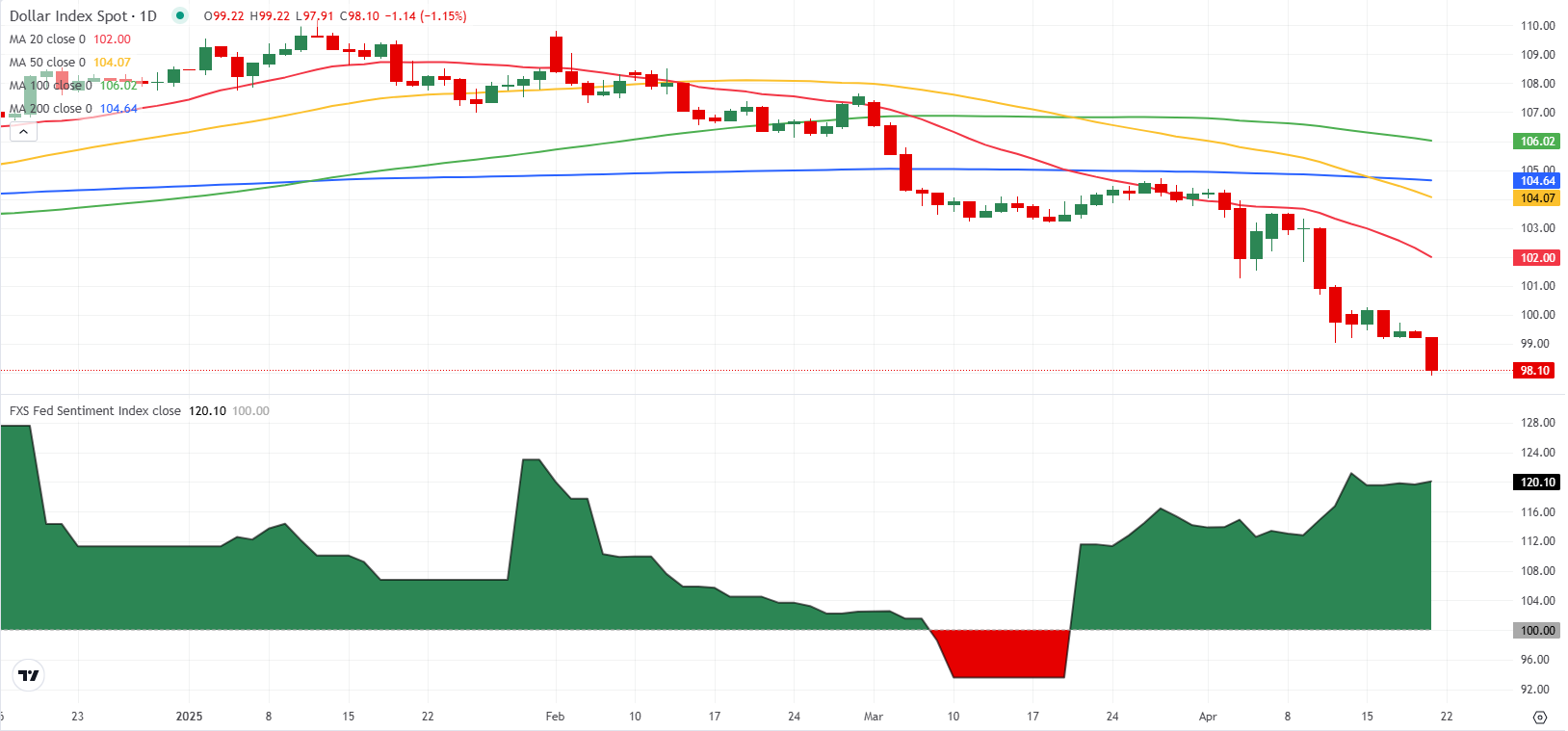
- The FXSTERET Fed feeling index remains in hard line territory about 120.
- The Fed silence period will begin on April 26.
- The criticisms of the US president, Donald Trump, to the Fed monetary policy grow in intensity.
The Federal Reserve (FED) will enter the period of silence on April 26 before holding a two -day meeting on May 6 and 7. The markets expect that the Fed maintains its unchanged policy rate, with the probability of the 25 basic points (PBS) at the May meeting of the CME Fedwatch Tool maintaining around 10%. Meanwhile, The FXSTERET Fed Feed Index (FXS) It remains about 120, pointing to a hard -line policy stance.
