- Sterling falls as US PPI data dampens appeal of risk-sensitive assets.
- The British economy is growing again after contracting in the second half of 2023.
- Investors are seeking fresh guidance for interest rates from the Bank of England.
The British pound (GBP) falls sharply against the US Dollar in the early hours of the American session, as US Producer Price Index (PPI) data for February turned out to be more encouraging than expected. GBP/USD falls as investors' risk appetite wanes on expectations that the stubborn US PPI will reinforce fears that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will delay its plans to cut interest rates. Markets currently expect the Federal Reserve to make this decision in June.
The US Dollar Index (DXY) rises to 103.00 as easing expectations for the Federal Reserve (Fed) to cut interest rates at the June policy meeting has improved safe-haven appeal. Meanwhile, retail sales data for February disappointed expectations. Retail sales grew moderately by 0.6% in February, compared to expectations of 0.8%. In January, retail sales data contracted significantly by 1.1%.
Daily Market Moves Summary: Sterling Falls Vertically as US PPI Turns Out Harder Than Expected
- The British Pound falls below 1.2800 against the US Dollar due to the stubborn February US PPI data. The pace at which the monthly headline PPI grew doubled expectations and the previous reading of 0.3%. The annual headline PPI accelerated to 1.6% from the consensus 1.1% and 1.0% in January.
- The annual core PPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, rose 2.0%, compared to the 1.9% expected. Meanwhile, monthly core PPI rose at a higher pace of 0.3% versus expectations of 0.2%. A stubborn PPI data indicates that consumer price inflation is expected to remain persistent, which could dampen expectations that the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates at the June policy meeting.
- Sterling could rally as monthly UK gross domestic product (GDP) and factory data for January was released on Wednesday, showing the economy grew 0.2%, as expected , driven by increased retail demand and sales of home building materials. Meanwhile, industrial production remained weak.
- The projected growth of the British economy in early 2024 has brought some relief to UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak ahead of the election, which must be held no later than the end of January 2025. The Chancellor of the Exchequer, Jeremy Hunt said: “Although the last few years have been tough, today's figures show we are making progress in growing the economy,” Reuters reported.
- The British economy has returned to growth after falling into a technical recession in the second half of 2023. However, it is too early to say that the recession was superficial and that the economy has emerged from it until the first quarter data in its set show an expansion. The Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) forecasts the British economy to grow by 0.8% in 2024.
