It seems that humanity is going through a period of incredible space discoveries. What is the work of SpaceX, which legalized the space beyond the Earth for private business, or the James Webb telescope, systematically studying distant galaxies, worth. However, it’s time to admit that the vast majority of us know absolutely nothing about open space. What can we talk about if the heat on our planet is associated with the incessant burning of the Sun?!
To the point:
Black holes suck everything in
→ planets and even stars strive to get there
Black holes suck life out of stars, even light cannot escape from their paws, and everything that gets inside is immediately crushed into particles smaller than atoms. In films and other fantasy fiction, they are depicted as huge space vacuum cleaners. However, this is a mistake. In practice, black holes behave in much the same way as all other massive objects in the universe. Yes, they have attraction, like stars or planets, but it can be avoided. To do this, you need to move fast enough – however, the farther from the object, the less speed is needed to run away from it. If instead of the Sun there was a black hole at the center of our star system, the Earth would continue to move in the same orbit.
▶︎ Fact: to “escape” from the Sun, you need to move at a speed of about 618 kilometers per second – this is fast enough, but not impossible. At the event horizon of known black holes (they are huge), the approximate speed it takes to fly away is 300,000 kilometers per second.
In summer, the Earth is closer to the Sun
→ how else to explain that it is getting warmer on it?!
The earth does not really move around the sun in a regular circle, so this statement looks realistic. However, it breaks to pieces when you realize that in the northern and southern hemispheres, summer comes at different times of the year. In fact, the Earth’s orbit is generally not as elliptical as many imagine it to be. The difference between the farthest and closest distances to the Sun is about 5 million kilometers – about 3% of the total distance. The real reason for the change of seasons lies in the axial tilt of the Earth – at different times of the year, the southern and northern hemispheres are at different angles with respect to the Sun.
The sun is a fireball that burns constantly
→ it is because of the “fire” that heat is released on the Sun
Mistake – period. The vital activity of fire is characterized by three processes: fuel consumption, heat release and the presence of oxygen. The Sun has no problems with the first one – it is almost entirely composed of hydrogen and helium. The second is also quite possible – the Sun generates a huge amount of thermal energy, and the temperature on its surface reaches 5500 ℃. However, in space there is no oxygen at all, so the process of burning on the Sun cannot occur. Yes, our star is not a fireball, as many people think – the heat that comes from it is the result of thermonuclear fusion. In the environment of high pressure and high temperature of the Sun, high-speed hydrogen atoms converge to one femtometer (0.000000000000001 meters). A collision at this distance allows the two nuclei to fuse together, forming helium and releasing huge amounts of energy in the form of gamma rays.
▶︎ Fact: every second, 700 million tons of hydrogen collide inside the sun. This process produces 650,000 tons of helium, which sets off a chain reaction and keeps this natural nuclear reactor running.
It is very difficult for a spacecraft to overcome the asteroid belt.
→ you need to fly around floating stones, like in Star Wars

Between Mars and Jupiter in the solar system is the asteroid belt, which consists of more than 3,000 minor planets and about 750,000 individual asteroids with a diameter of 1000 meters or more. These objects also sometimes collide, creating some new ones. That is why, when Han Solo pilots the Millennium Falcon into an asteroid field in Star Wars: The Empire Strikes Back, he is warned that the chance of successfully navigating the asteroid field is about 3,720 to one. If the Hoth asteroid field from the movie was anything like ours, the statistics are wrong, because in fact the distance between the asteroids in the field is so large (about 970,000 kilometers on average) that colliding with one of them is a “lucky” accident.
The stars in the constellations are close to each other
→ that’s why they create pictures in the sky

In the night sky, there was a place for 88 constellations that are associated with inanimate objects, animals, birds, and even fantasy creatures. Previously, they served as a guide for farmers and travelers, who have always considered such star “groups” as something of a creation of higher powers. In fact, the proximity of the stars in the constellations is an optical illusion. In fact, they are separated by tens and hundreds of thousands of light years. Moreover, the stars can differ in age, period of life and intensity of the glow – they seem to be close only from our point of view, nothing more.
▶︎ Fact: constellations are not scientifically significant groups of stars at all. However, they help break up the sky into recognizable and manageable parts, evoking associations between patterns of single dots and familiar animals or objects. Even astronomers use it.
The moon has a dark side
→ the third part of “Transformers” confirms this

