutions. Which usually leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the reverse process for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the wallet values that overcome in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.