- The British Pound falls below 1.2500 while the US Dollar strengthens ahead of the announcement of the latest Fed policy decision.
- In a week with a light economic calendar in the UK, speculation about a rate cut by the BoE is expected to boost the British pound.
- Investors expect the Fed to emphasize the need to maintain the current interest rate framework for longer.
The British Pound (GBP) extends its decline below the psychological support of 1.2500 against the US Dollar (USD) during the American session on Wednesday. Due to the light economic agenda in the United Kingdom, the volatility in the GBP/USD pair is all coming from the US Dollar side, as the United States faces a week full of data, starting with the decision of the Federal Reserve (Fed ) later on Wednesday.
The valuation of the British Pound will depend solely on the expectations of the Bank of England (BoE) regarding the reduction of interest rates. Financial markets are speculating that the BoE could decide to cut borrowing costs at its June or August meetings. BoE Governor Andrew Bailey has stated that he is confident that headline inflation will fall to 2% in April. In March, British inflation stood at 3.2%.
The recent correction in the GBP/USD pair reflects investor uncertainty ahead of the Fed's interest rate decision, which will be announced at 18:00 GMT. The Fed is expected to keep interest rates steady and adopt hawkish rhetoric as recent inflation data suggests price pressures persist, making it difficult for policymakers to be confident that U.S. prices sustainably return to the 2% target. This scenario of higher interest rates in the US improves the attractiveness of the US dollar and weighs on other currencies whose central banks are seen cutting rates before the Fed.
Daily summary of market movements: Pound sterling down, US dollar down after weak manufacturing PMI
- The British Pound undergoes a sharp correction and stands at 1.2480 against the US Dollar, as investors prepare for the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decision. The CME's FedWatch tool shows that traders expect interest rates to remain unchanged in the 5.25%-5.50% range for the sixth consecutive time. Although no action on borrowing rates is expected, investors will be keeping a close eye on the interest rate outlook by watching the Fed's statement and Chairman Jerome Powell's press conference.
- The Fed is expected to support the “higher interest rates for longer” argument, as a recent batch of inflation indicators has suggested that progress in lowering inflation to the 2% target has stalled.
- After the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index rose more than expected in March, the first-quarter Employment Cost Index also beat estimates by a wide margin . The index rose 1.2%, above the consensus of 1.0% and the previous reading of 0.9%. Rising employment costs are often driven by strong wage growth, which translates into increased consumer spending and fuels inflationary pressures.
- Meanwhile, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the value of the dollar against six major currencies, falls slightly from a two-week high of 106.50 following the sharp change in ADP employment and weak data from the US ISM Manufacturing PMI. The ADP report shows that US private employers hired 192K jobs, up from estimates of 175K and the previous reading of 184.
- The ISM showed that the manufacturing PMI fell sharply to 49.2 from the consensus of 50.0 and the previous reading of 50.3. Factory data remained below the 50.0 threshold, which in itself is a sign of contraction. New order entries fell significantly to 49.1 from 51.4 in March, suggesting weak demand prospects, which could be seen as a consequence of the Fed's interest rate hike.
