- The sterling pound falls about 1,3545 against the US dollar, while investors seek new clues about the perspective of war between Israel and Iran.
- Investors expect the Fed and the BOE to maintain stable interest rates this week.
- The United Kingdom inflation is expected to have grown moderately in May.
The Pound sterling (GBP) has a lower performance than its peers on Tuesday in the midst of the conflict between Israel and Iran. The growing tensions in the Middle East have decreased the appetite for risk of investors, which has resulted in an increase in the demand for shelter assets.
The dispute between Iran and Israel enters its fifth day. The Israeli army said during the last hours of Asia on Tuesday that they had identified missiles launched from Iran to Israel, according to the BBC News.
Earlier on the day, a Reuters report showed that Iran sought that their pairs of the Middle East urged the president of the United States (USA), Donald Trump, to press the Israeli prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, for a high immediate fire.
After Tehran’s request, Trump has asked the US vice president, JD Vance, and the middle of the Middle East they press for a meeting with the Iranians this week apart from the G7 meeting, The New York Times reported.
At the time of writing, the US dollar index (DXY), which tracks the value of the dollar against six main currencies, ranges around 98.15. Theoretically, the demand of the US dollar should have increased in the midst of the growing geopolitical tensions, given its appeal as a safe refuge. However, he is struggling to gain strength, while investors expect the Federal Reserve Monetary Policy (FED) on Wednesday.
What moves the market today: the low sterling pound against the US dollar
- The sterling pound falls about 1,3545 against the US dollar (USD) during European negotiation hours. The GBP/USD torque falls before the next Fed Monetary Policy ads and the Bank of England (BOE), scheduled for Wednesday and Thursday, respectively.
- According to the CME Fedwatch tool, the Fed is almost sure of maintaining stable interest rates in the range of 4.25% -4.50% this time. The operators are increasingly sure that the Central Bank will maintain interest rates unchanged, since officials have declared that monetary policy adjustments are inappropriate until they obtain clarity about how much new economic policies in inflation will impact and affect the perspectives.
- The main prominent point of the Fed policy will be the points chart, which shows where the officials who direct the interest rates in the short and long term are directed. In the last publication of the points chart in March, officials anticipated at least two cuts of interest rates for the end of the year. In addition to that, investors will also focus on the Monetary Policy Declaration and the Press Conference of the President of the FED, Jerome Powell, to know when the Central Bank could begin to reduce interest rates.
- In Wednesday’s monetary policy announcement, the Fed will also show forecasts about inflation and economic growth. It will be interesting to observe the degree of change in these key economic triggers amid the implementation of new policies by President Trump.
- In the United Kingdom (United Kingdom), the Bank of England (BOE) is expected to also maintain stable interest rates at 4.25%, since officials guided a “gradual and cautious” monetary relaxation approach at the May policy meeting, after a reduction of interest rates of 25 basic points (PBS).
- However, market participants expect the BOE to reassess their monetary policy guide, given the recent problems in the United Kingdom labor market. The latest employment data showed an increase in the unemployment rate and a slower growth of employment, since business owners reduced the workforce to compensate for the impact of an increase in employers’ contribution to social security schemes.
- Before the BOE monetary policy advertisement, investors will focus on consumer price index (CPI) of the United Kingdom for May, which will be published on Wednesday. Inflation data is expected to show that pressures on prices have cooled.
