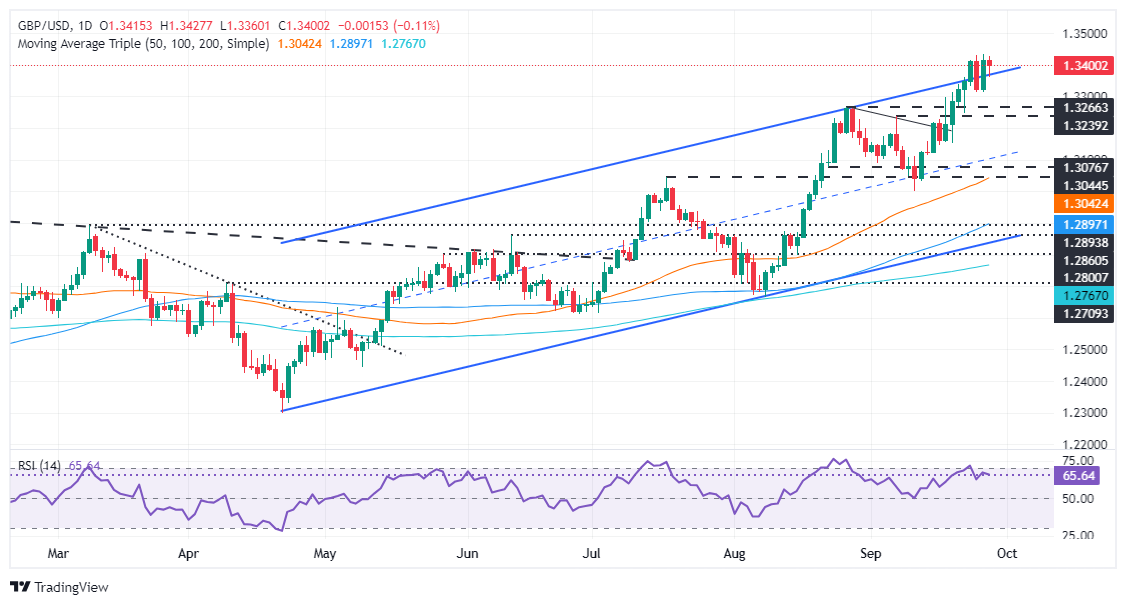
- GBP/USD is trading at 1.3403, down 0.08%, close to its two-year peak.
- Momentum fades with a possible negative divergence, but a break above 1.3437 could target 1.3450 and 1.3500.
- A drop below 1.3312 could see further declines towards the September 23 low of 1.3248.
The British pound posted minimal losses against the dollar but remains near two-year highs on Friday. The US Bureau of Economic Analysis revealed that inflation is close to reaching the Fed’s 2% target. At the time of writing, GBP/USD is trading at 1.3403, down 0.08%.
GBP/USD Technical Outlook
The pair has a bullish bias, although the trend has lost some strength as buyers failed to push GBP/USD to a new all-time high in 2024.
As the price action continues to rise, the momentum has faded. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) continues to decline, while spot prices point higher. Therefore, a negative divergence could be forming, but sellers need to push prices below the upper trend line of an ascending channel.
If GBP/USD extends its gains beyond the March 1, 2022 peak of 1.3437, the next resistance would be 1.3450, followed by 1.3500.
On the contrary, if the pair falls below the September 25-26 low of 1.3312, more losses are expected. The next support would be the September 23 low at 1.3248, followed by the 1.3200 figure.
GBP/USD Price Action – Daily Chart
The British Pound FAQs
The British Pound (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded currency unit in the world, with 12% of all transactions and an average of $630 billion per day, according to 2022 data.
Its key currency pairs are GBP/USD, also known as “Cable”, which represents 11% of the forex market, GBP/JPY, or the “Dragon” as it is known to traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The pound sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is the monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The Bank of England bases its decisions on achieving its main objective of “price stability”, that is, a stable inflation rate of around 2%. Its main tool to achieve this is the adjustment of interest rates.
When inflation is too high, the Bank of England tries to contain it by raising interest rates, which makes access to credit more expensive for individuals and companies. This tends to be positive for the GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
When inflation is too low, it is a sign that economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to make credit cheaper, so that companies borrow more to invest in projects that generate growth.
The published data gauges the health of the economy and may influence the value of the Pound sterling. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, and employment can influence the direction of the Pound.
A strong economy is good for the British pound. Not only does it attract more foreign investment, but it may encourage the Bank of England to raise interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Pound. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the pound is likely to fall.
Another significant data for the pound sterling is the trade balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports during a given period.
If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit exclusively from the additional demand created by foreign buyers wishing to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net trade balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.