- The US dollar index sees the relief rebound of the previous day completely cut on Friday.
- The House of Representatives has approved the expense bill of US President Trump.
- The US dollar index suffers more losses and is on the way to testing a new minimum of two weeks
The US dollar index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US dollar (USD) compared to six main currencies, falls even more on Friday and erases the recovery of the previous day, quoting about 99.40 at the time of writing. The new fall occurs after the House of Representatives approved the bill of expenses of President Donald Trump, which is now addressed to the Senate. The Congress Budget Office, not partisan, revealed that this “great and beautiful bill” comes with a high price: 3.8 billion dollars in additional debt to the total of 36.2 billion dollars of the federal government during the next decade, according to Reuters.
The markets, and in fact the bond market, have been very concerned about these numbers. The best example was the 30 -year -old bonus in the long term, where the yields rose to 5.15% on Thursday from 4.64% in early May, a maximum of more than a year since 5.18% seen at the end of December 2023. More concerns could further devalue the US dollar.
What moves the market today: the Fed takes control again
- President Trump threatens a 50% tariff to all EU products from June 1 and a 25% tariff to iPhones if they are not manufactured in the US.
- At 12:35 GMT, the president of the Fed of St. Louis, Alberto Musalem, participates in a talk with the chimney with the president of the Fed of Kansas City, Jeff Schmid, at the Heartland Institute of Heartland, Benthoville.
- At 14:00 GMT, the sales data of new April homes will be published.
- At 16:00 GMT, the governor of the Federal Reserve Bank, Lisa Cook, will talk about financial stability at the seventh annual conference of women in Macro.
- The shares are in positive territory this Friday with marginal profits for European indices and some small profits for US futures before the opening of the market.
- The Fedwatch of the CME tool shows that the probability of an interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve at the June meeting is only 5.3%. Later, the decision of July 30 is likely that rates are lower than current levels by 28.2%. The recent hard line comments of the FED officials have reduced the possibilities of a short -term rate cut.
- The yields of 10 years from the USA traded around 4.51%, cooling from their maximum yield earlier this week at 4.62%.
Technical analysis of the US dollar index: it has a downward margin
The American dollar index is back at the starting point, flirting with a new minimum of two weeks at the time of writing about 99.40. With the bill of expenses now having exceeded that first obstacle, the risk of a substantial shock effect on US debt could materialize even more. Even another cut in its credit rating could be under consideration, even more damaging the image of the US and the US dollar.
On the positive side, the Broken Ascending Trend Line and the level of 100.22, which kept the DXY in September-October, are the first resistance zone. Above, the simple mobile average (SMA) of 55 days in 101.49 is the following level to take into account, followed by 101.90, a crucial level throughout December 2023 and as a basis for the formation of head and shoulders inverted (H&S) during the summer of 2024. In case the dollar bundles push the even higher DXY, the crucial level of 103.18 comes into play.
If the downward pressure continues, a minced movement could materialize towards the minimum of the year to the date of 97.91 and the crucial level of 97.73. Below, a relatively thin technical support appears at 96.94 before looking at the lowest levels of this new price range. These would be 95.25 and 94.56, which would mean new minimums not seen since 2022.