The conditionally dark side of the moon has inspired many to create music albums, novels, television series, films, video games. However, the Earth’s satellite is somewhat different from its public representation – if some side of it is not visible from our planet, this does not mean that it is not illuminated. This myth is easily refuted by the phases of the moon. During a full moon, the side that can be seen is illuminated, while the other side is in complete darkness. However, at any other time of the month, only part of the moon can be seen – the rest of the light falls on the far side, which is called the dark side.
Mercury is the hottest planet in the solar system
→ it is closest to the hot Sun
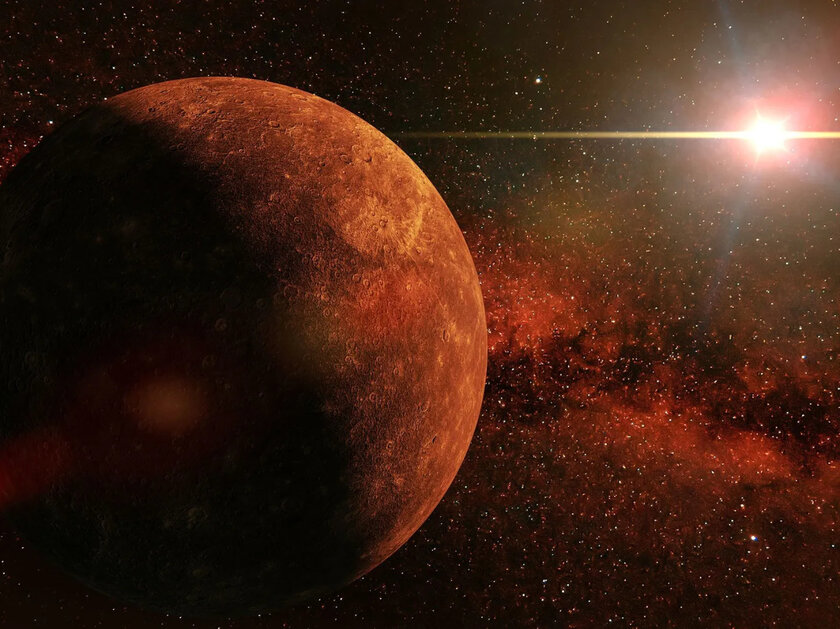

Every second, the Sun releases 3.8×1026 joules of energy, and Mercury is directly in the line of fire at a distance of only 58 million kilometers. It is really very hot here – the daytime temperature reaches 430 ℃. However, on Venus, despite twice the distance from the Sun, it is even higher – about 462 ℃. This difference is due to the atmosphere: on Venus, it is dense and consists of carbon dioxide, which retains heat; on Mercury it has a very small layer.
▶︎ Fact: due to the very “thin” atmosphere, when Mercury turns away from the Sun at night, the temperature on its surface drops to -180℃. This unequivocally hints that the planet gives off heat as quickly as it receives it.
Spacecraft get very hot due to friction with the air when returning to Earth
→ that is why they must be very strong
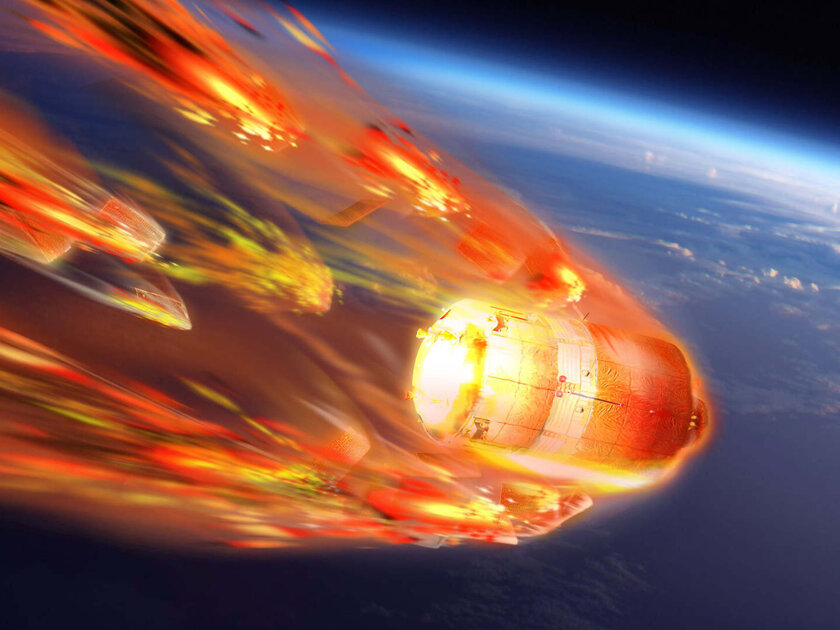

