- The British pound falls to 1.2540 as investors believe that the BoE will ease interest rates before the Fed does.
- British interest rates are expected to remain at 5.25% for the sixth consecutive time following Thursday's BoE meeting.
- Investors expect the BoE to begin cutting interest rates from August.
The British Pound (GBP) fell to 1.2540 against the US Dollar in the American session on Tuesday. The GBP/USD pair falls as the US Dollar extends its bullish trend, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) – which tracks the value of the Dollar against six major currencies – advancing to 105.25.
Investors appear to remain confident in the U.S. economic outlook despite recent weakness seen in a host of economic data such as weaker demand for labor, slowing wage growth and a contraction in the services PMI in April. The general good performance of the economy will allow the Federal Reserve (Fed) to take its time in cutting interest rates compared to other central banks in developed countries.
Still, weak U.S. economic data has fueled expectations that the Fed will cut interest rates starting at its September meeting. Uncertainty prevails over the Fed's rate cut schedule as policymakers view the current monetary policy framework as adequate. On Monday, New York Fed Bank President John Williams declared, “At some point we will have rate cuts,” but for now, monetary policy is in a “very good place,” Reuters reported.
Daily Market Summary: Pound falls ahead of BoE policy meeting
- The British Pound is falling sharply after facing significant selling pressure near the resistance round level of 1.2600. The GBP/USD pair weakens as investors remain convinced of the chances of the Bank of England cutting interest rates before the Fed.
- Financial markets anticipate that the BoE will begin cutting rates in August and that the Fed will do so in September. This fact is supporting the US Dollar even though the Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) and Services PMI data for April were not as expected.
- Investors will gain more clarity on the outlook for UK interest rates thanks to the BoE's monetary policy decision, due to be announced on Thursday. The BoE is expected to keep interest rates at 5.25% for the sixth time in a row. Therefore, any comments on the outlook for interest rates will be more useful to investors in predicting the next move of the British pound.
- BoE Governor Andrew Bailey stated last month that he expects headline inflation to return to the desired rate of 2% in April. Furthermore, at the last monetary policy meeting, he said that he was comfortable with market expectations of two or three rate cuts this year.
Technical analysis: Sterling falls from 1.2600
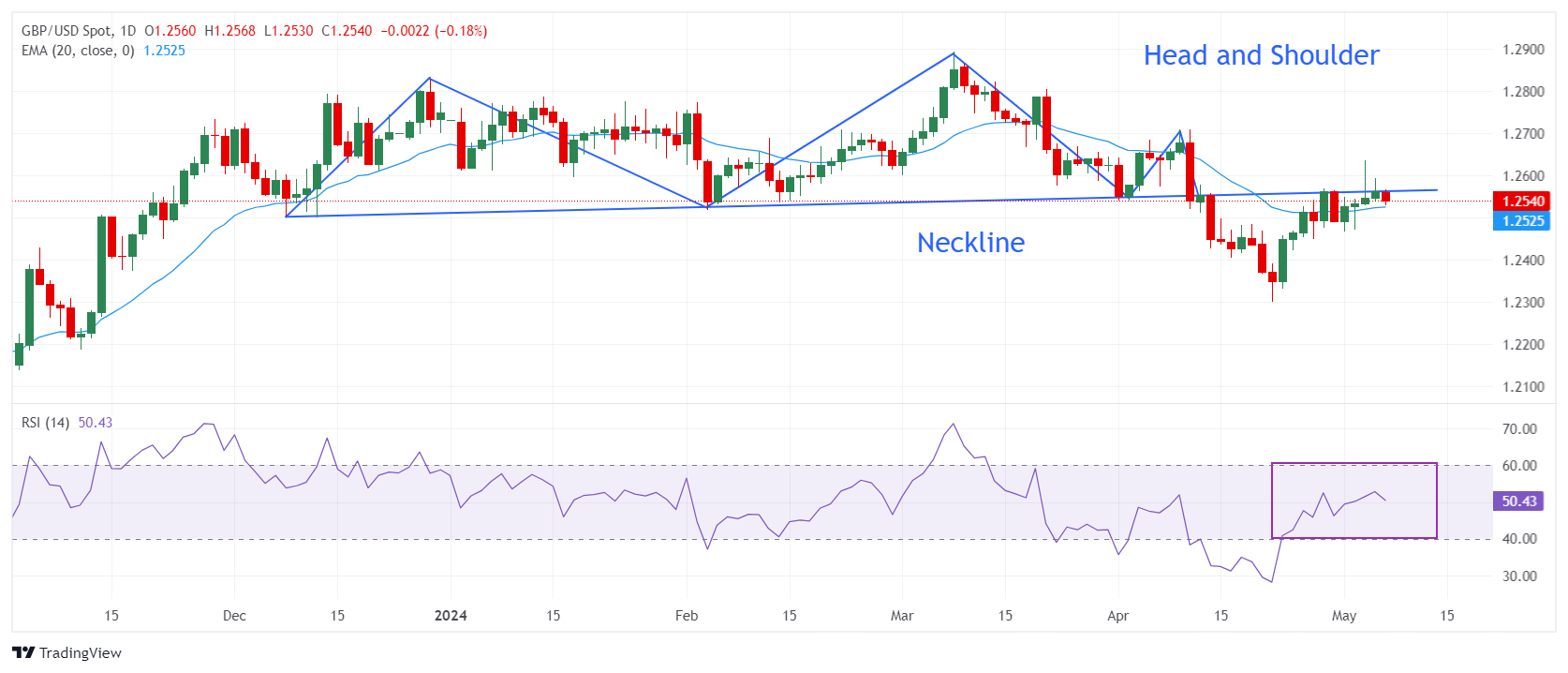
