- The Swiss franc is vulnerable as inflation data remains below official forecasts.
- The SNB expected average inflation of 1.9% in 2024 in its December forecasts, but it currently stands at 1.2%.
- The latest production and import prices showed the tenth consecutive month of deflation.
The Swiss franc (CHF) is trading flat at the end of the week, with a decline of just a few hundredths in its most traded peers. The overall fundamental outlook is not particularly favorable for the CHF, as Swiss inflation continues to decline and diverge from official estimates. This suggests that the Swiss National Bank may have to ease its monetary policy, a generally negative factor for the currency as it attracts fewer foreign capital inflows.
In its latest macroeconomic data release, Swiss producer and import prices continued their deflationary trend in February, recording deflation for the tenth consecutive month of -2.0% (from negative -2.3% in January), according to data from the Federal Office of Statistics.
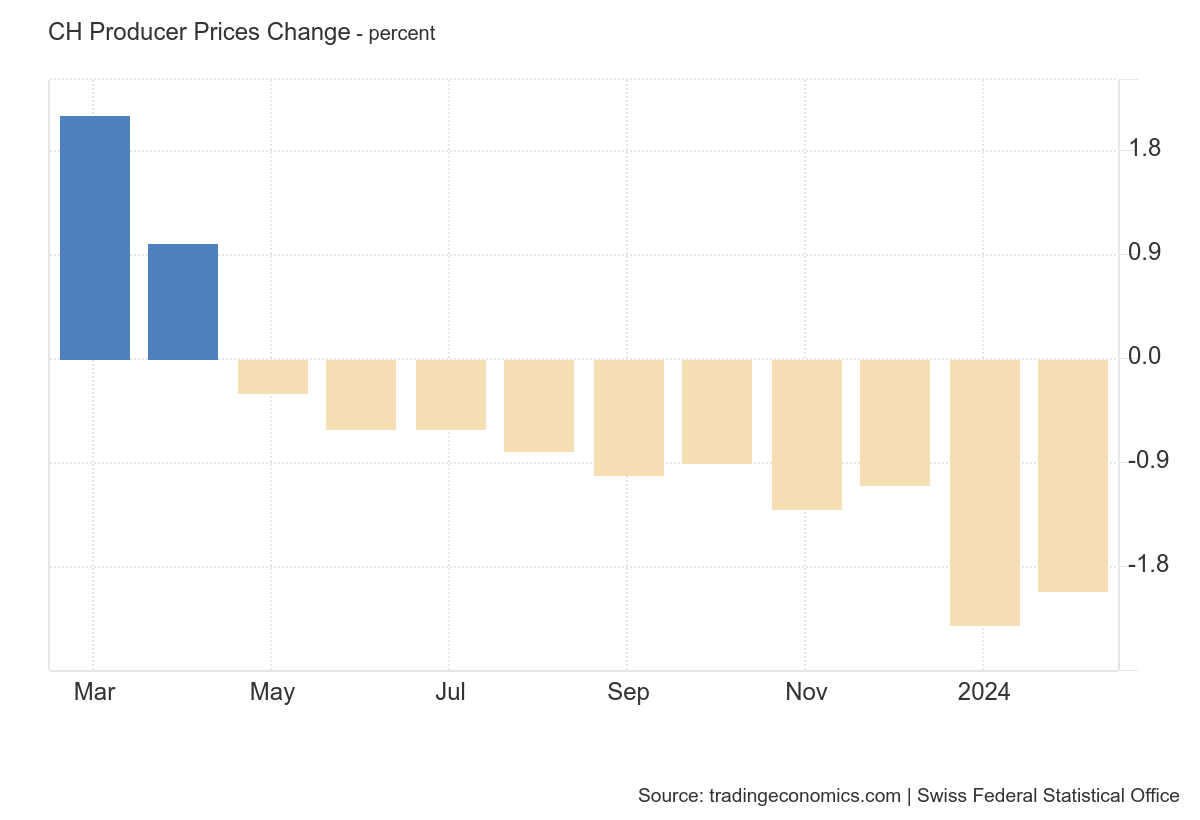
Risk for the Swiss Franc: inflation remains below SNB forecasts
The Swiss franc could weaken further as inflation in Switzerland looks increasingly likely to fall below official forecasts.
