- The US dollar index slides for the third consecutive day despite the increase in geopolitical uncertainty.
- Israel’s reported plans to attack Iranian nuclear facilities generate doubts among operators about Trump’s ability to handle tensions in the Middle East.
- The US dollar index falls below 100.00 while suffering more losses.
The American dollar index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US dollar (USD) compared to six main currencies, slides for the third consecutive day on Wednesday while the markets prepare for another geopolitical tensions field. Throughout the week, the USD has already paid the price for the volatile policy changes of the Trump administration, which faces difficulties on several fronts.
The president of the United States Trump apparently has no firm control over Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. On his tour of the Middle East, Trump announced that it was time for a new nuclear agreement with Iran and a second chance. However, in Tuesday’s negotiation hours, CNN reported that Israel considers to attack nuclear facilities in Iran, something that former President Joe Biden could avoid, and undo the diplomatic efforts of President Trump of the last days in the region.
The second front is the domestic, with another failure for what Trump calls the “great bill.” Trump was frustrated with the demands of significantly increasing the limit of the deduction of state and local taxes (Salt), indicating a stagnation in the approval of a gigantic bill of tax cuts. Trump told the legislators that they did not allow the Salt deduction or the differences on cuts in the Social Security network would hinder the bill, but the legislators of states with high taxes and the intransigent conservatives continue to oppose the project unless its changes are made, says Bloomberg.
What moves the market today: more of the same
- Weekly mortgage requests fell by -5.1% compared to the previous number that showed an increase of 1.1% last week.
- Around 16:15 GMT, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank (FED) of Richmond, Thomas Barkin, will give a speech with possible comments for the market. Barkin already spoke earlier this week, saying that he will take several months, even until summer, before the economic situation and US data stabilize. The governor of the Fed, Michelle Bowman, will also participate in the event.
- The actions are in recoil, with the future of the US in red by more than 0.50%.
- The CME Fedwatch tool shows that the probability of an interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve at the June meeting is only 5.4%. Later, the decision of July 30 is likely that rates are lower than current levels by 26.9%. The recent hard line comments of the FED officials have reduced the possibilities of a short -term rate cut.
- The yields of 10 years of the US are quoted around 4.53%, cooling after the strong rebound seen on Monday.
Technical analysis of the dollar index: could get worse
The US dollar index is giving under pressure and begins to look very bleak. In Wednesday’s first operations, the DXY extended the losses below the 100.00 threshold after closing below the solid support in 100.22 the previous day, which could lead to the index to make a minced movement. With recent geopolitical headlines, operators are increasingly reaching the conclusion that President Trump could face several substantial setbacks in his mandate and policy implementation.
On the positive side, the Broken Ascending Trend Line and the level of 100.22, which kept the DXY in September-October, are the first resistance zone. Above, 101.90 is the following great resistance again, since it already acted as a pivotal level throughout December 2023 and as a basis for the formation of inverted head and shoulders (H&S) during the summer of 2024. The simple mobile average (SMA) of 55 days in 101.94 reinforces this area as a strong resistance. In the event that the dollar bundles push the DXY even higher, the pivotal level of 103.18 comes into play.
If the downward pressure continues, a minced movement could materialize towards the minimum of the year to the date of 97.91 and the pivotal level of 97.73. Below, a relatively thin technical support appears at 96.94 before looking at the lowest levels of this new price range. These would be 95.25 and 94.56, which would mean new minimums not seen since 2022.
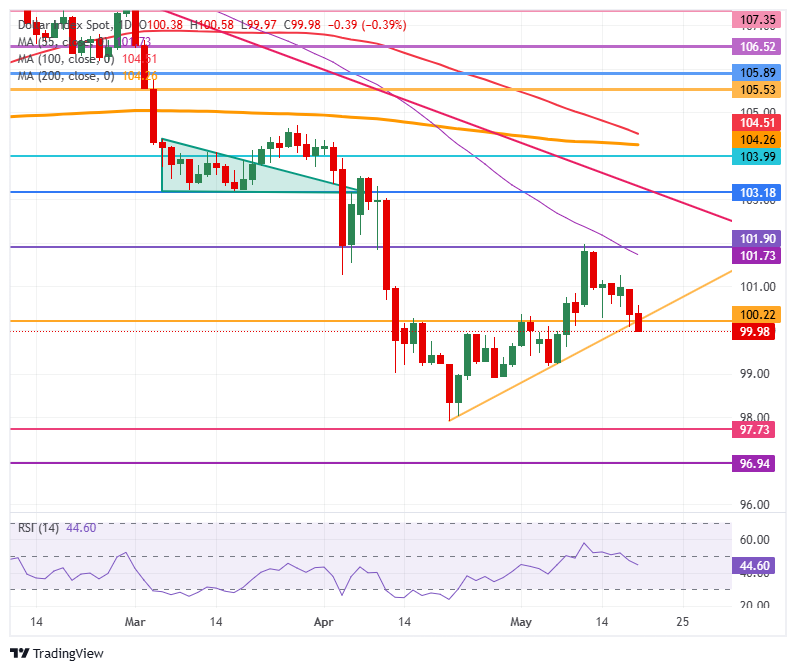
US dollar index: daily graphics
US dollar FAQS
The US dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation along with local tickets. According to data from 2022, it is the most negotiated currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency change operations, which is equivalent to an average of 6.6 billion dollars in daily transactions. After World War II, the USD took over the pound sterling as a world reserve currency.
The most important individual factor that influences the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% objective set by the Fed, it rises the types, which favors the price of the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and promulgate quantitative flexibility (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure that is used when the credit has been exhausted because banks do not lend each other (for fear of the default of the counterparts). It is the last resort when it is unlikely that a simple decrease in interest rates will achieve the necessary result. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed to combat the contraction of the credit that occurred during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy bonds of the US government, mainly of financial institutions. Which usually leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the reverse process for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the wallet values that overcome in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