The British Pound falls from 1.2600 but consolidates in a tight range around 1.2550. The pound's short-term outlook appears uncertain as it has not stabilized above the 20-day exponential moving average (EMA), which is trading around 1.2520.
The GBP/USD pair is facing selling pressure near the neck line of the head and shoulder chart pattern formed on a daily time frame. On April 12, the Pound saw an intense sell-off after breaking below the neck line of the head and shoulder pattern, which is drawn from the low around 1.2500 on December 8.
The 14-period RSI is oscillating in the 40.00-60.00 range, suggesting indecision among market participants.
BoE FAQ
What does the Bank of England do and how does it impact the Pound?
The Bank of England (BoE) decides the UK's monetary policy. Its main objective is to achieve price stability, that is, a constant inflation rate of 2%. Its instrument to achieve this is the adjustment of basic loan rates. The BoE sets the rate at which it lends to commercial banks and at which banks lend to each other, determining the level of interest rates in the wider economy. This also influences the value of the British Pound (GBP).
How does the Bank of England's monetary policy influence the Pound Sterling?
When inflation exceeds the Bank of England's target, it responds by raising interest rates, which makes access to credit more expensive for citizens and companies. This is positive for the British Pound, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to invest their money. When inflation falls below target, it is a sign that economic growth is slowing, and the Bank of England will consider lowering interest rates to make credit cheaper in the hope that companies will borrow to invest in projects that generate growth, which is negative for the Pound sterling.
What is Quantitative Easing and how does it influence the Libra?
In extreme situations, the Bank of England can apply a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the BoE substantially increases the flow of credit into a clogged financial system. QE is a policy of last resort when lowering interest rates does not achieve the necessary result. The process of QE involves the Bank of England printing money to buy assets, typically government bonds or AAA-rated corporate bonds, from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weakening of the British pound.
What is Quantitative Hardening and how does it influence the British Pound?
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE, and is applied when the economy is strengthening and inflation begins to rise. While in QE the Bank of England (BoE) buys government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to encourage them to lend, in QT the BoE stops buying more bonds and stops reinvesting the maturing principal of the bonds that you already own. It is usually positive for the British pound.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