In its latest set of data, Swiss headline inflation rose 1.2% year-on-year in February, up from 1.3% in January, and 0.6% month-on-month, up from 0.2% in January.
The data shows that inflation is undermining the Swiss National Bank's (SNB) own forecasts, which at its December policy meeting expressed the view that inflation would start to rise from the 1.4% recorded in November.
“However, inflation is likely to rise somewhat again in the coming months due to rising electricity and rental prices, as well as rising VAT,” the SNB said in its December monetary policy statement. .
The SNB implemented a 0.25% rate hike in June 2023, raising rates from 1.50% to 1.75% to combat the threat of higher inflation. However, since the opposite has happened and inflation has fallen faster than expected, there is now a risk that it will cut interest rates, which would be negative for the Swiss franc, as lower rates attract fewer inflows. of foreign capital.
The possibility of a policy change is increased by the fact that inflation is well below the 1.9% forecast by the SNB for 2024. Although there are only two months of data so far, it will have to rise substantially to meet the forecast from the bank before the end of the year. The SNB's next monetary policy meeting is on March 21.
SNB's Jordan thinks the Swiss franc is too expensive
The president of the SNB, Thomas Jordan, has expressed concern about the excessive strength of the Swiss franc, especially its impact on Swiss companies, especially exporters. These concerns are reflected in data from Switzerland's foreign exchange reserves (CHFER), which shows a recovery in foreign exchange reserves in 2024, indicating that the SNB could be selling Swiss francs to lower the exchange rate.
Technical Analysis: Swiss Franc Oscillating in Short-Term Range Against USD
The USD/CHF pair, which measures the number of Swiss francs one US dollar can buy, has been oscillating within a relatively tight range between 0.8900 and 0.8740 roughly since mid-February.
Overall, the pair is in a short-term uptrend, with the expectation that it will eventually break the current range and begin to rise. However, the resistance of a long-term trend line and the 50-week simple moving average (SMA) present considerable obstacles to a trend extension.
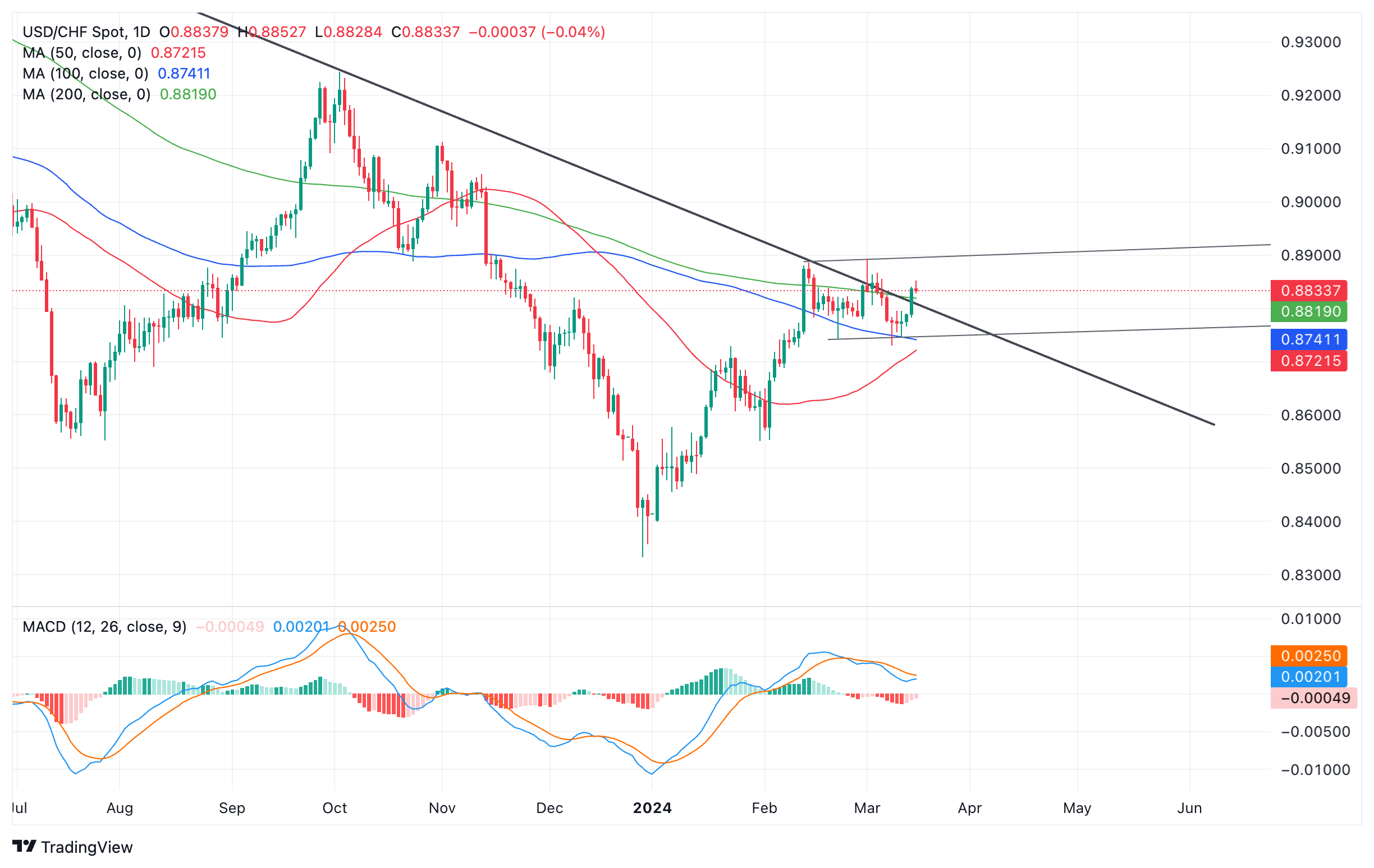
US Dollar vs. Swiss Franc: 4-hour chart