- Looking ahead, market expectations of the Bank of England's rate cut will determine the next moves in the Pound. Investor bets that the Bank of England will cut interest rates at its August meeting have strengthened following slower-than-expected wage growth in the three months to January.
Technical analysis: British pound falls below 1.2800
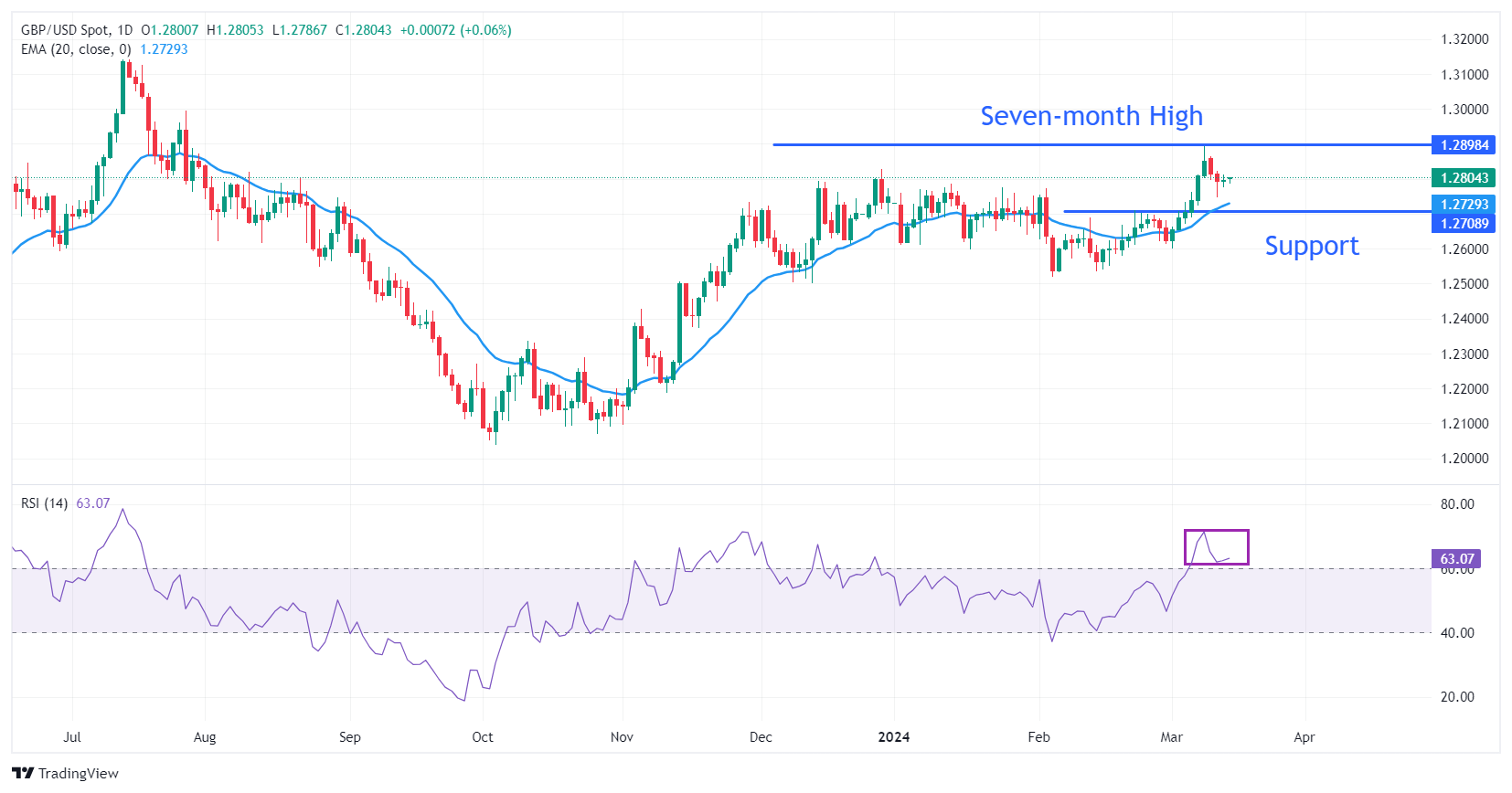
The British Pound falls below 1.2800 after market discouragement. The 20-day EMA near 1.2730 continues to tilt higher, indicating moderate short-term demand. Support at 1.2700 would be a good cushion for the British Pound bulls.
The 14-period Relative Strength Index (RSI) is oscillating in the 60.00-80.00 range, indicating that strong bullish momentum persists.
Inflation FAQ
What is Inflation?
Inflation measures the rise in prices of a representative basket of goods and services. General inflation is usually expressed as a month-on-month and year-on-year percentage change. Core inflation excludes more volatile items, such as food and fuel, which can fluctuate due to geopolitical and seasonal factors. Core inflation is the figure economists focus on and is the target level of central banks, which are mandated to keep inflation at a manageable level, typically around 2%.
What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the variation in prices of a basket of goods and services over a period of time. It is usually expressed as a percentage of inter-monthly and inter-annual variation. Core CPI is the target of central banks as it excludes food and fuel volatility. When the underlying CPI exceeds 2%, interest rates usually rise, and vice versa when it falls below 2%. Since higher interest rates are positive for a currency, higher inflation usually translates into a stronger currency. The opposite occurs when inflation falls.
What is the impact of inflation on currency exchange?
Although it may seem counterintuitive, high inflation in a country drives up the value of its currency and vice versa in the case of lower inflation. This is because the central bank will typically raise interest rates to combat higher inflation, attracting more global capital inflows from investors looking for a lucrative place to park their money.
How does inflation influence the price of Gold?
Gold was once the go-to asset for investors during times of high inflation because it preserved its value, and while investors often continue to purchase gold for its safe haven properties during times of extreme market turmoil, this is not the case. most of the time. This is because when inflation is high, central banks raise interest rates to combat it.
Higher interest rates are negative for Gold because they increase the opportunity cost of holding Gold versus an interest-bearing asset or placing money in a cash deposit account. On the contrary, lower inflation tends to be positive for Gold, as it reduces interest rates, making the shiny metal a more viable investment alternative.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







