When a computer running Windows 10 is left unattended, it goes into one of the low power consumption modes. It’s about “Sleep” and “Hibernation”. Both can be activated automatically as well as manually from the operating system power control menu. Let’s discuss their differences.
What are the differences between the “Sleep” and “Hibernation” modes
Many Windows 10 users equate “Sleep” with “Hibernation”. There are indeed obvious similarities between these operating system modes for low computer power consumption. They differ, first of all, in the type of information stored, as well as in the way the data is stored.
Retention of information
- “Sleep” – open files, along with unsaved data in them, are saved in RAM.
- “Hibernation” – open files, as well as data that you did not manage to save, are written to disk.
Power consumption
- “Sleep” – the computer in this mode consumes very little power.
- “Hibernation” – in this mode, power consumption is reduced to zero, and the system actually turns off.
Mode availability
- “Sleep” – this mode of operation of the Windows 10 operating system is available on absolutely all computers.
- “Hibernation” – it is not available on all computers under the control of Windows 10. For example, if the system uses InstantGo (special sleep mode while maintaining the Internet connection), the specified mode will not be in it. Moreover, energy saving with its help can be trivially turned off by default.
Damage to SSD
- “Sleep” – within this mode, solid-state drives cannot be damaged, their service life will not be reduced.
- Hibernate – This mode is known to shorten the lifespan of early SSDs. However, newer SSDs are not so susceptible to this misunderstanding.
HDD damage
Neither “Sleep” nor “Hibernation” can negatively affect the useful time of the hard drive or unexpectedly damage it.
Indicator activity
- “Sleep” – in this mode, hardware indicators of the computer, if any, can show the operation of the drive, as well as other signs of activity.
- “Hibernation” – any hardware indicators in this case will be inactive. When looking at a computer, it will be impossible to understand whether it is currently running or turned off.
Getting started
- “Sleep” – this mode is characterized by the fastest transition to use after a pause.
- “Hibernation” – the Windows 10 operating system comes out of this mode for a long time.
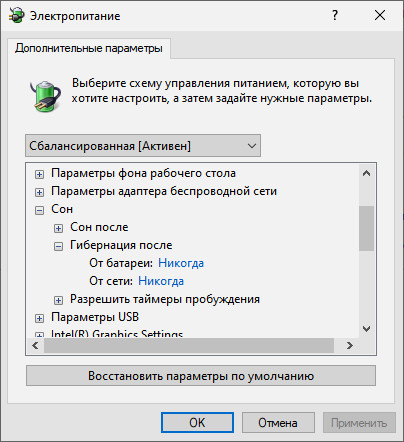
Exiting the mode
- “Sleep” – you can get out of it using the power key, any button on the keyboard or mouse.
- “Hibernation” – you can wake up the computer from this mode only with the power key.
When to use “Sleep” and when “Hibernation”
Since the Sleep and Hibernation modes are often available on the same system, the user has a choice. Usually “Sleep” is recommended when you need to take a short period of work with the computer lasting from 15 minutes to one hour. As for “Hibernation”, then it is included when a long period of use of Windows 10 is planned. After the resumption of use in this case, the work of absolutely all active software will continue from the same place at which the pause was taken – this is how “Hibernation” differs from turning off the computer.
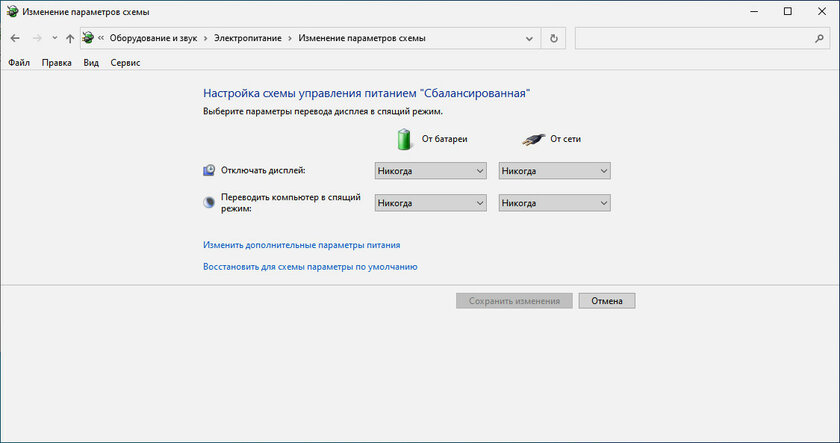
“Hibernation” is not used by everyone only because the average computer comes out of it for a long time. That is why, for a long period of using Windows 10, many people simply turn off the machine. During the activation of this process, users are prompted to save all open files, so there is no need to worry about losing data. Moreover, turning on the computer in time is comparable to its exit from the “Hibernation” mode, so not everyone wants to bother with it. The only thing is that after shutting down and starting the system, all applications will have to be launched again.
Windows 10 also has a special “Hybrid Sleep”. It is a cross between the traditional “Sleep” and “Hibernation”. Within its framework, the data that is necessary to continue working is written to disk, and not stored in RAM. However, they are periodically updated when needed. The computer enters active from “Hybrid Sleep” faster than from “Hibernation”, but slower than from “Sleep”. When Windows 10 is in the specified state, the operating system continues to consume power, but it does so at a slower pace than in Sleep mode.
When choosing between “Sleep” and “Hibernation”, users are usually guided by the performance of the computer. If he is very fast and quite nimble with the “Hibernation” mode, then it can be actively used. Otherwise, it is better to give preference to the traditional “Sleep”.
A source: AddictiveTips.
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.





.jpg)
