- The Bank of England is expected to maintain its policy rate by 4.25%.
- The inflation figures of the United Kingdom remain well above the target of the BOE.
- The GBP/USD maintains its price at the upper end of the range about 1,3600.
The Bank of England (BOE) is ready to reveal its last monetary policy decision on Thursday, coinciding with its fourth 2025 fees establishment meeting.
Market analysts anticipate that the Central Bank will maintain its stable reference interest rate at 4.25% after the reduction announced during the May 8 meeting.
The decision of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) will be followed by the publication of the minutes of the meeting, which will detail the internal discussions that shape the result.
Since the decision on the rate seems to be largely anticipated, investors are likely to displace their attention to the anticipated performance of the United Kingdom economy, which presents mixed signals. The key considerations will include the possible trajectory of interest rates, the ongoing debate on tariffs and recent developments around the commercial agreement between the US and the United Kingdom.
Rates, high inflation and tariffs
The Bank of England has reduced its policy rate by a quarter to 4.25% from May 8, after a remarkably divided vote between the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC): Swati Dhingra and Alan Taylor supported a more significant half -point cut, while the chief economist Huw Pill and Catherine Mann advocated to maintain interest rates without changes.
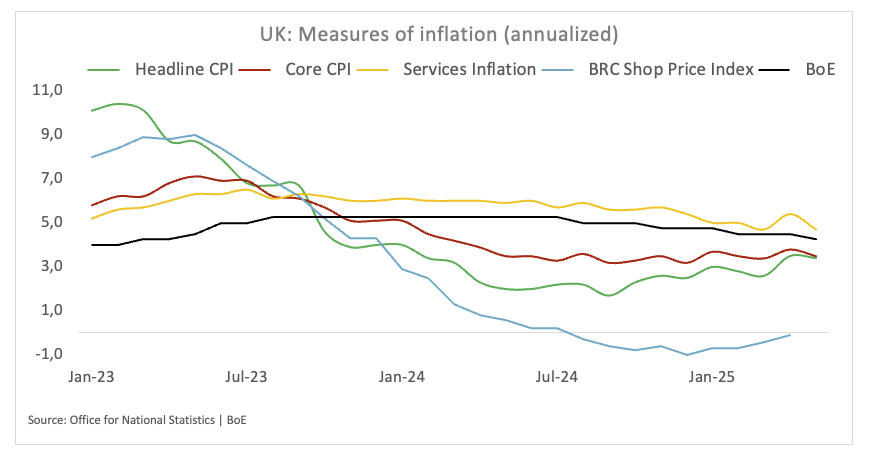
The “old lady” has updated its inflation prognosis for the year and now projects a peak of around 3.50%. This adjustment means a reduction of an earlier estimate of 3.75%, while reflecting an increase with respect to the last official figure of 2.60% observed in March. Experts predict that inflation will reach the objective of 2% for the first quarter of 2027.
The Central Bank has forecast a 1% growth rate for the economy this year, an increase with respect to the previous estimate of 0.75%. The review reflects a solid closing of 2024, backed by official promising data of the beginning of 2025, which reveal a quarterly growth rate of 0.60% for the first quarter.
The report indicates that the increase in the growth observed in the period from January to March seems to be an isolated incident. As a result, the growth forecast by 2026 has been reviewed down to 1.25%, a decrease with respect to the previous estimate of 1.5%.
The most recent data published by the Office of National Statistics (ONS) indicate that the annual consumer price index (CPI) increased to 3.4% in May. The underlying inflation, excluding fluctuating costs of food and energy, increased by 3.50%, indicating a continuous trend of relief of the underlying price pressure. Inflation of services, meanwhile, increased 4.70% in the last 12 months.
Meanwhile, some members of the fees committee, including Governor Bailey, showed some caution with respect to the relief cycle in the future, as well as the still high consumption prices:
Going to the Treasury Committee, Governor Andrew Bailey said his approach to reduce interest rates would be “gradual and careful.” He emphasized that these words served as their guiding principles. He said that, although he continued to anticipate a decrease in rates, the trajectory had become “wrapped in much more uncertainty” and had become “unpredictable” due to agitation in global commercial policy.
The attached governor Sarah Breeden informed the committee that she believed that there was a case for a rate cut in May, regardless of international developments. He evaluated that the domestic disinflation process was advancing as anticipated and expected to persist.
