- The USD/CAD weakens around 1,3695 in the Asian session on Friday.
- Trump is still considering whether to order an American attack on Iran’s nuclear program.
- The hard line posture of the Fed and the lowest prices of crude oil could help limit torque losses.
The USD/CAD pair weakens about 1,3695, breaking a three -day winning streak during Friday’s Asian negotiation hours. The US dollar (USD) goes back slightly after US President Donald Trump announced that he will decide on US participation in the Israel-Iran conflict within two weeks. The manufacturing index of the US Philadelphia Fed will be published later on Friday.
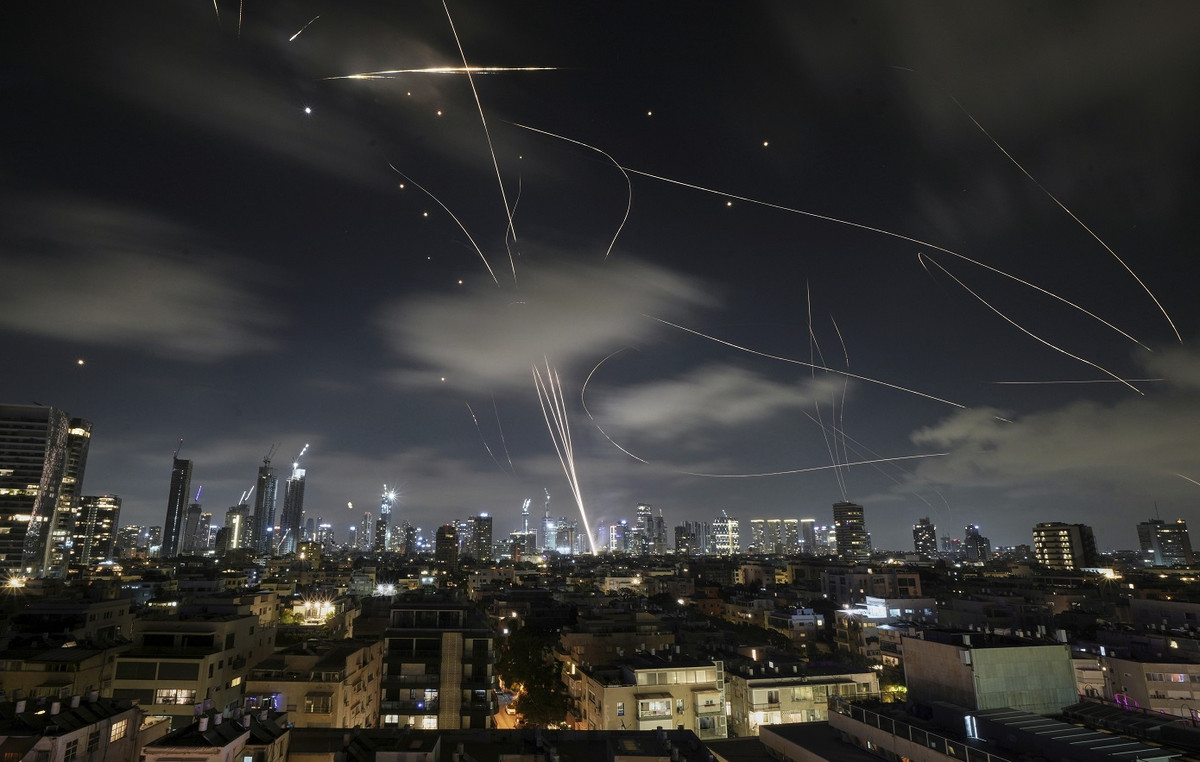
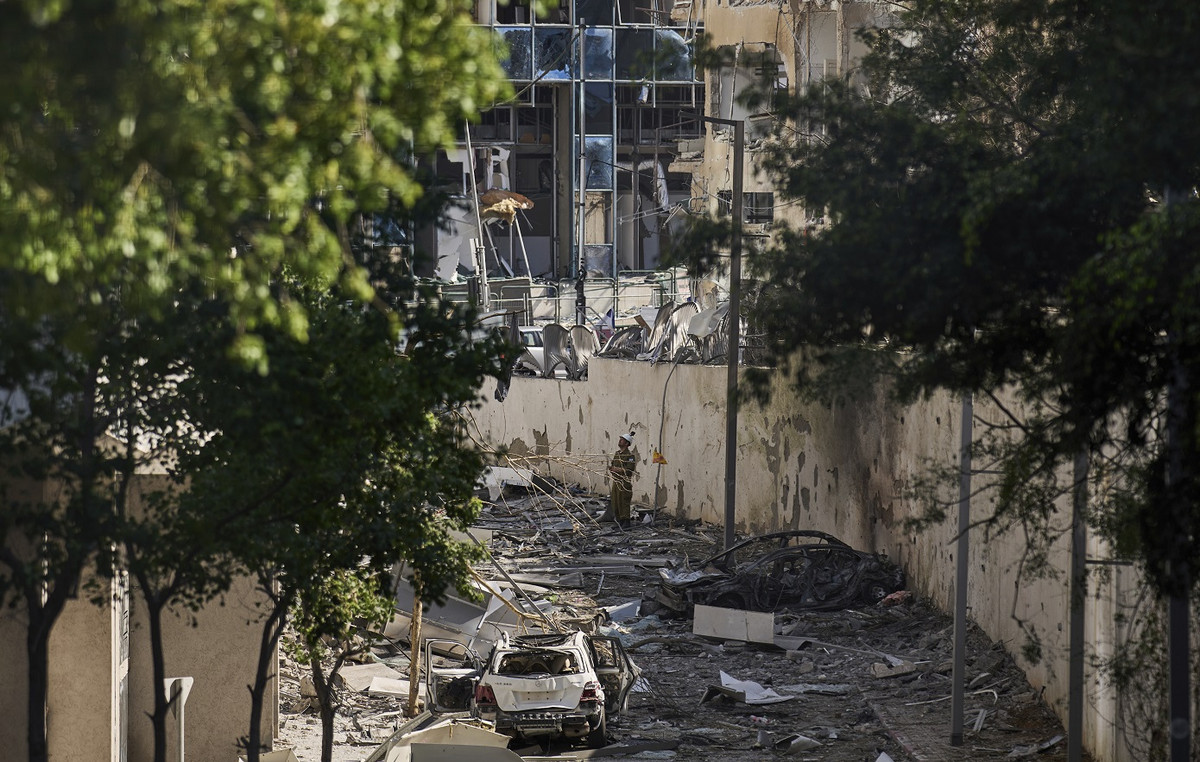
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu ordered the Armed Forces to intensify attacks on “strategic objectives” in Iran. His decision to climb the military operation against Iran occurs after an Iranian missile allegedly impacts an important hospital in the southern city of Beersheba.
However, the White House said late on Thursday that Trump would decide within two weeks if he orders an American attack on Iran’s nuclear program. His last position indicates a setback after a series of hard rhetoric, which raises the riskiest assets such as the Canadian dollar (CAD) and creates a wind against for the pair. Investors will be attentive to signs of whether the US will increase their participation in the conflict.
The US Federal Reserve (FED) decided to keep the stable interest rates at its June meeting on Wednesday. The US Central Bank pointed out a slower pace of cuts in the future amid the concern that Trump’s tariffs could increase consumer prices. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) hopes to make two rates cuts later this year, according to the “Point Graph”. The Fed hard line posture could provide some support to the dollar in the short term.
Meanwhile, a fall in crude oil prices could undermine the Loonie linked to raw materials. It is worth noting that Canada is the largest oil exporter to the US, and the lowest prices of crude oil tend to have a negative impact on the value of the CAD.
Canadian dollar faqs