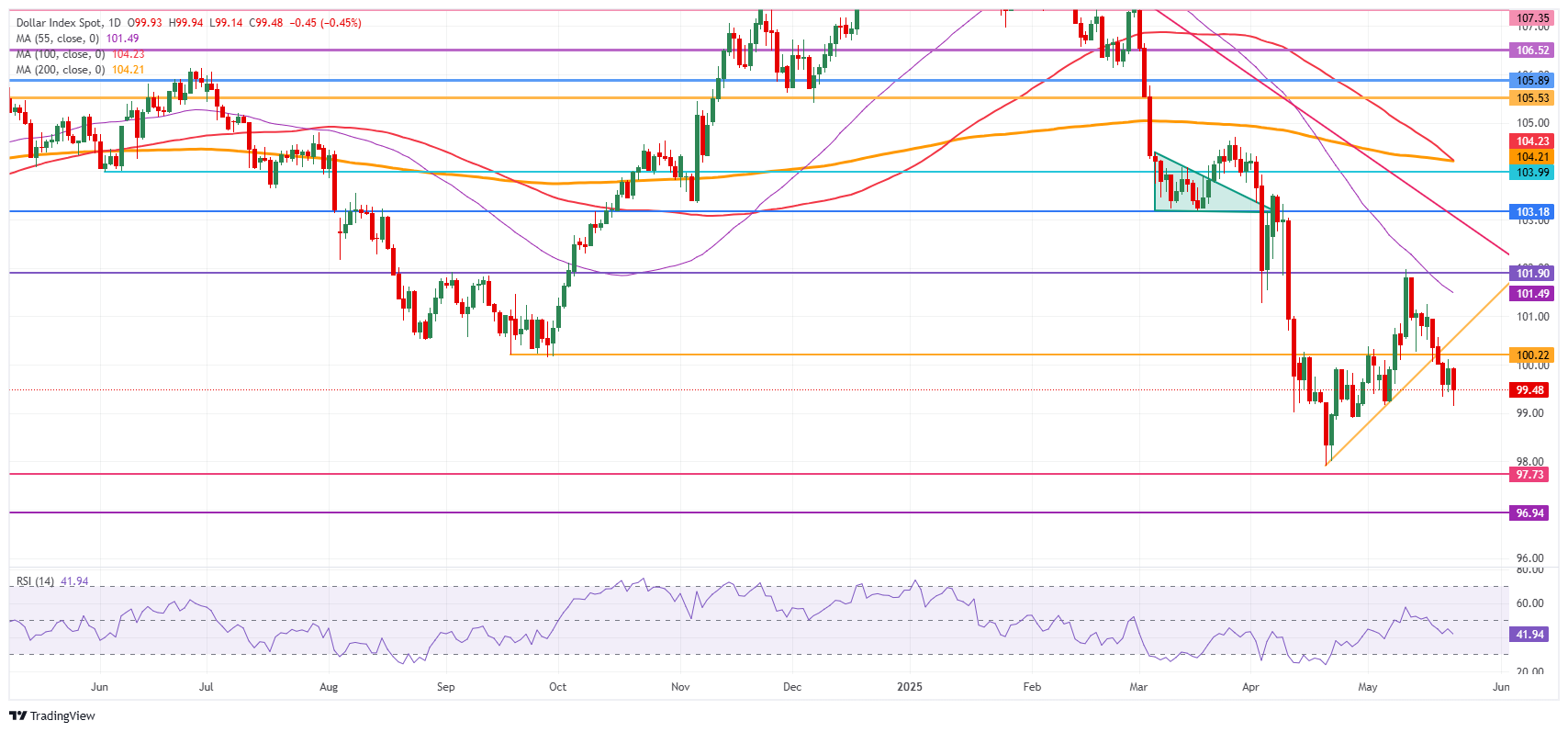
US dollar index: daily graphics
Commercial War between the US and China Faqs
In general terms, “Trade War” is a commercial war, an economic conflict between two or more countries due to the extreme protectionism of one of the parties. It implies the creation of commercial barriers, such as tariffs, which are in counterbarreras, increasing import costs and, therefore, the cost of life.
An economic conflict between the United States (USA) and China began in early 2018, when President Donald Trump established commercial barriers against China, claiming unfair commercial practices and theft of intellectual property by the Asian giant. China took retaliation measures, imposing tariffs on multiple American products, such as cars and soybeans. The tensions climbed until the two countries signed the Phase one trade agreement between the US and China in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes in China’s economic and commercial regime and intended to restore stability and confidence between the two nations. Coronavirus pandemia diverted the attention of the conflict. However, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept the tariffs and even added some additional encumbrances.
Donald Trump’s return to the White House as the 47th US president has unleashed a new wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump promised to impose 60% tariff particularly in investment, and directly feeding the inflation of the consumer price index.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







