Despite the current epidemiological situation in the world, which is unlikely to cease to be a reality in the near future, the research community of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) nevertheless found the strength to make a number of amazing scientific discoveries in 2021. All of them are really amazing, some turn the perception of reality, and a couple will save many lives in the future.
Combined approach for effective cancer treatment
💡 In simple words
In October 2021, researchers discovered a new way to get the immune system to attack harmful tumors. The method consists in combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy – it stimulates the corresponding cells and makes them work as efficiently as possible. Scientists hope the new discovery will help fight more types of cancer.
🔬 In detail
One of the classes of drugs used today for cancer immunotherapy are checkpoint blockade inhibitors, which turn off cells that are depleted and cannot attack tumors. These drugs have been shown to be effective in treating some types of cancer, but have remained useless against many others. Researchers have tried to improve the effectiveness of these drugs by combining them with cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs, in the hope that chemotherapy will help stimulate the immune system to kill tumor cells. This approach is based on a phenomenon known as immunogenic cell death, in which dead or dying tumor cells send signals that attract the attention of the immune system. And it turned out to be more than successful.
Creation of 3D holograms in real time
💡 In simple words
In 2021, based on the work of neural networks, a technology was developed that makes it possible to create three-dimensional holograms almost instantly. It will be useful both for interacting with virtual reality and in 3D printing or medical imaging. The efficiency of the system is so high that even a smartphone can handle it.

👨🔬 In detail
The approaches for creating three-dimensional holograms, which were used earlier, were quite time consuming, therefore they took seconds and minutes of real time. To speed up this process, the researchers applied deep learning technologies. They developed a convolutional neural network that roughly mimics the way humans process visual information. 4000 pairs of complex images with different shapes and colors were used to train the network. After finishing processing the content, the algorithm learned to create three-dimensional holograms almost instantly, even on mobile hardware.
Inhaled vaccines for drug delivery to the lungs
💡 In simple words
Scientists at the Koch Institute have developed a new method of delivering vaccines directly to the lungs of a patient using inhalation. A fresh approach has already been tested in mice and found that it can provide a faster immune response to viruses that infect through the mucous membranes.
👨🔬 In detail
Many vaccines consist of live, attenuated viruses that pass easily through mucous membranes. An alternative would be peptide vaccines, which are safer and easier to manufacture, but more difficult to overcome mucosal barriers. To facilitate the delivery of peptide vaccines to the lungs, the researchers turned to an approach that they first explored in 2014. They included albumin in the vaccine, which was supposed to help get through the membrane surrounding the lungs. In a mouse test, this approach had more than a positive effect. In the future, it is planned to use it to create inhaled vaccines against influenza and other viral diseases.
A New Approach to Assessing the Risk of COVID-19 Transmission
💡 In simple words
A couple of MIT professors have proposed changing the approach to assessing the risk of COVID-19 transmission in confined spaces. They advised the world to use not only the distance between potential vectors, but also the size of the room, the number of people, their occupation, the presence of masks on their faces, and the speed of ventilation and air filtration.

👨🔬 In detail
In the analysis, the scientists emphasized that in confined spaces, microscopic airborne droplets, potentially carrying pathogens, will float in the air for a long time. According to them, airborne spread in confined spaces plays an important role in the increase in the number of cases of COVID-19. In various spheres today, everyone is usually guided only by the distance of 1.5 meters between people, and this is a mistake. Instead, it is more appropriate to use a whole matrix with a large number of variables, which will more accurately determine the possible risks.
Adaptation of neural networks based on new data
💡 In simple words
Researchers at CSAIL have come up with a new deep learning engine that can independently change the equations that underlie it. This is necessary in order to more effectively adapt to new data that enter the neural network. The discovery could be potentially interesting both in medical diagnostics and in the autonomous movement of vehicles.

👨🔬 In detail
Researchers have coded the neural network with a focus on how neurons interact. The equations used for structuring allowed parameters to change over time based on the results of a nested set of differential equations. This flexibility has become key, because usually the behavior of most neural networks is captured after the training phase. As a result, they do not adapt well to changes in the incoming data stream. The mobility of the new system makes it more resilient to unexpected data. For example, if heavy rain makes it difficult to see cameras that are used for autonomous driving, the vehicle will still be able to move and its smart system will not fail.
Programming fabric fibers in new generation clothing
💡 In simple words
The first digital fiber was launched in June. It can perceive, store, analyze and draw conclusions about data or human activity. The fiber can be sewn into clothing and used to monitor physical performance, detect disease, and for medical purposes, the researchers say.

