- The Dollar gains 0.61% daily against the Chilean Peso, reaching highs in almost five weeks.
- US building permits rise to 1,505 million in November, surpassing market projections.
- The Central Bank of Chile has cut its interest rates by 25 basis points, as expected.
- Investors will be paying attention today to the interest rate decision by the Federal Reserve.
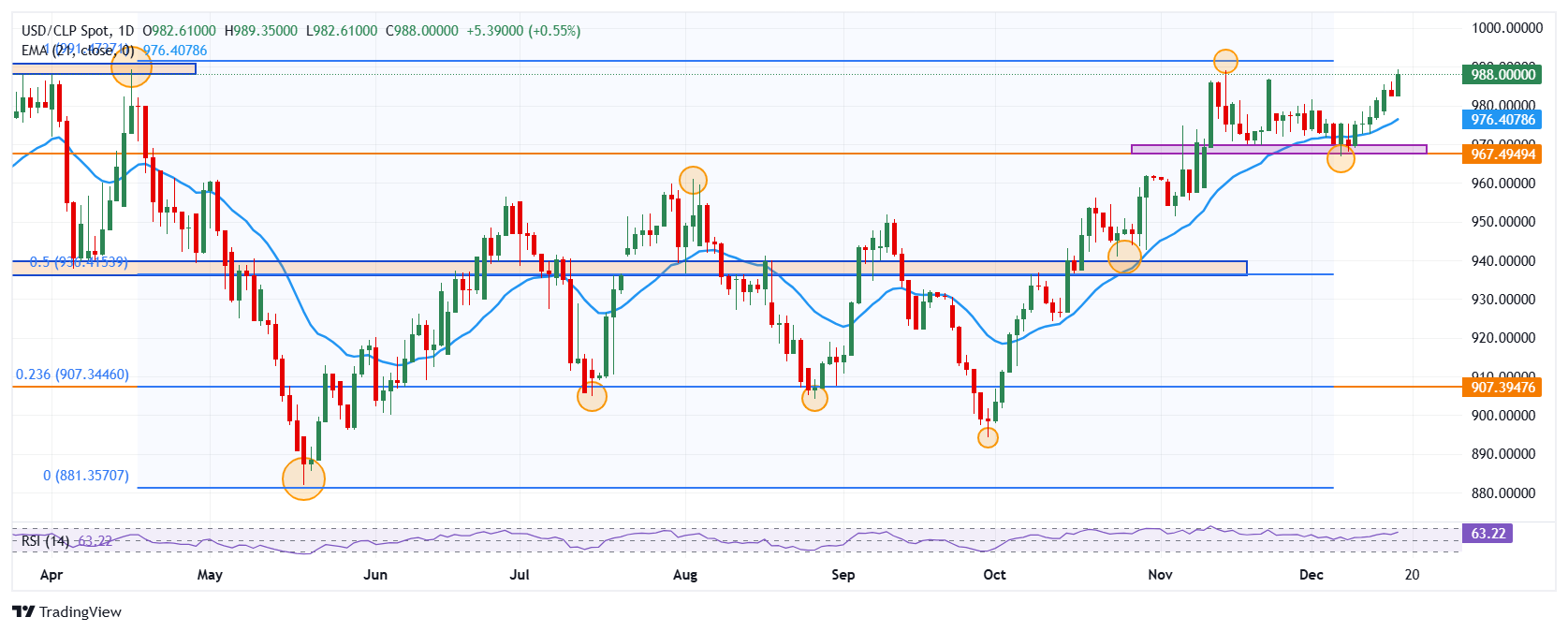
USD/CLP posted a daily reading of 982.61, finding aggressive buyers that took the pair to a near five-week high not seen since November 14 at 989.10. At the time of writing, USD/CLP is trading at 988.52, up 0.61% on Wednesday.
The Chilean peso reaches highs of almost five weeks prior to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decision
According to data presented by the United States Census Bureau, housing starts decreased 1.8% in November to 1.289 million units, below the 1.34 million projected. On the other hand, construction permits increased to 1.505 million, exceeding the 1.43 million expected by consensus.
The Central Bank of Chile reduced its reference rate by 25 basis points to 5.00% from 5.25%, in line with analysts’ expectations. Today all eyes will be on the Federal Reserve and its interest rate decision, a cut to 4.50% from 4.75% is expected.
Technical levels in the USD/CLP
USD/CLP formed short-term support given by the December 6 low at 966.89 in convergence with the 78.6% Fibonacci retracement. The next key support level is at 940.90, October 24 low. To the upside, the nearest resistance is at 989.40, the April 16 pivot point.
USD/CLP Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The United States Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation alongside local banknotes. According to 2022 data, it is the most traded currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency exchange operations, equivalent to an average of $6.6 trillion in daily transactions. After World War II, the USD took over from the pound sterling as the world’s reserve currency.
The single most important factor influencing the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Your main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% target set by the Fed, the Fed raises rates, which favors the price of the dollar. When Inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the Dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit into a clogged financial system. This is an unconventional policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks do not lend to each other (for fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when a simple lowering of interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy US government bonds, primarily from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weakening of the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process by which the Federal Reserve stops purchasing bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal of maturing portfolio securities in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







