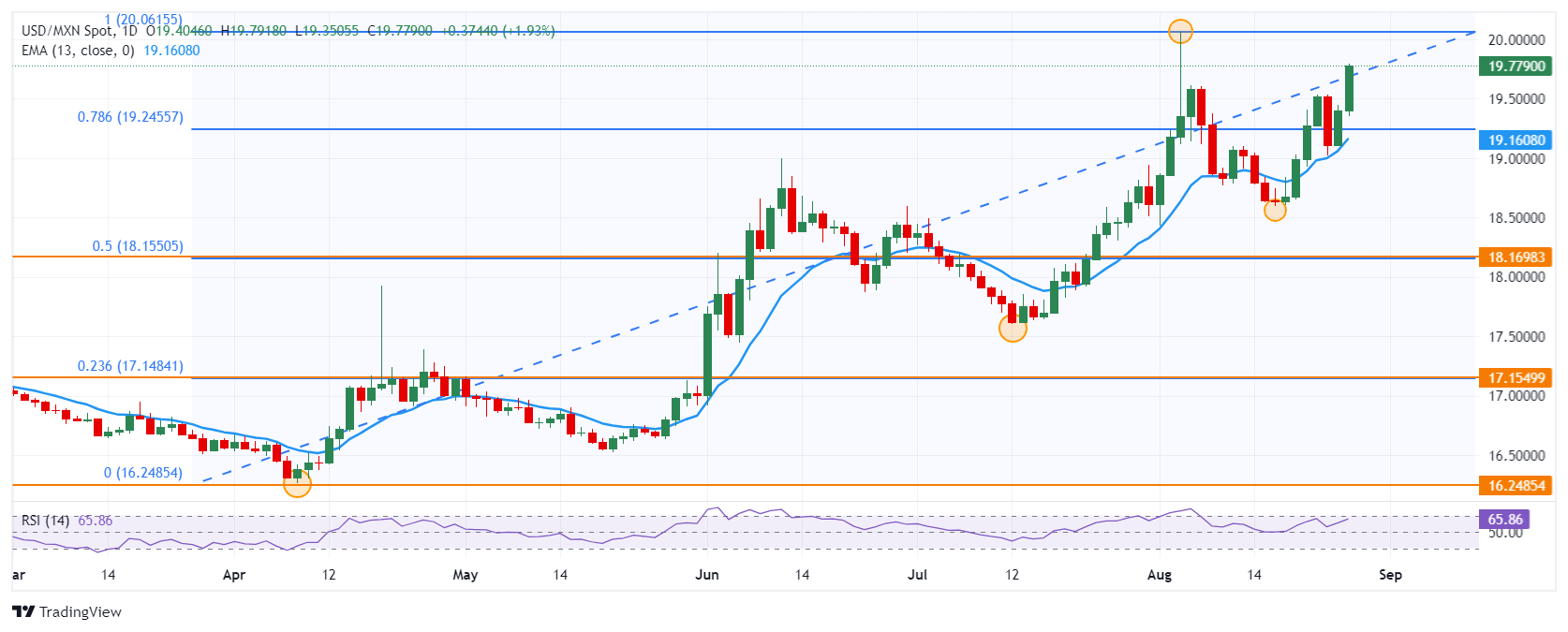
- USD/MXN surges 1.94% today.
- The Constitutional Affairs Committee has approved the general opinion to reform the judiciary.
- López Obrador says relations with the US and Canadian embassies are on hold following criticism of the reform.
The USD/MXN set a daily low at 19.35, where it found buyers that led the pair to close the American session at almost two-year highs at 19.79. The Mexican Peso had not closed at these levels since December 2023. At the time of writing, the price of the US Dollar against the Mexican Peso is trading above 19.77, gaining 1.90% on the day.
Mexican Peso Plummets as Judicial Reform Moves Forward
After a heated debate, the Constitutional Affairs Committee approved the judicial reform in general terms with 22 votes in favor and 17 against. The judicial reform contemplates the election of judges by popular vote, the complete renewal of the Supreme Court of Justice of the Nation, half of the circuit magistrates and judges next year, as well as a reduction of ministers from 11 to 9 members and the reduction of the period of office from 15 to 12 years. For citizens who want to apply to be judges, work experience will not be necessary nor will there be an age limit.
In this context, the United States ambassador to Mexico, Ken Salazar, stressed that the election of judges by popular vote represents a risk to the functioning of democracy in Mexico. On the other hand, the Canadian ambassador to Mexico, Graeme Clark, mentioned that the reform has increased doubts regarding the legal framework in Mexico, which is a key component to maintain and increase investor confidence in the country.
Following comments by Ken Salazar and Graeme Clark, President López Obrador said he has put relations with the United States and Canadian embassies on hold.
Technical levels in the USD/MXN
US Dollar FAQs
The United States Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the de facto currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation alongside local banknotes. As of 2022, it is the most traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange transactions, equivalent to an average of $6.6 trillion in daily transactions. Following World War II, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency.
The single most important factor influencing the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and to promote full employment. Its main tool for achieving these two goals is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed raises rates, which helps the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a jammed financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks are not lending to each other (for fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy US government bonds, primarily from financial institutions. QE typically leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal of maturing securities in new purchases. It is generally positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







