- Natural Gas prices fall close to 1%.
- Traders are putting downward pressure on Gas prices, while Germany blocks any possibility of military intervention in Ukraine.
- US Dollar Index consolidates below 104.00 ahead of key data.
Natural Gas (XNG/USD) is turning lower after rising almost all morning in European trading. The traders' sudden change of heart comes after French President Emmanuel Macron's comments could be quickly defused by German Prime Minister Olaf Scholz and NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg, saying the boots on the ground are not an option. This means that the situation in Ukraine is not about to escalate further with NATO remaining on the sidelines.
The US Dollar (USD) faces a hit, with a basket of currencies advancing against the Dollar. The Japanese Yen leads the trend and advances around 0.50% against the Dollar. In the United States, durable goods figures and some confidence indicators will be published.
Natural Gas is trading at $1.76 per MMBtu at the time of writing these lines.
Movements in the Natural Gas market: Geopolitics provokes an instinctive reaction
- Russian gas supplies through Ukraine will stop at the end of 2024, when the transit agreement between Russia and Ukraine ends. Under current conditions, a new deal appears unlikely, leaving Europe struggling to replace already reduced exposure to Russian gas through external flows.
- Bloomberg has reported on natural gas supply and estimated that markets will need 1.8% more volume over the summer to meet demand growth compared to a year ago.
- Several European trading desks report that Asian buyers are flocking to European markets to buy at low prices, creating further upward pressure on European gas prices.
- BP has appointed James Cheeseman, its LNG chief executive, to head up the ammonia trading business, as demand for more green energy keeps pace with conventional energy sources such as oil and gas.
- Russia and the United States are fighting for the largest share in the gas market. Russian supply is at risk of further sanctions and bottlenecks, while the US tries to ensure stable and secure supply. Australia is falling further behind in market share as production declines due to aging fields.
Natural Gas operators can change their minds and points of view just like that. French President Emmanuel Macron's comments were quickly contradicted by both German Prime Minister Olaf Scholz and NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg. No boots on the ground means no NATO involvement in Ukraine, which is a red line from the start for Russia, which now means tensions are not escalating further and escalation remains stalled.
