In 2020, Qualcomm lost the top spot in mobile processor market share to MediaTek for the first time. Despite this and some mistakes in recent years, Snapdragon chips continue to be trusted. But which model to choose today, when the number of presented models goes off scale, and the rule “the larger the numerical index of the chipset, the cooler it is” does not always work. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the Snapdragon typology and identifies the best representatives of each of the lineups with a description of the key features – it also has a side-by-side comparison of the Snapdragon of each line.
What is really important for a mobile chip
First of all, a few words about terminology. The part of a smartphone responsible for performance is traditionally called the processor. In fact, on one chip of any Snapdragon chip there is not only a processor, but also a video core, a modem, all the necessary controllers, as well as many other auxiliary components. Their unity forms a single-chip system (from the English System-on-a-Chip – SoC) or a chipset. Knowing the power of habit, I don’t hate the word “processor”, but it is necessary to understand the difference and remember this important nuance.
That is why the characteristics of a single-chip are not limited to the number of cores and their clock frequency. However, it is unlikely that it will be possible to understand all the nuances right off the bat, so we will concentrate on the main thing.
Characteristics of processors that you should pay attention to when buying a device:
- Process technology: chipset manufacturing technology, characterized by the resolution of the equipment used in the production of processors. Ceteris paribus, the thinner the process technology – fewer nanometers (nm), the more economical and colder the chip turns out.
- Number and composition of processor cores: the more cores the better, but not always. It’s all about the composition and generation of nuclei. Energy-efficient Cortex-A5X, high-performance Cortex-A7X and mega-performance Cortex-XX can be combined in different ways, and it will depend on this performance, efficiency of distribution of tasks and, as a result, the final economy. Qualcomm uses its own slightly modified Kryo cores based on Cortex in most situations. That is why this article will also give the name of the original Cortex architecture.
- Core clock speed: again, the higher the frequency, the better, but only when comparing cores of the same architecture. Depending on the load I of each core, there may be a different current frequency, the comparative table indicates the maximum for each of the clusters.
- Graphics accelerator: in other words, it is a smartphone video card integrated into a single-chip system. Qualcomm traditionally uses its own Adreno series accelerators and rarely shares technical details. Fortunately, a clear numbering helps to navigate: the larger the numerical index of the GPU, the better the content.
- DSP digital signal processor: Without getting into hard-to-understand definitions, a DSP is a cost-effective custom chip for processing sound and sensor data. Snapdragon chips use their own Hexagon series DSPs, so the logic “the higher the numerical index, the cooler” is relevant here too. Also, any chip has other coprocessors (ISP and NPU) for processing images, photos and videos from the camera, as well as calculations using neural networks.
- Modem: in most cases, a single-chip system is responsible for the network capabilities of smartphones. At least Qualcomm equips its chips with branded modems. And even though smartphone manufacturers for each model can somehow cut specific network interfaces, their quality of work still depends on the base.
For clarity, each chip in the plates will be marked with colors depending on its relevance.
🟢 – a good modern representative of the series;
🟡 – an average, which is still relevant, but is not the best choice;
🔴 – even if it is a popular, but for various reasons, suboptimal model.
Snapdragon 6 is the entry ticket to the world of Qualcomm
Once the Snapdragon 600 was the flagship, then the series was reformatted into the middle one, and now it de facto occupies the basic positions.
An exception may be Snapdragon 695 and Snapdragon 690, which gravitate towards the middle segment and can even compete with slightly outdated 7-series chips due to the layout of 2 + 6 cores and a thin technical process. Qualcomm’s base chip today is Snapdragon 680used in smartphones for about 20 thousand rubles. It cannot be called very productive, since the already outdated Cortex-A73 and Cortex-A53 cores operate at low frequencies, and the Adreno 610 accelerator is unlikely to launch AAA projects with good graphics. The chip is in a thin 6 nm process technology, with which, with such power, you can forget about heating.
Snapdragon 678, 675 and 670 deserve attention only in a very inexpensive segment, but in fact there are not many smartphones based on them. Yes, they use a more advanced architecture of Cortex cores, more powerful graphics and better modems. But the outdated process technology thicker than 10 nm hides performance over a long distance. Consider Snapdragon 665 and older chips are not worth it at all, because they combine a thick manufacturing process with outdated cores.
Snapdragon 7 is a decent mid-ranger
In 2018, the Snapdragon 700 series was announced, taking a place one step below the flagship Snapdragon 800 chips.
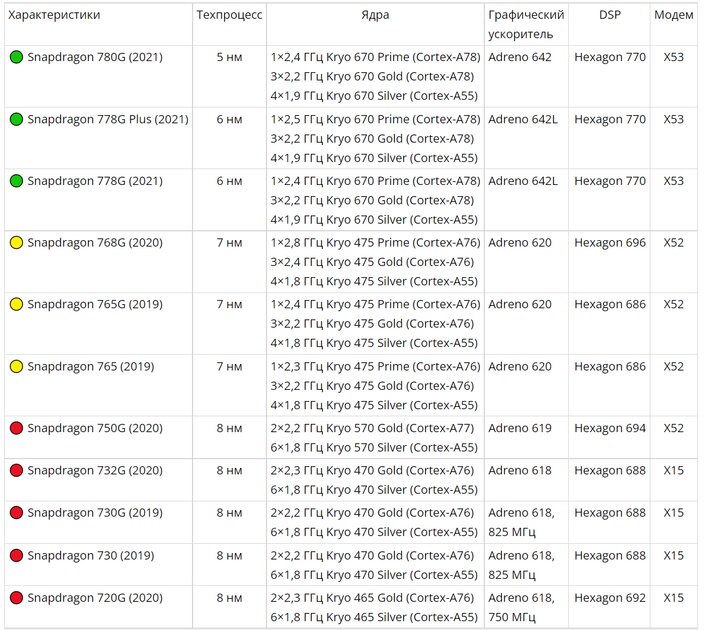
Snapdragon 780G, 778G Plus and 778G are relevant chips for sub-flagships: fresh and productive, on a thin technical process – they will be at the top of performance for a couple of years.
