- Eurostat will publish key data on inflation in Europe on Wednesday.
- Annual inflation is expected to remain at 2.6% in March.
- The European Central Bank (ECB) is expected to cut rates in June.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures inflation in the euro zone, will be published on Wednesday, April 3. The European Central Bank (ECB) will closely examine the inflation data of the old continent in the face of growing speculation that the bank could begin its relaxation cycle as early as its June meeting.
A look at the latest European data shows that consumer prices in the Euro bloc rose by an annualized 2.9% in the year to December 2023, before falling in the following two months to 2.8% and 2.6 %, a move that mirrored that of other G10 nations.
In her latest comments on March 20, ECB President Christine Lagarde expressed difficulty in determining whether current price pressures stem simply from delays in adjusting wages and service prices, combined with cyclical fluctuations in productivity, or whether they indicate persistent inflationary trends.
Lagarde added that, unlike previous phases of her political cycle, there are signs that the expected disinflationary trajectory will persist. If the data reveals a significant correlation between the underlying inflation trend and the ECB's forecasts, Lagarde believes the bank can move into the tapering phase of its policy measures.
What to expect from the next report on European inflation?
Consequently, economists expect core CPI inflation to rise 3.0% annually in March (from 3.1%), while the headline indicator will rise 2.6% over the previous year, matching the rise seen. The last month.
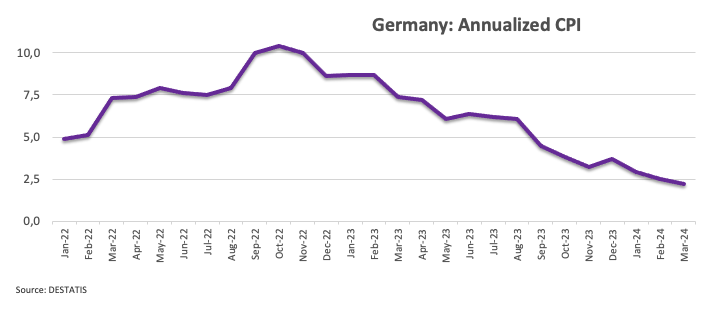
Reinforcing the view that disinflationary pressures persist, Germany's flash Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 2.2% annually in March, up from 2.5% in February.
According to the ECB's Consumer Expectations Survey (CES), the median inflation forecast for the next twelve months fell from 3.3% to 3.1%. However, inflation expectations three years ahead remained stable at 2.5%.
When will the Consumer Price Index be released and how could it affect EUR/USD?
The Eurozone preliminary CPI will be published on Wednesday at 09:00 GMT.
On the eve of the long-awaited inflation release in Europe, the Euro (EUR) is struggling below the round 1.0800 level against the US Dollar (USD), as investors continue to assess the likelihood of the start of the inflation cycle. easing by the Federal Reserve (Fed) in June.
According to Pablo Piovano, Senior Analyst at FXStreet, “Looking forward, EUR/USD is forecast to find initial resistance at the key 200-day SMA at 1.0833. A move above this zone convincingly should restore the constructive bias and potentially allowing further gains on the short-term horizon.”
Pablo adds: “On the opposite side, a reach of the so far April low at 1.0724 (April 2) could trigger a deeper decline towards the 2024 low at 1.0694 (February 14).”
Economic indicator
Eurozone Consumer Price Index (monthly)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures changes in the prices of a representative basket of goods and services in the European Monetary Union. The CPI, published monthly by Eurostat, is harmonized because the same methodology is used in all Member States and their contribution is weighted. The monthly data compares the prices of goods in the reference month with those of the previous month. Generally, a high reading is considered bullish for the Euro (EUR), while a low reading is considered bearish.
Read more.
Next post: 03/04/2024 09:00:00 GMT
Frequency: Monthly
Fountain: Eurostat
Frequently asked questions about the Euro
What is the Euro?
The Euro is the currency of the 20 countries of the European Union that belong to the euro zone. It is the second most traded currency in the world, behind the US dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily volume of more than $2.2 trillion per day.
EUR/USD is the most traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% of all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2% ).
What is the ECB and how does it influence the Euro?
The European Central Bank (ECB), headquartered in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank of the euro zone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy
The ECB's main mandate is to maintain price stability, which means controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its main instrument is to raise or lower interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – tend to benefit the Euro and vice versa.
The Governing Council of the ECB takes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by the heads of the eurozone's national banks and six permanent members, including ECB President Christine Lagarde.
How do inflation data influence the value of the Euro?
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), are important econometric data for the euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if it exceeds the 2% target set by the ECB, it is forced to raise interest rates to bring it back under control.
Relatively high interest rates compared to their peers tend to benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
How do economic data influence the value of the Euro?
Data releases measure the health of the economy and can influence the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, employment and consumer sentiment surveys can influence the direction of the single currency.
A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment, but it may encourage the ECB to raise interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Conversely, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall.
The economic data for the four largest economies in the eurozone (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they represent 75% of the eurozone economy.
How does the trade balance affect the Euro?
Another important release for the euro is the trade balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports during a given period.
If a country produces highly sought-after export products, its currency will appreciate due to the additional demand created by foreign buyers wishing to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net trade balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