👨🔬 In detail
To create a smart new material, hundreds of extremely small silicon chips were integrated into polymer fiber. By controlling it with high precision, the researchers were able to create a canvas with a continuous electrical connection between the chips for tens of meters. The material itself turned out to be thin and flexible – it can be pierced with a needle and sewn into ordinary fabric. Clothes made from this fiber can be washed at least 10 times without the risk of destruction. In this case, the sensations when worn do not change. Interestingly, digital fiber can store a large amount of information in memory, which can also be useful in a wide variety of scenarios.
Confirmation of the limited effectiveness of data visualization
💡 In simple words
To confirm the limitations of data visualization, anthropologists and computer scientists have analyzed how conspiracy theorists are flipping data on the COVID-19 pandemic. They came to the conclusion that any visual information can be deployed in such a way that it acquires a diametrically opposite message. Roughly speaking, from the same data, you can create both visualization for the effectiveness of masks against the spread of the virus, and against.

👨🔬 In detail
To confirm the limited effectiveness of visualizations for presenting data, the team sampled hundreds of Twitter topics related to wearing masks. To prove their point, really high-quality illustrations were used by both supporters of such personal protective equipment and their opponents. Therefore, visual alone without a deep analysis of the topic can be considered useless in order to understand any of the issues.
Face mask with COVID-19 detection capability
💡 In simple words
Engineers at MIT and Harvard University have created a prototype face shield that can diagnose a user with COVID-19 in about 90 minutes. To do this, tiny disposable sensors have been built into it, which, among other things, can be adapted to interact with other viruses.
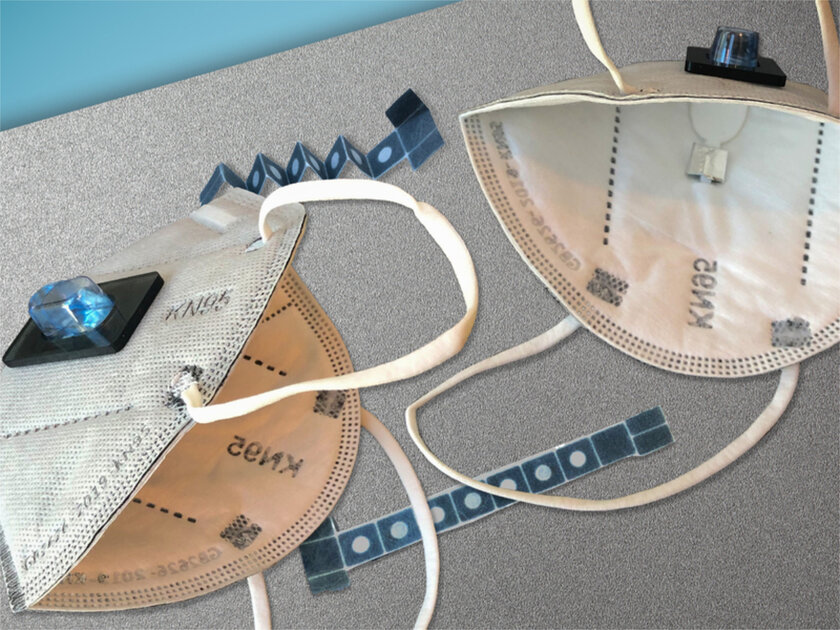
👨🔬 In detail
In 2014, scientists found that the proteins and nucleic acids needed to create synthetic gene networks that respond to specific target molecules can even be embedded in paper. In 2017, a cell-free sensing system known as SHERLOCK was developed, which allowed highly sensitive detection of nucleic acids and proved to be stable for many months. In 2021, all this began to be introduced into textiles, the first of which were disposable masks. The special indicators used in them can change color when a specific target molecule is detected.
Confirmation of Stephen Hawking’s black hole theorem
💡 In simple words
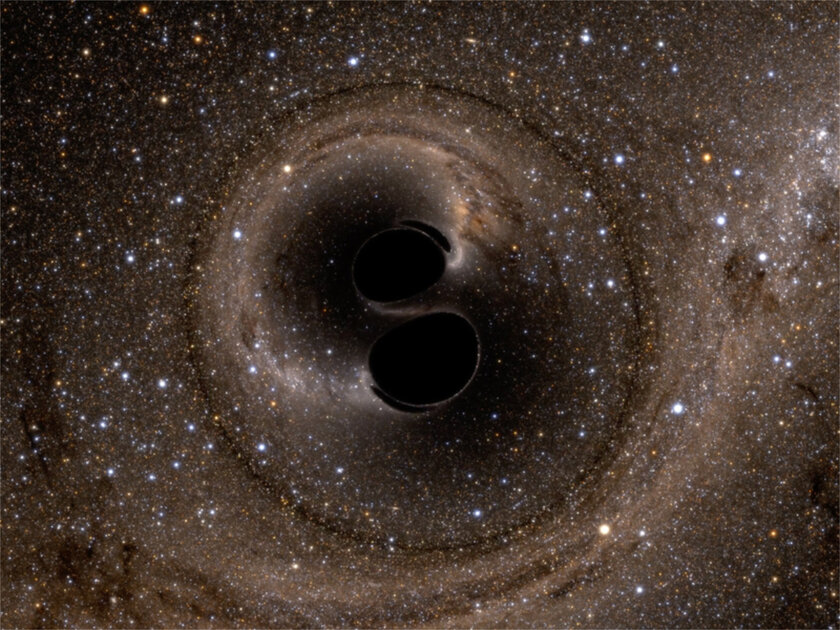
Physicists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and other organizations have confirmed the main theorem, created by Stephen Hawking in 1971. The theorem states that the region of the black hole’s event horizon – the boundary beyond which nothing can escape – will never shrink. For this, observations of gravitational waves were used.