On the bullish side, Natural Gas faces some fundamental technical levels to return to. Next up is $1.99, – the level that, when broken, saw an accelerated decline. After that, the green line at $2.13 is in sight, with the 2023 triple bottom. If Natural Gas experiences a sudden spike in demand, $2.40 could come into play.
On the downside, $1.64 and $1.53 (the 2020 low) are targets to keep in mind. Another decline could occur if global growth starts to slow and there is less demand. If we add to this equation that the US and Canada are trying to release more volume of Natural Gas extraction, the balance could quickly tip towards a market with excess supply and more falling prices.
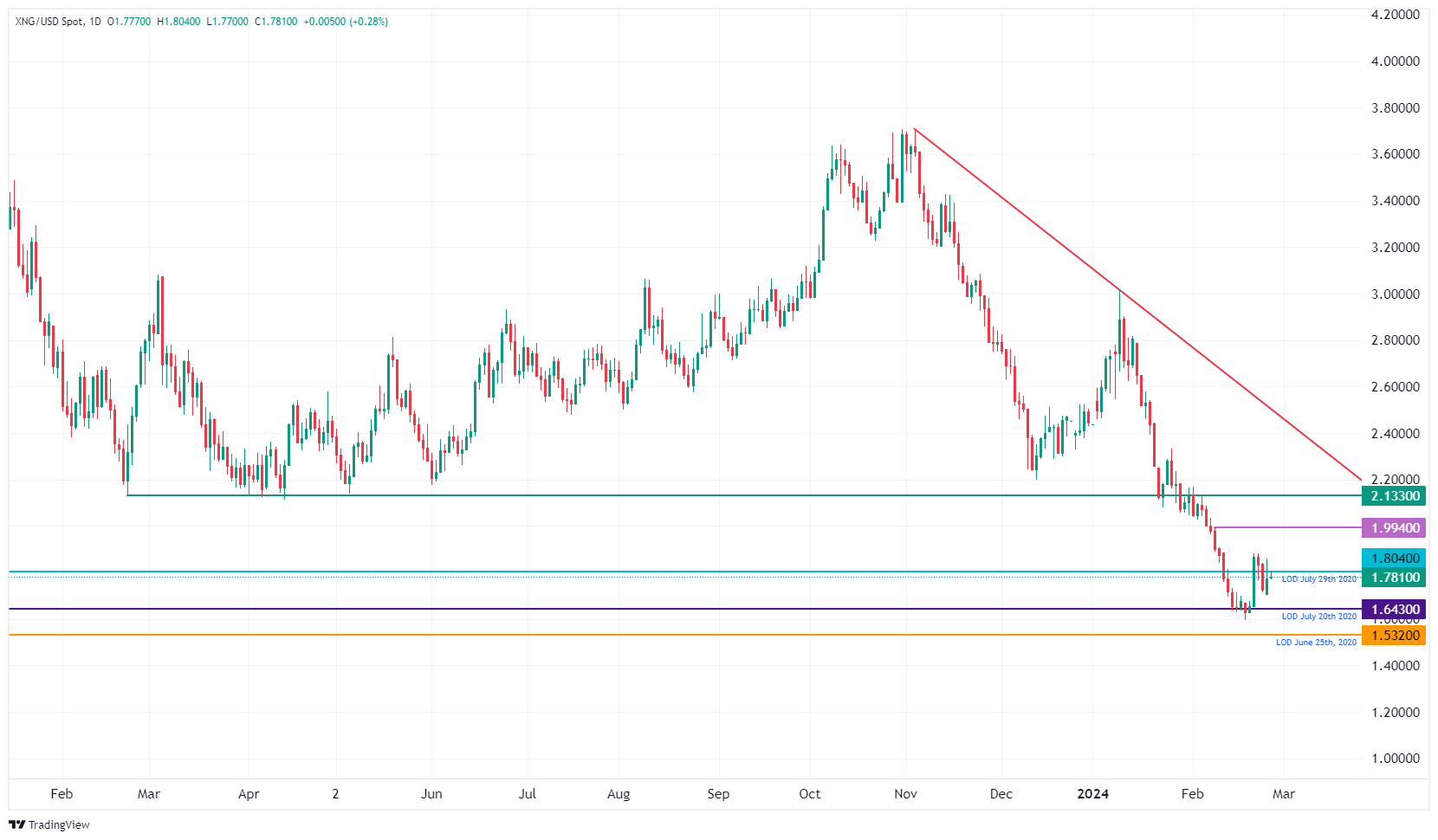
XNG/USD (Daily Chart)
Frequently asked questions about Natural Gas
What fundamental factors determine the price of Natural Gas?
The dynamics of supply and demand is a key factor that influences Natural Gas prices, and is in turn influenced by global economic growth, industrial activity, population growth, production levels and inventories. Climate influences Natural Gas prices because more Gas is used during cold winters and hot summers for heating and cooling. Competition from other energy sources influences prices as consumers may opt for cheaper sources. Geopolitical events, such as the war in Ukraine, also play a role. Government policies related to extraction, transportation and environmental issues also influence prices.
What are the main macroeconomic publications that influence Natural Gas Prices?
The main economic publication that influences Natural Gas prices is the weekly inventory bulletin of the Energy Information Administration (EIA), a US government agency that produces data on the gas market in the United States. The EIA Gas bulletin usually comes out on Thursday at 14:30 GMT, the day after the EIA publishes its weekly Oil bulletin. The economic data of the large consumers of Natural Gas can influence supply and demand, among which China, Germany and Japan stand out. Natural gas is primarily priced and traded in US dollars, so economic releases affecting the US dollar are also factors.
How does the dollar influence Natural Gas prices?
The US dollar is the world's reserve currency and most commodities, including natural gas, are priced and traded in international markets in US dollars. Therefore, the value of the dollar influences the price of Natural Gas, since if the dollar strengthens, fewer dollars are needed to buy the same volume of gas (the price falls), and vice versa if the dollar strengthens.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