💡Some 7-series models have a G-version: thus Qualcomm labels special editions more adapted to mobile gaming. They are distinguished by increased frequencies of the video core, and sometimes the processor.
The rest of the 2020 and 2019 lineup has a lot of monotonous chips from Snapdragon 720G to Snapdragon 750G, some of which are not even widely used. However, all of them, as well as the Snapdragon 765 (G), take the place of the middle peasants and compete with the Snapdragon 690 and Snapdragon 695. As a result, I recommend buying them if the selected smartphone has better specifications or a more attractive price.
Snapdragon 8 – and to this day the standard
When you need an uncompromising chip, but do not want to understand the nuances, you should take the Snapdragon 8-series. They have the best modems, the best DSPs, a guarantee of high performance with a margin of safety for several years to come.
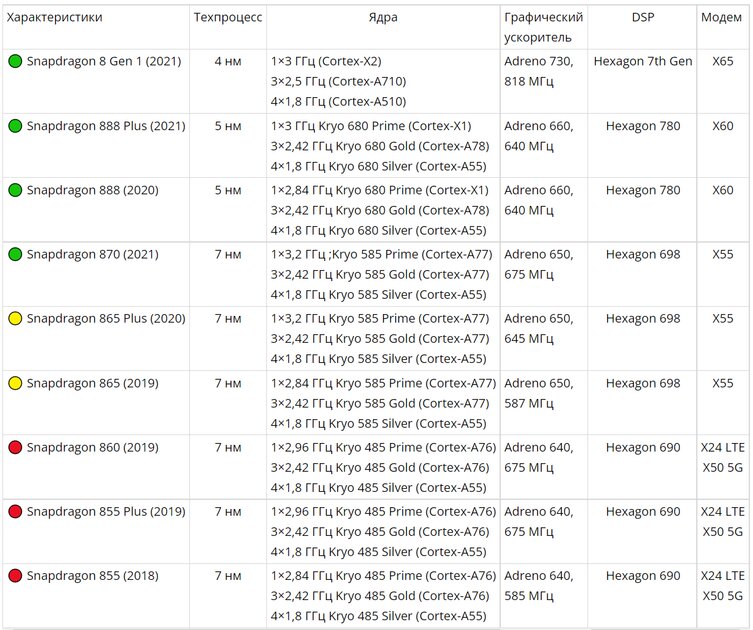
However, all innovations are tested on Qualcomm flagships, which sometimes leads to the appearance of unsuccessful single-crystals. This is exactly what happened at the very end of 2020, when it was announced Snapdragon 888and a bit later overclocked Snapdragon 888 Plus. They use a fundamentally new core layout with one mega-performance Cortex-X1 core for super-heavy tasks. It forms a true third cluster instead of a single overclocked Cortex-A7X core in previous models. The chips are certainly productive, but hot. Without exception, all smartphones based on them heat up, and stability and throttling (decrease in performance due to overheating) float from model to model. The chip is generally good, but it requires you to be careful when choosing a particular smartphone.
💡Some models of the 8-series have a Plus version, slightly higher clock speeds. Such single-chip chips often form the basis of gaming smartphones with a good cooling system.
his follower Snapdragon 8 Gen1 switched to a new numbering principle, received a thinner process technology, a new Cortex-A710 and Cortex-A510 architecture, graphics and a modem – pure performance has become even higher. But Qualcomm has not yet been able to curb the mega-efficient Cortex-X core – the above problems have remained unresolved, check every smartphone you like for throttling.
That is why anyone who is looking for a stable flagship chip should pay attention to Snapdragon 870 – the latest SoC, tailored according to proven patterns over the years. Hence, a slightly lower peak, but consistently high performance and the complete absence of problems with throttling and overheating. It, as a rule, is received by sub-flagships of the last two years. Remain relevant Snapdragon 865 and Snapdragon 865 Pluswhich differ from the 870th model only in lower frequencies.
Pay attention to Snapdragon 860, Snapdragon 855, its Plus version and earlier models are no longer followed. After all, modern Snapdragon 7 is comparable to them in performance with better energy efficiency.
Which Snapdragon chips should not be taken
Those who follow and follow the mobile market will remember the Qualcomm Snapdragon 200-series, which previously occupied the ultra-budget segment. This line has not been updated since 2019 and has de facto exhausted itself. With Snapdragon 400 chips, the situation is more interesting. At the beginning of 2021 was introduced Snapdragon 480, and a little later its Plus version. They are eight-core, contain two clusters and in some places are ahead of the Snapdragon 680, but they have not yet found popularity, so there are no real reviews.
Snapdragon Mobile Platforms for Notebooks
Among other things, Qualcomm has been producing chips for ARM laptops on Windows for several years. They are comparable to their smartphone counterparts of the same age, but adapted for use on a desktop system. Comparative tables and recommendations will not be given due to the lack of practical experience – ARM laptops are still not very common.
Source: Trash Box
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.







