With the coronavirus still here After almost two years, the scientific journal Nature makes its choice regarding the most important scientific achievements of 2021.
The pioneering coronavirus vaccines are among these most important scientific discoveries, with the list being rich.
So these are the greatest scientific achievements of 2021, as presented by the magazine Nature and healthstories.gr…
Innovation of the year: Two vaccines against COVID-19
When the pandemic started in January 2020, scientists in various biotechnology companies turned to mRNA technology to develop vaccines. Until January 2021, when we had 1.5 million deaths from him coronavirus worldwide, two vaccines have already been approved for emergency use in the US.
The Pfizer / Biotech and Moderna vaccines are unlike any other vaccine on the market today. They are the first so-called mRNA vaccines – a technology that has been around for decades. They work by utilizing messenger RNA, the genetic code that tells our cells what proteins they need to produce to make antibodies against the coronavirus. MRNA technology is revolutionizing the way it can be used to treat a variety of diseases.
Protein folding with artificial intelligence
In July, Google’s DeepMind subsidiary announced that it had solved one of nature’s most difficult problems: predicting the complex three-dimensional shape in which amino acids will fold when they form a functional protein.
Using the extremely accurate AlphaFold deep learning model, DeepMind was able to predict the three-dimensional structure of 350,000 proteins – including almost every protein expressed in the human body – from their amino acid sequences. This technology will be able to help detect and treat diseases.
That’s why the leading scientific review “Science” announced that this was the most important scientific achievement of this year. According to the magazine, this is an achievement on two “fronts”: on the one hand, a scientific problem that remained unsolved for five decades has been solved and, on the other hand, scientists now have in their hands “an innovative technique that will accelerate to a great degree of scientific discoveries.
Alzheimer’s drug approval

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first new drug for Alzheimer’s disease in 18 years. Biogen, a biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, has shown that the antibody drug can clear clusters of amyloid-β protein, which some scientists believe is the main cause of Alzheimer’s, from the brain.
The World Health Organization has approved the first vaccine against malaria
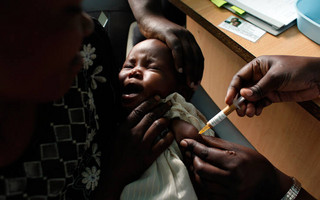
In October, The World Health Organization has approved the first vaccine against malaria. The approval was not only the first for malaria, but also for any parasitic disease. Malaria kills nearly half a million people each year, including 260,000 children under the age of five. Most of these victims live in sub-Saharan Africa.
The new vaccine fights the deadliest of the five malaria pathogens and the most common in Africa and is given to children under the age of five in a series of four injections. The vaccine covers only about 30% of severe malaria cases. However, one mathematical model showed that it could still prevent 5.4 million cases and 23,000 deaths in children under five each year. Experts say the vaccine is a valuable tool that should be used in conjunction with existing methods – such as combination therapies and the use of insecticide-treated mosquito nets – to fight the deadly disease.
Gene processing directly inside the body
The CRISPR gene processing technique has been touted as a game changer for treating diseases. But realizing this dream for many diseases will require researchers to successfully deliver the CRISPR – Cas9 mechanism to a person’s body and prove that it can safely and effectively process the target gene. On June 26, Intellia Therapeutics of Cambridge, Massachusetts, and Regeneron, Tarrytown, New York, published clinical trials proving just that. The biotech companies tested their treatment on six people with a rare condition called transhyuretic amyloidosis, which causes abnormally accumulated protein in the body’s organs and tissues. All participants experienced a drop in malformed protein levels – and two high-dose patients saw protein levels fall by an average of 87%.
Extension of life expectancy
The proportion of the world’s population aged 60 and over will almost double, from 12% to 22%, between 2015 and 2050, according to the World Health Organization. Aging is associated with both acute and chronic conditions such as cancer, type 2 diabetes, dementia and heart disease.
Researchers have partially understood the molecular mechanisms of aging and are exploring ways to extend life expectancy. Using omics technologies that can simultaneously quantify all gene activity or the concentration of all proteins in a cell, and epigenetic knowledge, researchers can identify biological markers that are prognostic and target for preventive treatments.
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.