The MPC Swati Dhingra member also said that it receives downward risks for the United Kingdom inflation forecast. He said that recent increases in inflation are mainly attributed to the increase in energy costs instead of fundamental price pressure.
The monetary policy Megan Greene argued that, although the bank anticipates a decrease in the recent increase in inflation, it is not “optimistic” regarding perspectives. Warned about the considerable risk that the possible effects of second round represented.
How will the BOE interest rate impact to GBP/USD impact?
Investors expect the BOE to maintain its reference rate at 4.25% on Thursday at 11:00 GMT.
While the result is completely discounted, attention will focus on the division of votes between MPC members, which could be a determining factor for the British Pound if it indicates an atypical vote.
In the prelude to the meeting, the GBP/USD seems to have found a good containment around the 1,3400 zone, driven by the dynamics of the US dollar (USD) and the change of feeling towards the US commercial policy, as well as by the reactivation of the geopolitical nerves.
“The cable was subjected to a low -convincing down pressure after reaching maximums of more than three years above 1,3600 on June 13,” said Pablo Piovano, a senior analyst at FXSTERET. He pointed out that a decisive rupture above the annual maximums could potentially trigger a movement towards the maximum of 2022 of 1,3748 (January 13).
At the bottom, Piovano identified the simple mobile average (SMA) of 55 days in 1,3329 as an initial provisional support, followed by the minimum of May in 1,3139 (May 12). Once the cable exceeds the latter, the most relevant 200 SMA could be again in the radar of investors in 1,2922, just before the floor of April 1,2707 (April 7).
FAQS Central Banks
Central banks have a key mandate that consists in guaranteeing the stability of prices in a country or region. Economies constantly face inflation or deflation when the prices of certain goods and services fluctuate. A constant rise in the prices of the same goods means inflation, a constant decrease in the prices of the same goods means deflation. It is the Central Bank’s task to keep the demand online by adjusting its interest rate. For larger central banks, such as the US Federal Reserve (FED), the European Central Bank (ECB) or the Bank of England (BOE), the mandate is to maintain inflation about 2%.
A central bank has an important tool to raise or lower inflation: modify its reference interest rate. In precommunicated moments, the Central Bank will issue a statement with its reference interest rate and give additional reasons of why it maintains or modifies it (cut it or the SUBE). Local banks will adjust their savings and loan rates accordingly, which in turn will make it difficult or facilitate that citizens obtain profits from their savings or that companies ask for loans and invest in their businesses. When the Central Bank substantially rises interest rates, there is talk of monetary hardening. When it reduces its reference rate, it is called monetary relaxation.
A central bank is usually politically independent. The members of the Central Bank Policy Council go through a series of panels and hearings before being appointed for a position in the Policy Council. Each member of that council usually has a certain conviction on how the Central Bank should control inflation and the consequent monetary policy. Members who want a very flexible monetary policy, with low types and cheap loans, to substantially boost the economy, while comprising with inflation slightly greater than 2%, are called “pigeons.” Members who prefer higher types to reward savings and want to control inflation at all times are called “hawks” and will not rest until inflation is located at 2% or just below.
Normally, there is a president who directs each meeting, has to create a consensus between the hawks or the pigeons and has the last word when the votes must be divided to avoid a draw to 50 on whether the current policy must be adjusted. The president will pronounce speeches, which can often be followed live, in which he will communicate the current monetary position and perspectives. A central bank will try to boost its monetary policy without causing violent oscillations of the fees, the actions or their currency. All members of the Central Bank will channel their position towards the markets before a monetary policy meeting. A few days before a monetary policy meeting is held and until the new policy has been communicated, the members are prohibited from speaking publicly. It is what is called a period of silence.
Economic indicator
Decision on the BOE interest rate
He Bank of England Announce your decision on the interest rate at the end of your eight meetings scheduled per year. If the BOE adopts a hard line posture on the inflationary perspectives of the economy and elevates interest rates, it is generally bullish for sterling pound (GBP). Similarly, if the BOE adopts a moderate vision of the United Kingdom economy and keeps interest rates without changes, or reduces them, it is considered bassist for the GBP.
Read more.
Last publication:
play May 08, 2025 11:02
Frequency:
Irregular
Current:
4.25%
Dear:
4.25%
Previous:
4.5%
Fountain:
Bank of England
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