The key factors that determine the contribution of the Canadian dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BOC), the price of oil, the main export product of Canada, the health of its economy, inflation and commercial balance, which is the difference between the value of Canadian exports and that of its imports. Other factors are market confidence, that is, if investors bet on riskier assets (Risk-on) or seek safe assets (Risk-Off), being the positive risk-on CAD. As its largest commercial partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor that influences the Canadian dollar.
The Canada Bank (BOC) exerts a significant influence on the Canadian dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can provide with each other. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main objective of the BOC is to maintain inflation between 1% and 3% by adjusting interest rates to the loss. Relatively high interest rates are usually positive for CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative relaxation and hardening to influence credit conditions, being the first refusal for CAD and the second positive for CAD.
The price of oil is a key factor that influences the value of the Canadian dollar. Oil is the largest export in Canada, so the price of oil tends to have an immediate impact on the value of the CAD. Generally, if the price of oil rises, the CAD also rises, since the aggregate demand of the currency increases. The opposite occurs if the price of oil drops. The highest prices of oil also tend to give rise to a greater probability of a positive commercial balance, which also supports the CAD.
Although traditionally it has always been considered that inflation is a negative factor for a currency, since it reduces the value of money, the opposite has actually happened in modern times, with the relaxation of cross -border capital controls. Higher inflation usually leads to central banks to raise interest rates, which attracts more capital of world investors who are looking for a lucrative place to save their money. This increases the demand for the local currency, which in the case of Canada is the Canadian dollar.
The published macroeconomic data measure the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian dollar. Indicators such as GDP, manufacturing and services PMIs, employment and consumer confidence surveys can influence the CAD direction. A strong economy is good for the Canadian dollar. Not only attracts more foreign investment, but it can encourage the Bank of Canada to raise interest rates, which translates into a stronger currency. However, if the economic data is weak, the CAD is likely to fall.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.