- The Mexican Peso has reversed its short-term upward trend.
- The move comes after the IMF revised downward its economic growth forecasts for Mexico.
- USD/MXN is rising after comments from Fed Chair Jerome Powell suggested that interest rate cuts could be delayed further.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) registers a downward trend in most of its most traded pairs on Wednesday. This is due to a combination of factors, including the decision of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to lower its economic growth forecasts for Mexico in 2024-2025, as well as the drop in oil prices, a key export product. for the country.
The impact of stubbornly high inflation in the US and recent statements by Federal Reserve (Fed) Chairman Jerome Powell suggesting that the Fed may not cut interest rates until September (versus previous expectations of June), were other factors that were postulated as influential in the reversal of the fortunes of the Mexican Peso.
The Mexican peso falls after the downward revision of growth by the IMF
The Mexican peso falls again after the IMF revised downwards its growth forecasts for Mexico in the next two years on Tuesday. It lowered its forecast for 2024 to 2.4% from 2.7% and to 1.4% in 2025 from the previously estimated 1.5%.
“The forecast for Mexico is revised downwards due to weaker-than-expected results for late 2023 and early 2024, with a contraction in the manufacturing sector,” the IMF said in its latest World Economic Outlook report.
This follows a similar downgrade by Banxico in February, when it reduced its growth forecast to 2.8% from 3.0% in 2024, according to The Wall Street Journal.
The drop in growth is expected as a result of lower public spending in an effort to reduce the budget deficit.
“The Mexican Ministry of Finance expects the fiscal deficit to decrease from 5% to 2.5% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) next year, which would imply a cut in spending of 833.6 billion pesos, according to the Pre- General Economic Policy Criteria of 2025”, says Christian Borjon Valencia, editor of FXStreet.com
At its March meeting, Banxico reduced interest rates from 11.25% to 11.00% due to evidence of lower inflation and growth. However, the measure failed to completely reverse the long-term upward trend of the Mexican Peso.
On the other hand, rising inflation in the US and recent comments from Fed Chairman Powell could have reversed the trend of the Peso, particularly against the US Dollar.
On Tuesday, Powell said that “recent data show a lack of further progress in inflation this year,” adding: “If higher inflation persists, the Fed can maintain the current rate as long as necessary.”
Higher interest rates are usually positive for a currency, as they increase foreign capital inflows. The opposite occurs with lower interest rates. Given the divergence in the monetary policy stances of both countries, with Banxico cutting rates and the Fed maintaining them, the long-term appreciation of the Mexican Peso against the Dollar appears to be at risk of breaking down.
Technical analysis: USD/MXN reverses its short-term trend
The USD/MXN (the value of one US Dollar in Mexican pesos) has likely reversed its short-term bearish trend.
