Lazarus Group is a group of hackers, presumably from the DPRK, whose activity can be coordinated by the authorities of North Korea. The group is known for many pseudonyms – in addition to “Lazarus Group” in different reports, you can find “Guardians of Peace”, “Whois Team”, “Dark Seoul”, “Hidden Cobra”, “Zinc” and others.
Quite often, Lazarus is used as a collective term uniting different clusters or subgroups, such as Andariel, Bluenoroff, Apt37, Apt38 and Kimsuky.
US authorities evaluate Lazarus as a “constant serious threat” in terms of cybersecurity typology. It is known that the FBI is looking for members of the group. In particular, the service published information about Pak Chin Heke, the existence of which the DPRK denies.

Pak Chin Hyk probably studied in Pyongyang and worked for some time in IT in China. The search card states that he is “a programmer sponsored by North Korea, whose hacker attacks led to theft of money from many victims,” and also that he is associated with APT 38. In addition to Pak, the FBI is allocated among the wanted John Hyok) and Kim Il (Kim Il).

The wanted hackers, according to the FBI, can be directly related to the hacking of Sony and the spread of the mercuris of Wannacry.
Attack on Sony
In 2014, Lazarus Group made a cyber attack on Sony Pictures, hacking the IT system of the company and using Windows vulnerability for large-scale data leakage. This was a kind of answer to the film “Interview”, in which the DPRK leader Kim Jong -un was satirically.
Hacking, discovered on November 24, was carried out for several months. Attackers managed to access, extract, and ultimately remove the wide range of confidential information from Sony servers, including private data of employees and unpublished films.
The incident caused a wide resonance – so much that Barack Obama, who at that time was the presidency of the United States, promised to take “decisive measures” in response. Most likely, the threat of Lazarus was political in nature. Here is an example of a message to the victim after hacking:

Attack on the Central Bank Bangladesh
The next major attack dates back to 2016, when Lazarus tried to steal almost $ 1 billion from the account of the Central Bank of Bangladesh in the US Federal Reserve. Hackers used malicious software for the SWIFT system and sent fake translation requests to the New York Federal Reserve Bank. Them succeeded To withdraw $ 81 million to accounts in the Philippines, but further transactions were stopped due to a random error in one of the requests that caused suspicion from the federal backup bank. This suggests that hackers possessed a rich experience in attacks on traditional financial systems, like Swift, even before BYBIT hacking.
Mass attack Wannacry
Although there is no unambiguous evidence of Lazarus involvement in Wannacry, the signatures of the virus code are similar to the signatures of the code of earlier codes used by the group. Wannacry was a robber virus who encrypted user data and required a ransom in bitcoins within three days from the date of infection. If the payment was not received on time, the amount of ransom was doubled. If the payment was not received within seven days, the user’s data was deleted.
The beginning of a mass attack was in May 2017. The interface of the Monk virus was as follows:
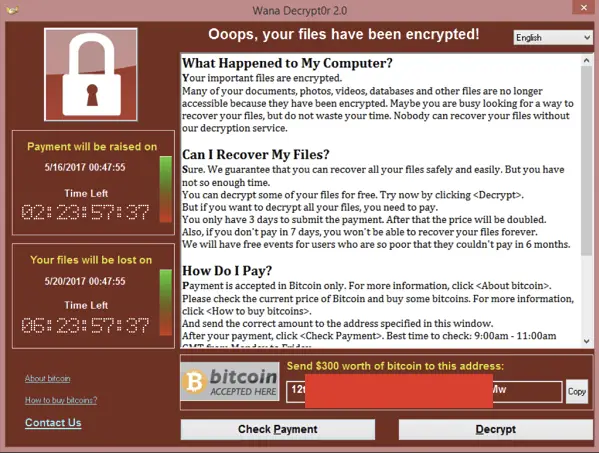
It is interesting that the hackers left a link to the special section “On Bitcoin” for users who first encountered payments in cryptocurrency. Hundreds of thousands of computers were injured from the virus, including devices that worked in banks, hospitals and airports.
Lazarus Group methods
Given the “track record” Lazarus Group, it is not surprising that the set of funds used by the group is extensive. The first attack attached to the group, which occurred in 2009 and was called Operation Troy, was a relatively simple DDOS-Atak against government websites in the USA and South Korea. But since then, Lazarus has significantly increased its arsenal of methods, and now among the main ones it can be called:
-
Zero-day vulnerability is vulnerability against which protection has been developed. The existence of such vulnerability becomes already known from the fact of the attack;
-
Social engineering – Lazarus Group actively uses phishing attacks, sending malicious letters and masking infected files for documents. For example, on behalf of the stand -up employers, they send to applicants infected files;
-
Malicious software and bacdors are also used by the group. So, in mid-March, it became known that Lazarus spreads the Beavertail harmful to the Node.js NPM packets for the stealing of accounting data and the deployment of permanent backdor. Hackers also created compromised libraries on the GitHub and Pypi developers.
Lazarus Group demonstrates the possession of a wide range of tools, and therefore poses a real danger to crypto-streaks and blockchain projects. Consider which particular exchanges, trading platforms and services were attacked by North Korean hackers.
Horizon Bridge
In June 2022, Lazarus Group hacked Horizon Bridge, stole $ 100 million in cryptocurrency. This has become one of the largest hacks in the Defi industry.
Like many other inter -grid bridges, Horizon Bridge has a procedure for validation of transactions conducted through the bridge. In this case, a multi -signature diagram with five validators was used, and two of them signatures were necessary to approve the transaction. That is, it was enough for the attacker to compromise only two accounts. This happened – according to the FBI, Lazarus Group hackers gained access to two closed keys necessary for approving transactions. Having received control, they withdrawn funds and pierced them through Tornado Cash.
After hacking the requirements for signing transactions in Horizon Bridge, increased to four out of five validators.
Axie Infinity
A similar incident occurred with the popular game Axie Infinity. The project stolen $ 615 million.
Ronin is an inter -grid bridge that works on Proof of Authority (POA) with nine validators. To confirm the transaction, the signatures of five of them were required. Lazarus did not look for vulnerabilities in the code, but gained access using social engineering methods. Four out of five validators were controlled by Sky Mavis, which also had access to the fifth belonging to Axie DAO.
According to the main version of the events, hackers used a fake work offer for an employee Sky Mavis, sending him a PDF file with a malicious code. This file gave the attacking point of entering the corporate network, after which they were able to obtain control over the validators of Sky Mavis and Axie DAO, which allowed to sign transactions and withdraw funds.
Bybit
In February 2025, the founder of the BYBIT crypto -tank Ben Zhou said that the trading platform was subjected to a hacker attack and lost about $ 1.4 billion from one cold wallet with a multi -signature.
A few days after the incident, the US Federal Bureau of Investigations confirmed the involvement in the Lazarus group incident. Hackers were able to replace the user interface and display 400,000 ETH. The famous blockchain analyst Zachxbt also paid attention to the attack.
BITHUMB and South Korean companies
Often under the sight of Lazarus are South Korean platforms. So, in 2017, hackers were able to steal about $ 7 million from the South Korean Exchange. Besides Bithumb, Lazarus victims at different times They became Both other cryptocurrencies, such as Youbit, and companies that are not related to a cryptot, including the media.
The later report of the Ciphertrace analytical company said that hackers used “cleansing addresses” to cover traces of theft, and even “laundered” stolen cryptocurrency through other centralized platforms (CEX), despite the availability of KYC user verification procedures.
Atomic Wallet
In 2023, mass reports of hacks of user versions of the Atomic Wallet cryptocide appeared. Unknowns brought the cryptocurrency from the victim’s wallet to the new address. The ZACHXBT also also managed to pay attention to suspicious activity. A few days later, stolen funds began to enter services related to Lazarus.
This is far from the only case of an attack on the cryptocurrents. For example, just recently, in early March 2025, the Socket Research group said that Lazarus conducts a new cyberataka aimed at vulnerability of the SOLANA and Exodus cryptocurrencies through fake NPM packets.
Conclusion
Lazarus is one of the largest groups in the world of cybercrime. She pushes a serious threat to crypto, making large -scale attacks on the largest players. At the same time, Lazarus operates with a wide range of methods and techniques for cyber attacks, therefore it is extremely problematic to determine a specific pattern, against which it would be possible to build a defense strategy.
Source: Bits
I am an experienced journalist, writer, and editor with a passion for finance and business news. I have been working in the journalism field for over 6 years, covering a variety of topics from finance to technology. As an author at World Stock Market, I specialize in finance business-related topics.