Technical Analysis: The sterling pound falls about 1,3540
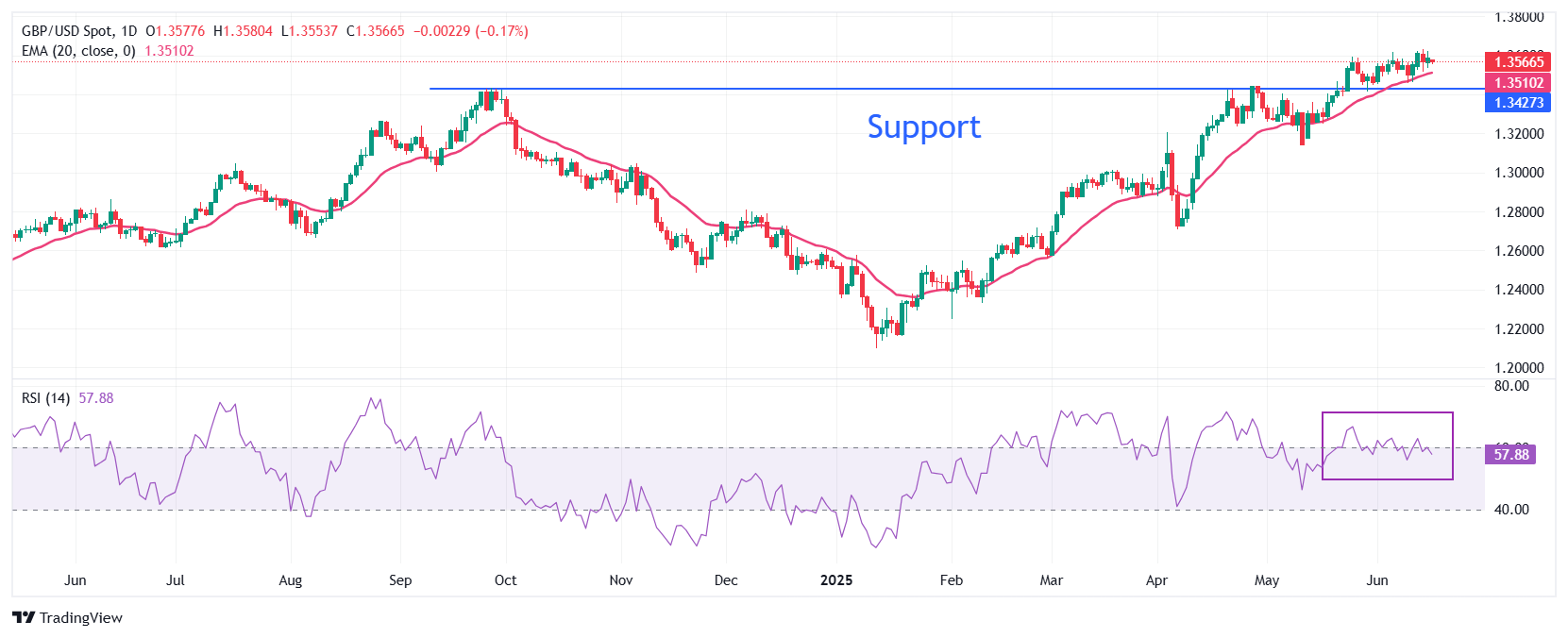
The sterling pound oscillates within the negotiation range of Monday around 1,3565 against the US dollar on Tuesday. The GBP/USD pair fights again to visit the maximum of three years around 1,3630. The short -term trend of the cable remains bullish, since the 20 -day exponential mobile average (EMA) is inclined to rise around 1,3508.
The 14 -day relative force (RSI) index struggles to break decisively above 60.00. A new bullish impulse would arise if the RSI remains above that level.
On the positive side, the maximum of January 13, 2022 of 1,3750 will be a key obstacle to the pair. Looking down, the horizontal line drawn from the maximum of September 26, 1,3434 will act as a key support zone.
US dollar FAQS
The US dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation along with local tickets. According to data from 2022, it is the most negotiated currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency change operations, which is equivalent to an average of 6.6 billion dollars in daily transactions. After World War II, the USD took over the pound sterling as a world reserve currency.
The most important individual factor that influences the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% objective set by the Fed, it rises the types, which favors the price of the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and promulgate quantitative flexibility (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure that is used when the credit has been exhausted because banks do not lend each other (for fear of the default of the counterparts). It is the last resort when it is unlikely that a simple decrease in interest rates will achieve the necessary result. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed to combat the contraction of the credit that occurred during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy bonds of the US government, mainly of financial institutions. Which usually leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the reverse process for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the wallet values that overcome in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