On the 4-hour chart, used by many analysts to evaluate the short-term trend, the price highs and lows are rising. This suggests that the pair is now in an uptrend, favoring the bulls.
USD/MXN 4-hour chart
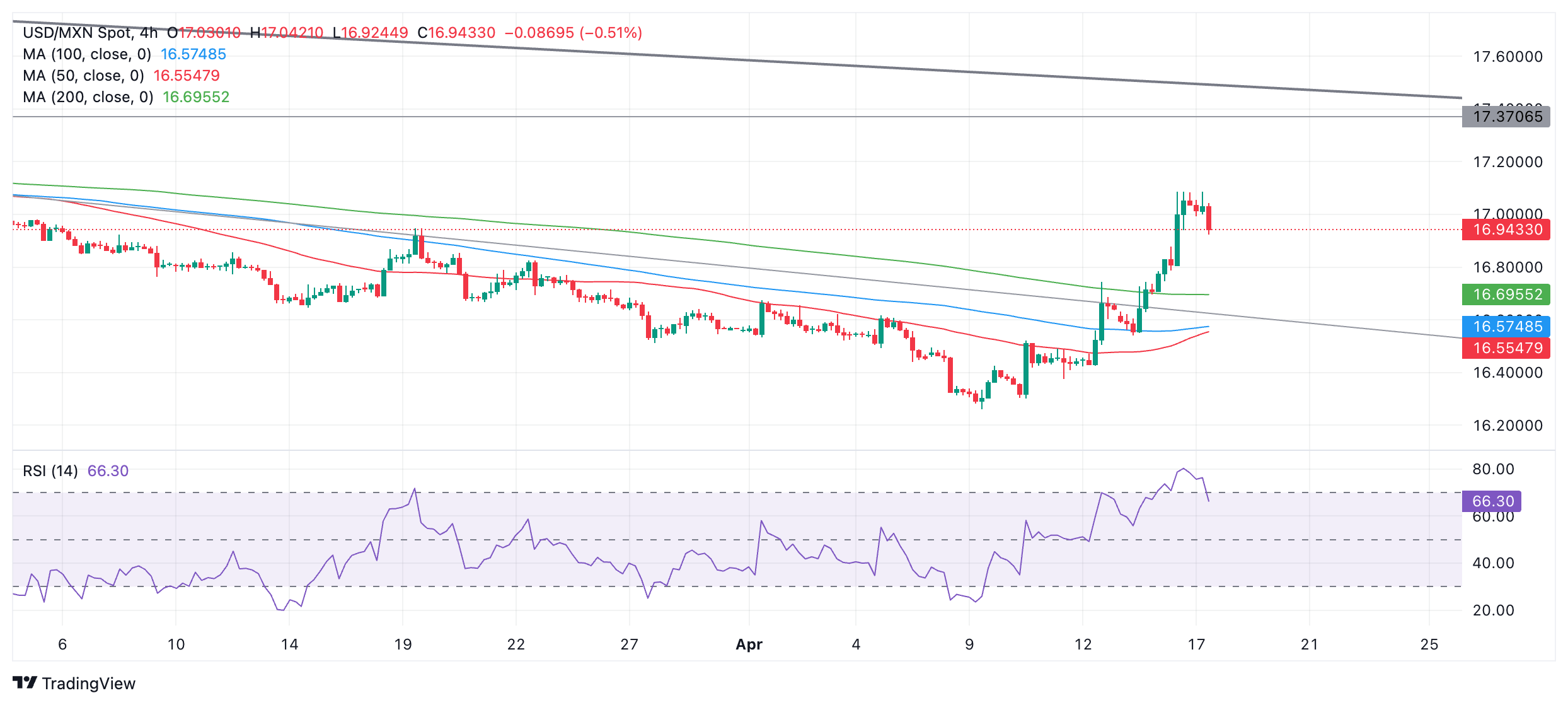
One caveat to the bullish outlook is that the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is retreating from overbought to neutral territory. Since the price is also falling, the combination of the two could signal the start of a correction. When the RSI breaks out of the overbought zone, it is a signal for short-term traders to close long positions and open short trades.
If the pair continues to retreat, it could fall to the 50-day SMA at 16.82 and find support there. However, given the dominance of the short-term uptrend, it is likely that it will eventually recover and start rising.
A break above Tuesday's high at 17.09 would indicate a continuation of the uptrend towards the next target, possibly located at 17.17, where the 200-day SMA lies, followed by trendline resistance at long term and a resistance level around 17.37.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Mexican Peso
What is MXN?
The Mexican Peso is the legal tender of Mexico. The MXN is the most traded currency in Latin America and the third most traded on the American continent. The Mexican Peso is the first currency in the world to use the $ sign, prior to the later use of the Dollar. The Mexican Peso or MXN is divided into 100 cents.
What is Banxico and how does it influence the MXN?
Banxico is the Bank of Mexico, the country's central bank. Created in 1925, it provides the national currency, the MXN, and its priority objective is to preserve its value over time. In addition, the Bank of Mexico manages the country's international reserves, acts as a lender of last resort to the banks and advises the government economically and financially. Banxico uses the tools and techniques of monetary policy to meet its objective.
How does inflation impact the MXN?
When inflation is high, the value of the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to decrease. This implies an increase in the cost of living for Mexicans that affects their ability to invest and save. At a general level, inflation affects the Mexican economy because Mexico imports a significant amount of final consumption products, such as gas, fuel, food, clothing, etc., and a large amount of production inputs. On the other hand, the higher the inflation and debt, the less attractive the country is for investors.
How does the Dollar influence the Mexican Peso (MXN)?
The exchange rate between the USD and the MXN affects imports and exports between the United States and Mexico, and may affect demand and trade flows. The price of the Dollar against the Mexican Peso is affected by factors such as monetary policy, interest rates, the consumer price index, economic growth and some geopolitical decisions.
How does the Fed's monetary policy affect Mexico?
The exchange rate between the USD and the MXN affects imports and exports between the United States and Mexico, and may affect demand and trade flows. The price of the Dollar against the Mexican Peso is affected by factors such as monetary policy, interest rates, the consumer price index, economic growth and some geopolitical decisions.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.