- The USD/JPY rises above 147.00 while investors look towards the publication of the US consumer price index on Tuesday.
- The US dollar remains firm in front of the Japanese Yen, considered safe refuge, since the yield differentials continue to support the strength of the USD/JPY.
- The impulse of the USD/JPY becomes bullish as the RSI rises to 64.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) remains at a disadvantage against the US dollar (USD) on Monday, since rate expectations and tariffs continue to drive feeling.
With the action of the USD/JPY price, heading towards the psychological level of 148.00 at the time of writing, the attention moves towards the publication of the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) on Tuesday on Tuesday
For the Bank of Japan (BOJ), the low interest rates of 0.5% have continued to drive funds to higher yields such as the US dollar.
As the Federal Reserve (FED) maintains rates within the current range of 4.25%-4.50%, performance differentials remain a prominent USD/JPY torque engine.
However, with the US president, Trump, intensifying criticism against the president of the FED, Jerome Powell, the attention is focused on the publication of the data of the consumer price index on Tuesday.
The CPI is expected to show a monthly increase of 0.3% in June, with the expected annual rate to rise to 2.7%, from 2.4% in May.
Meanwhile, it is expected that the underlying CPI figure, which excludes food and energy, also increases 0.3% intermensual, with the expected annual rate to increase to 3%, from 2.8% in May.
With the USD/JPy pair, remaining vulnerable to changes in rates expectations, Tuesday’s data are crucial for the next movement of the pair.
USD/JPY DAILY GRAPH
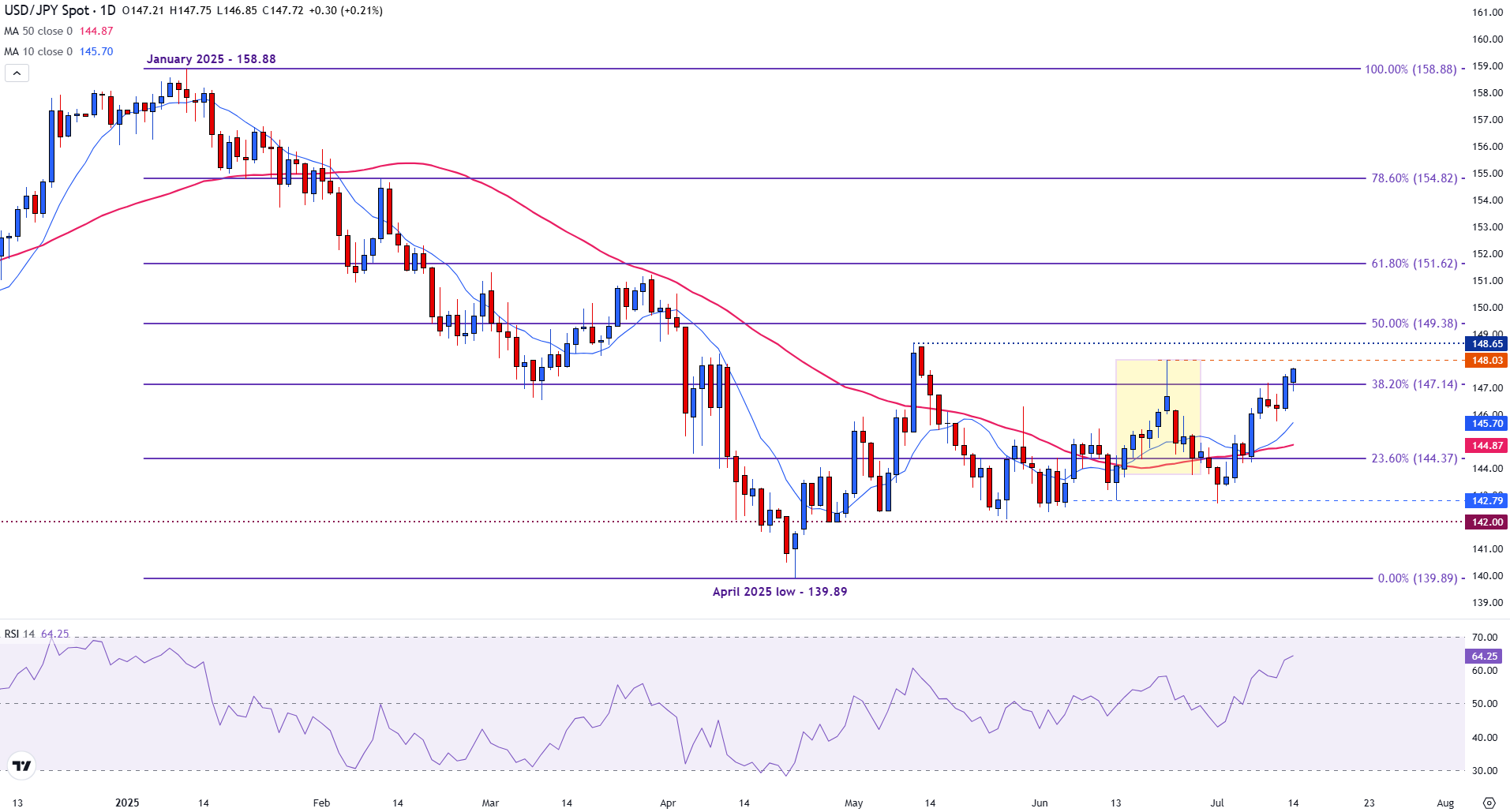
From a technical point of view, the USD/JPY continues to advance, with support emerging at the Fibonacci setback level of 38.2% of the fall from January to April in 147.14.
With the price action around 147.60 at the time of writing, the psychological resistance remains firm in 148.00. A clear break of this level could see the bullies try again the maximum of May 148.65, paving the path for the 50% fibo level in 149.38.
In contrast, below the 38.2% FIBO level is the level of psychological support of 146.00 and the simple mobile average (SMA) of 145.69. A break down could see bassists to gain confidence, allowing them to test the 50 -day SMA support level in 144.87.
With the relative force index (RSI) reading about 64 at the time of writing, the impulse is operating in favor of the bulls, pushing the torque closer to the overcompra territory.
US Dollar – Frequently Questions
The US dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation along with local tickets. According to data from 2022, it is the most negotiated currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency change operations, which is equivalent to an average of 6.6 billion dollars in daily transactions. After World War II, the USD took over the pound sterling as a world reserve currency.
The most important individual factor that influences the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% objective set by the Fed, it rises the types, which favors the price of the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and promulgate quantitative flexibility (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure that is used when the credit has been exhausted because banks do not lend each other (for fear of the default of the counterparts). It is the last resort when it is unlikely that a simple decrease in interest rates will achieve the necessary result. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed to combat the contraction of the credit that occurred during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy bonds of the US government, mainly of financial institutions. Which usually leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the reverse process for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the wallet values that overcome in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







