- The dollar index weakens while the Fed speakers point to a moderate inclination, while the tensions increase in the Middle East.
- The Fed speaker, Michelle Bowman, points out a possible cut in July before Powell’s testimony on Tuesday.
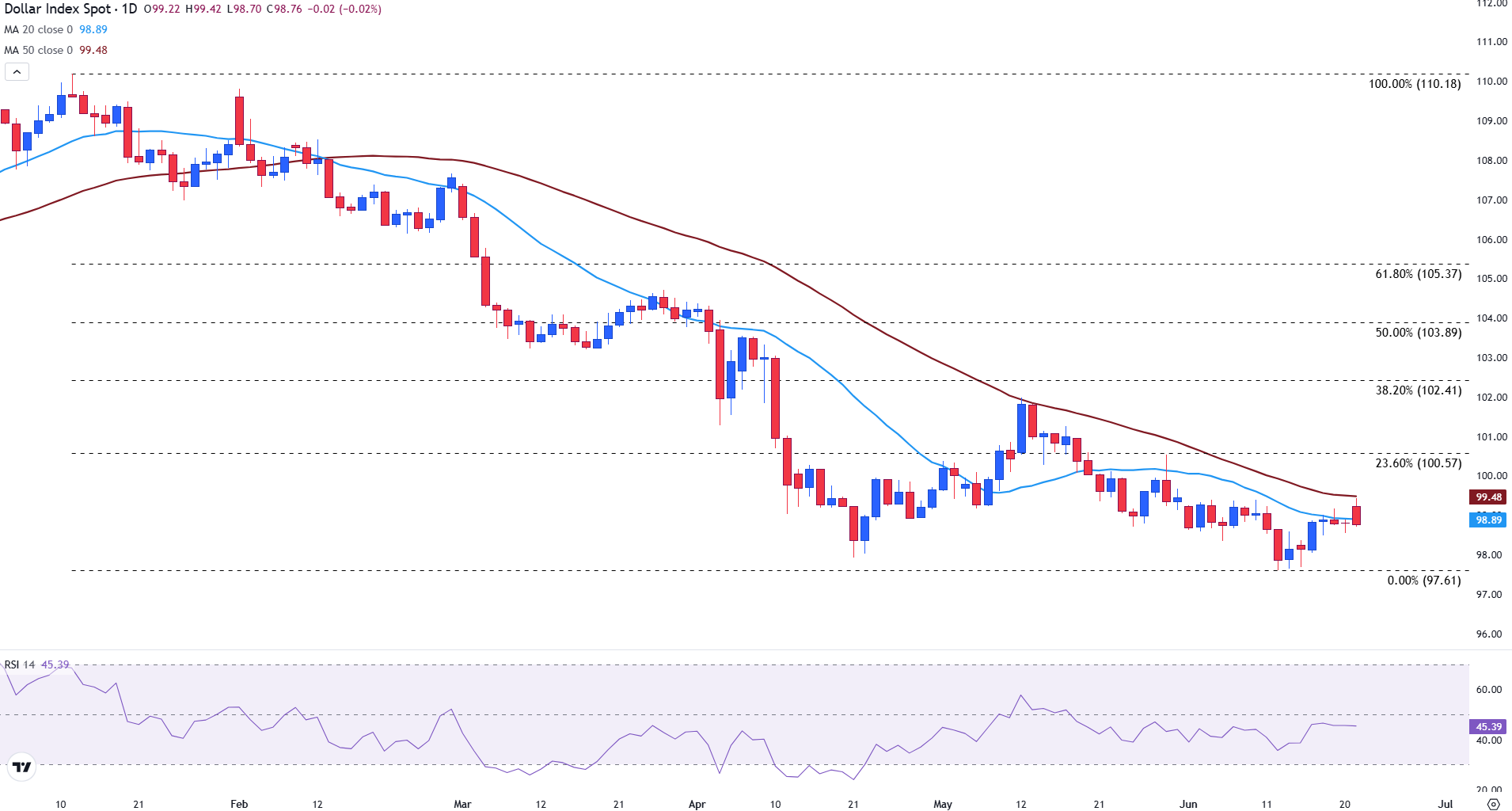
- The US dollar index is rejected by resistance in the single mobile average (SMA) of 50 days, which is currently above 99.00.
The American dollar index (DXY) is going down after a strong start on Monday, while the markets monitor the risks of an Iranian retaliation against the United States (USA) and expect the next testimony of the president of the Federal Reserve (FED), Jerome Powell, on Tuesday.
During the weekend, US President Donald Trump confirmed that American forces attacked three Iranian nuclear sites, which generated reprisal fears by Tehran. The possibility that Iran responds by interrupting oil trafficking through the Ormuz Strait – a maritime critical point – the sensation of tension risk has maintained.
The dollar index, which measures the USD against a basket of main currencies, began the week with a stronger foot, rising above the previous level of psychological resistance of 99 before sliding down.
Adding to the initial impulse, the preliminary Global S&P Preliminary S&P (PMI) index was published on Monday. The manufacturing index was 52, without changes compared to May, but above the expectations of the consensus of 51. The services component moderated slightly to 53.1 from 53.7, but still indicated expansion. These figures underlined the resilience of the US economy, helping to stabilize the yields of the bonds and support the US dollar.
However, during the US session, attention was again focused on monetary policy. The governor of the Fed, Michelle Bowman, joined an increasing choir of officials who lean towards a moderate position, saying that the central bank should stay open to the possibility of a rate cut in July as the inflationary pressures decrease. His comments resonated with those of Governor Christopher Waller last week, who suggested that a cut in July could be justified if the deflation continues.
With President Jerome Powell scheduled to deliver his semiannual testimony to Congress on Tuesday, the operators are preparing for a potentially crucial update about the thought of the Fed. After the last graph of points of the Fed, which foresaw two cuts by 2025, Powell’s tone about inflation, growth and global uncertainty will probably shape the short -term movements in the US dollar.
Technical perspective: The dollar index is softened below 99.00
From a technical perspective, the American dollar index has bounced from the support about 98.00 and tried to recover the simple mobile average (SMA) of 50 days in 99.48, which remains an important level of resistance. With the prices currently flirting with the 20 -day SMA about 98.89, a downward movement could bring back the level of psychological support of 98.00.
However, if prices manage to recover above the 50 -day SMA, a closure above this area could open a path to 100.57, the fibonacci setback of 23.6% of the fall from the January peak to the recent minimum of June. The relative force index (RSI) about 45 suggests a slight bassist impulse.
Fed Faqs
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve prices stability and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the objective of 2% set by the Federal Reserve, it rises interest rates, increasing the costs of loans throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US dollar (USD), since it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to foster indebtedness, which weighs on the green ticket.
The Federal Reserve (FED) celebrates eight meetings per year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is made up of twelve officials of the Federal Reserve: the seven members of the Council of Governors, the president of the Bank of the Federal Reserve of New York and four of the eleven presidents of the regional banks of the Reserve, who exercise their positions for a year in a rotary form.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non -standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy high quality bonds of financial institutions. The one usually weakens the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the inverse process to the QE, for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the bonds that it has in portfolio that they expire, to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.