For the bullish trend to be confirmed, it would be necessary to break above the range highs at 0.8900. This move would likely extend to an initial target at 0.8992, the Fibonacci ratio 0.618% of the range height extrapolated upwards, followed by 0.9052, the full height extrapolated upwards.
However, a decisive break below the range low at 0.8729 could signal a short-term trend reversal and the start of a deeper decline. The first target for the move lower would be the 0.618 extrapolation of the range height at 0.8632, followed by the full extrapolation at 0.8577, which is also near the January 31 lows at 0.8551, another key support level to lowers it.
US Dollar FAQ
What is the US Dollar?
The United States Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation alongside local banknotes. According to 2022 data, it is the most traded currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency exchange operations, equivalent to an average of $6.6 trillion in daily transactions.
After World War II, the USD took over from the pound sterling as the world's reserve currency.
How do the decisions of the Federal Reserve affect the Dollar?
The single most important factor influencing the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Your main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates.
When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% target set by the Fed, the Fed raises rates, which favors the price of the dollar. When Inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the Dollar.
What is Quantitative Easing and how does it influence the Dollar?
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit into a clogged financial system. This is an unconventional policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks do not lend to each other (for fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when a simple lowering of interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed's weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy US government bonds, primarily from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weakening of the US Dollar.
What is quantitative tightening and how does it influence the US dollar?
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process by which the Federal Reserve stops purchasing bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal of maturing portfolio securities in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