👨🔬 In detail
Scientists have developed a model corresponding to two spiraling black holes to determine the mass and rotation of a pair of similar objects before merging. They calculated the total area of their event horizon and used a special technique to extract the “ring wave” – the reflection of the newly formed black hole. Based on this, mass and rotation were calculated, as well as, ultimately, the area of the event horizon. The data showed that it is highly probable that the area of the event horizon has increased after the merger, so the law is fulfilled with an extremely high probability. Scientists will continue to work in this direction, but the result in certain circles still seems amazing today.
The most powerful and efficient magnetic field ever
💡 In simple words
In September, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology increased the power of a high-temperature superconducting electromagnet to a field strength of 20 Tesla. Thus, they managed to create the most powerful magnetic field of this kind in history. This discovery will help build the world’s first fusion power plant that produces more energy than it consumes.
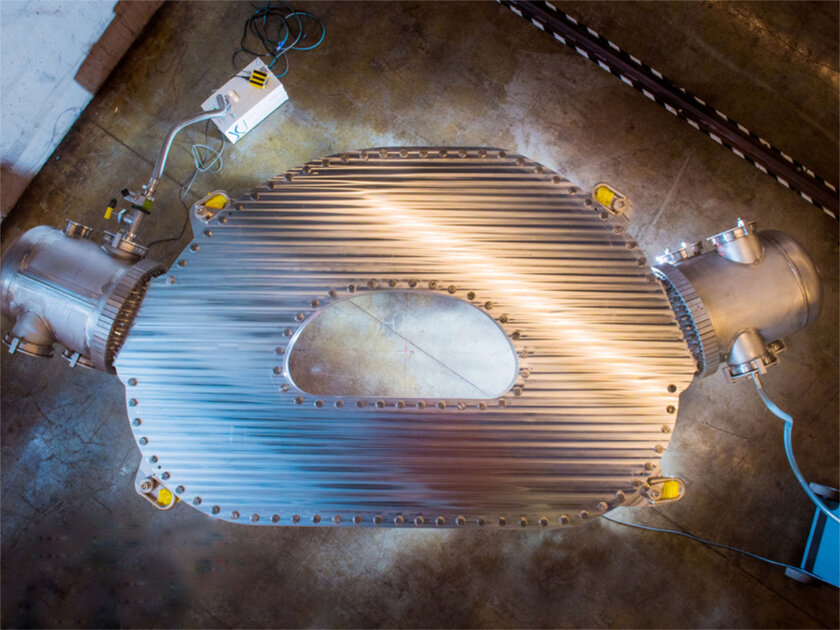
👨🔬 In detail
Until now, the only way to get incredibly powerful magnetic fields was to simply increase their size. But when using a new high-temperature superconducting material made in the form of a flat ribbon, it turns out to achieve a more powerful magnetic field with noticeably smaller dimensions. When comparing size and power, the scientists were able to increase the efficiency by about 40 times. This amazing discovery could turn the way towards energy in the foreseeable future.
Source: MIT.
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.