While talking to the Chicago Economic Club earlier, the president of the Fed, Jerome Powell, repeated that they are well positioned to expect greater clarity before considering any change in the policy position. Commenting on the new commercial regime of the president of the US, Donald Trump, “the inflationary effects of tariffs could be more persistent, it ultimately depends on inflation expectations,” Powell said.
Meanwhile, the president of the Fed of St. Louis, Alberto Musalem, declared that they would have to prioritize the fight against inflation if inflation expectations would be disagree due to tariffs. In a similar note, “in the Fed, our work is to maintain inflation under control so that the rate is not even higher,” said Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari.
Related news
-
USD weakness in focus this week – dbs
-
Five fundamental data of the week: Traders will be pending commercial war, important surveys and a key speech of the Fed
Is the independence of the Fed threatened?
In spite of the general tone of the Fed responsible for those responsible, as reflected in the FXS feeling index, and the assessment of the market of a strong probability of maintaining the policy in May, the US dollar (USD) has been weakened in front of its main rivals. The USD index, which measures the valuation of the USD compared to a basket of six main currencies, has dropped around 6% in April after losing more than 3% in March. The growing fears about an economic slowdown in the US, as a result of the aggressive Trump administration tariffs, seem to be the main engine behind the sale of the USD.
Lately, concerns about the loss of independence of the Fed have been putting an additional weight on the shoulders of the USD.
US dollar price this month
The lower table shows the percentage of the US dollar change (USD) compared to the main currencies this month. American dollar was the weakest currency against the Swiss Franco.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | Aud | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -6.35% | -3.61% | -6.16% | -4.10% | -2.75% | -5.52% | -8.91% | |
| EUR | 6.35% | 2.88% | 0.16% | 2.36% | 3.79% | 0.85% | -2.77% | |
| GBP | 3.61% | -2.88% | -2.66% | -0.51% | 0.88% | -1.98% | -5.51% | |
| JPY | 6.16% | -0.16% | 2.66% | 2.20% | 3.63% | 0.67% | -2.92% | |
| CAD | 4.10% | -2.36% | 0.51% | -2.20% | 1.40% | -1.48% | -5.02% | |
| Aud | 2.75% | -3.79% | -0.88% | -3.63% | -1.40% | -2.84% | -6.33% | |
| NZD | 5.52% | -0.85% | 1.98% | -0.67% | 1.48% | 2.84% | -3.59% | |
| CHF | 8.91% | 2.77% | 5.51% | 2.92% | 5.02% | 6.33% | 3.59% |
The heat map shows the percentage changes of the main currencies. The base currency is selected from the left column, while the contribution currency is selected in the upper row. For example, if you choose the US dollar of the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese yen, the percentage change shown in the box will represent the USD (base)/JPY (quotation).
In a publication publication published just before the monetary policy ads of the European Central Bank (ECB) on April 17, Trump accused the president of the Fed, Powell, of being “too late and wrong.”
“The ECB is expected to cut the interest rates for the seventh time, and yet,” too late “Jerome Powell of the Fed, which is always too late and wrong, yesterday a report issued that was another, and typical, complete disaster!” Trump said. While talking with the reporters a day later, the Economic Advisor of the White House, Kevin Hassett, said President Trump and his team were studying whether to say goodbye to the president of the Fed, Powell, was an option in a way that was not before. In turn, the USD began the week under strong sales pressure, with the USD index falling to its lowest level in approximately three years about 98.00.
Evaluating the market reaction to this development, “investors seem less than happy with the idea of a politicized Fed – the US dollar and long -term government bonds have weakened,” said UBS economist Paul Donovan. “There are controls on the author’s authority. The governors of the Fed need to be confirmed by the Senate. The president of the FOMC does not have to be the president of the Fed. However, some of these controls depend on the rule of law.”
Fed Faqs
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve prices stability and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the objective of 2% set by the Federal Reserve, it rises interest rates, increasing the costs of loans throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US dollar (USD), since it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to foster indebtedness, which weighs on the green ticket.
The Federal Reserve (FED) celebrates eight meetings per year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is made up of twelve officials of the Federal Reserve: the seven members of the Council of Governors, the president of the Bank of the Federal Reserve of New York and four of the eleven presidents of the regional banks of the Reserve, who exercise their positions for a year in a rotary form.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non -standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy high quality bonds of financial institutions. The one usually weakens the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the inverse process to the QE, for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the bonds that it has in portfolio that they expire, to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