When spacecraft enter the earth’s atmosphere, they move faster than the speed of sound, so their temperature rises dynamically from -155℃ to 1650℃. Is it because of the air? Friction on it in spacecraft is indeed a serious problem for engineers – the more air comes into contact with the surface when launching a rocket, the higher the heating. However, vehicles designed for descents are usually hardly streamlined, and friction is not the main cause of their heating. As the spacecraft zips through the atmosphere, the gas molecules cannot get out of the way fast enough and begin to pile up to form a “cushion”. This keeps most of the gas away from the surface, preventing heat transfer to the apparatus. But heating still occurs – it is achieved due to high pressure: the closer the compressed molecules are to each other, the higher the temperature.
Space is a completely empty vacuum
→ there is nothing at all in outer space
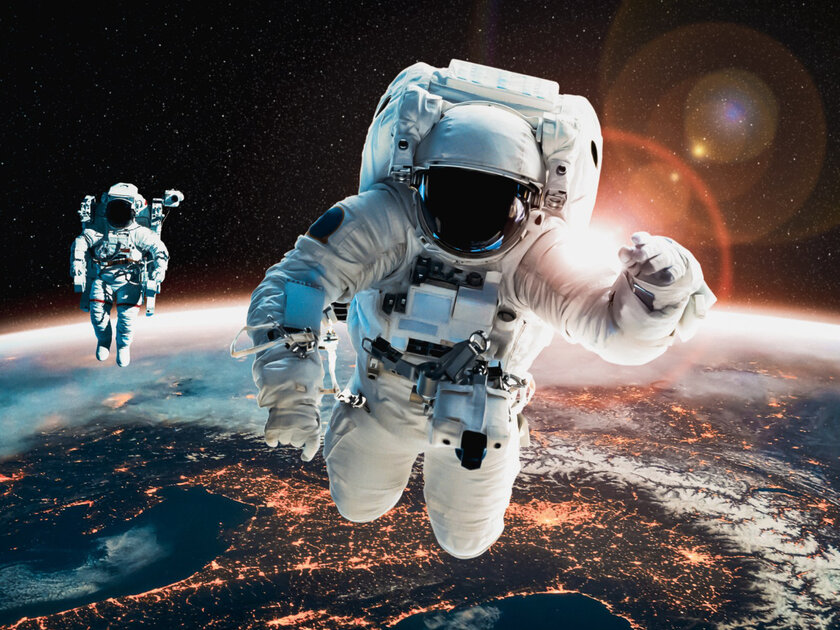

Outer space is indeed the closest place in the universe to a true vacuum. However, there is so much hydrogen there that several atoms can be found in every cubic meter of space. Yes, in fact, this is already something close to vacuum (especially in comparison with the Earth’s atmosphere rich in atoms), but it is far from ideal.
▶︎ Fact: scientists do not know of a single place in the universe in which there is an absolute vacuum with a complete absence of any elements.
There is no gravity at all in space
→ therefore, artificial gravity is needed at the stations
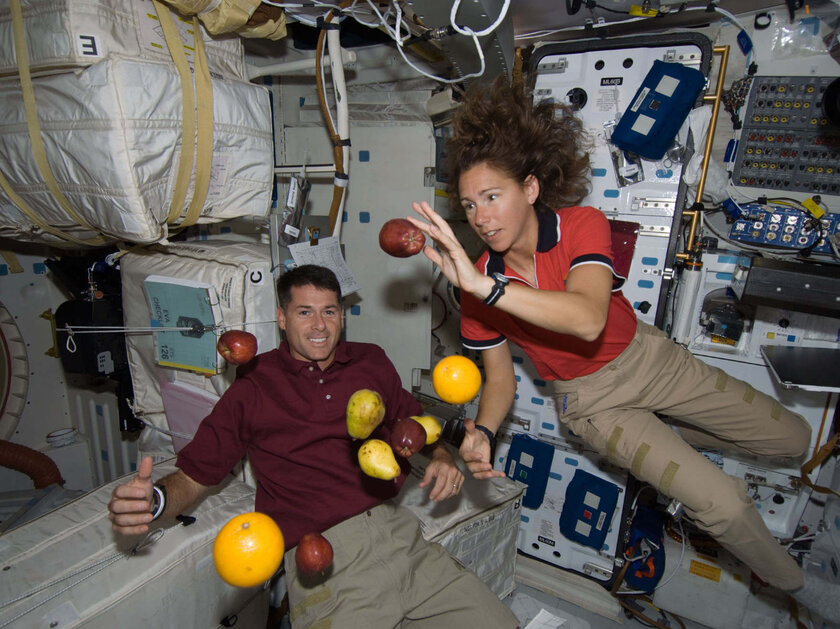

This is not true. Spacecraft like the International Space Station are constantly under the influence of gravity – it is it that keeps them in orbit. The weightlessness experienced by astronauts is explained by the fact that they gradually descend towards the Earth. Gravity pulls the station toward the planet’s surface, but the station moves so fast that it rushes over the horizon, falling around the planet’s curvature. In fact, the astronauts inside are simply in constant free fall.
Source: Trash Box
Charles Grill is a tech-savvy writer with over 3 years of experience in the field. He writes on a variety of technology-related topics and has a strong focus on the latest advancements in the industry. He is connected with several online news websites and is currently contributing to a technology-focused platform.







