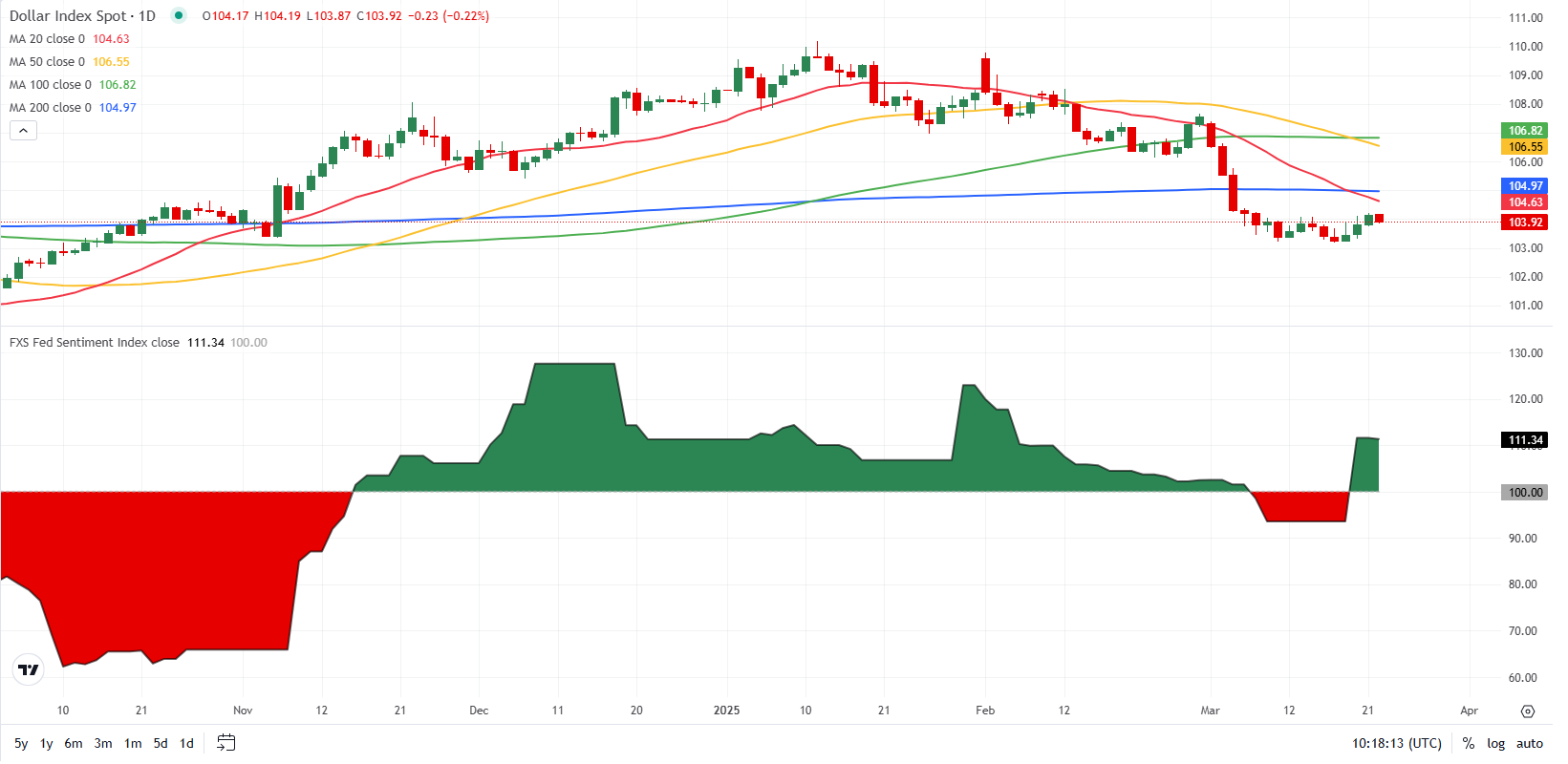
- The FXSTERET Fed feeling index rises to hard line territory above 100.
- The Fed left the policy rate without changes after the March policy meeting.
- Markets see a probability of less than 20% of a Fed fees cut in May.
The Federal Reserve (FED) announced that it left the interest rate without changes in 4.25% -4.5% after the policy meeting of March 9-19. The revised summary of economic projections showed that those responsible for the policy still projected a total reduction of 50 basic points (BPS) at the interest rate in 2025.
While talking at the press conference after the meeting, the president of the FED, Jerome Powell, reiterated that the Central Bank will not be in a hurry to make feats of fees, adding that they can maintain the restriction of the policy for longer if the economy remains strong.
Related news
-
American dollar prognosis: inflation, tariffs and cautious fed
-
The Fed has tools available to mitigate unexpected disturbances in the market – Christopher Waller
-
Fed: The current modestly restrictive monetary policy is completely appropriate – John C. Williams
Commenting on the policy perspectives, Chicago Fed president, Austan Goolsbee, told CNBC that Fed needs to be a firm hand and have a long -term vision of the economy. Similarly, the president of the Fed in New York, John Williams, said there is much uncertainty in the economy, adding that they are in no hurry to make the next monetary policy decision.
According to the CME Fedwatch tool, markets are currently valuing in approximately 15% the probability of a 25 basic points in May.
Meanwhile, The FXSTERET Fed Feed Index (FXS) It rose above 110 after falling below 100 just before the FED period of silence began, highlighting a hard line inclination in the general language of the Fed. This coincided with a three -day recovery in the US dollar index (USD).
Fed Faqs
The monetary policy of the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve prices stability and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the objective of 2% set by the Federal Reserve, it rises interest rates, increasing the costs of loans throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US dollar (USD), since it makes the United States a more attractive place for international investors to place their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Federal Reserve can lower interest rates to foster indebtedness, which weighs on the green ticket.
The Federal Reserve (FED) celebrates eight meetings per year, in which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) evaluates the economic situation and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is made up of twelve officials of the Federal Reserve: the seven members of the Council of Governors, the president of the Bank of the Federal Reserve of New York and four of the eleven presidents of the regional banks of the Reserve, who exercise their positions for a year in a rotary form.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non -standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy high quality bonds of financial institutions. The one usually weakens the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the inverse process to the QE, for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the bonds that it has in portfolio that they expire, to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.