Technical analysis: British pound remains below 1.2500
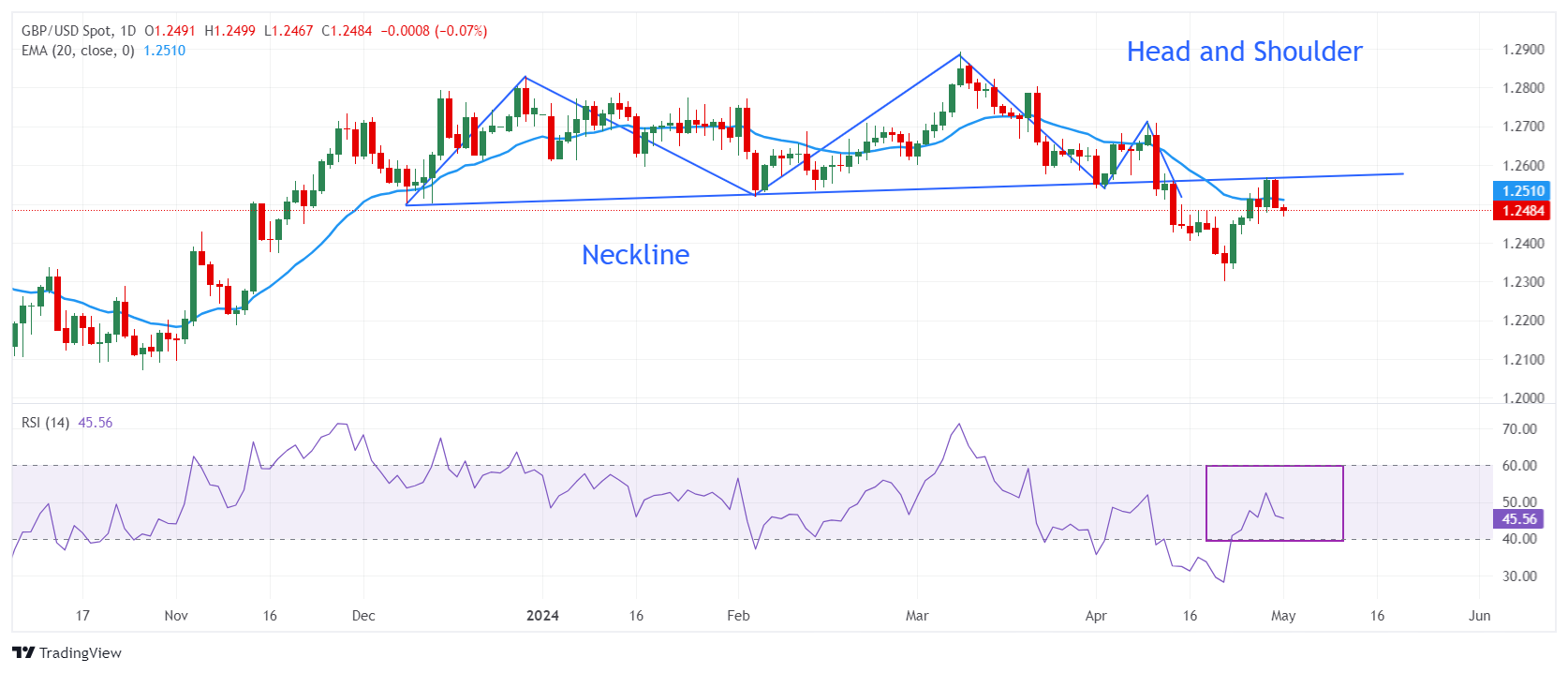
The British Pound falls sharply against the US Dollar after failing to extend its rise above the crucial resistance of 1.2570. The GBP/USD pair also fails to hold above the 20-day EMA around 1.2510, indicating that the near-term outlook remains uncertain.
The neck line of the head and shoulders (H&S) pattern has acted as a strong barrier for the British pound bulls. On April 12, the Pound experienced an intense sell-off after breaking below the neck line of the head-and-shoulder pattern drawn from the December 8 low around 1.2500.
The 14-period RSI is oscillating in the 40.00-60.00 range, suggesting indecision among market participants.
Frequently asked questions about the Fed
What does the Federal Reserve do and how does it affect the dollar?
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: achieving price stability and promoting full employment. Your main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates.
When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% target set by the Federal Reserve, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the United States Dollar (USD), as it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money.
When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the greenback.
How often does the Federal Reserve hold monetary policy meetings?
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight meetings a year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions.
The FOMC is made up of twelve Federal Reserve officials: the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the eleven presidents of the regional Reserve banks, who serve for one year on a rotating basis.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE) and how does it affect the USD?
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit into a clogged financial system.
It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed's weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy high-quality bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US dollar.
What is Quantitative Tightening (QT) and how does it affect the US Dollar?
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the capital of the maturing bonds it has in its portfolio to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







