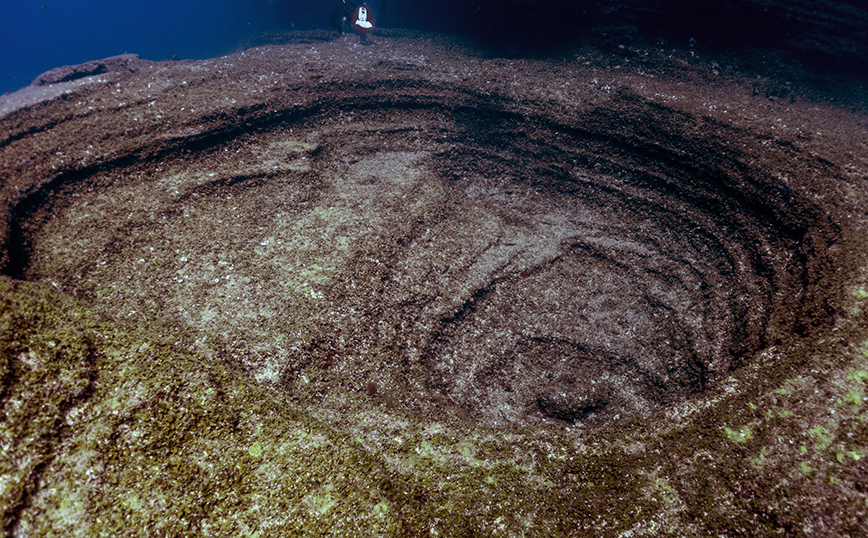
Solid evidence for the existence of a possible large submarine crater impact asteroid off the West coast Africa have British and American scientists. Their discovery came through analysis of seismic data.
The researchers, led by assistant professor of geosciences Wisdin Nicholson of Scotland’s Heriot-Watt University, who made the relevant publication in the journal “Science Advances”, estimate that the crater has a similar age of 66 million years to the famous and much larger 200-diameter Chicxulub crater. km in the Gulf of Mexico. Chicxulub has been linked to the fall of a large asteroid 10 to 12 km in diameter that led to the flightless mass extinction dinosaurs (as well as three-quarters of all plant and animal species) at the end of the geological Cretaceous Period.
Nadir is located at a distance of about 400 km from the coast of Guinea
Nadir – as the African crater with a diameter of at least 8.5 kilometers was named – is buried under sediments 300 to 400 meters thick on the seabed, at a sea depth of 900 meters, about 400 km off the coast of Guinea in West Africa. Scientists do not rule out that the two craters – Chixulub and Nadir – are connected.
If it is confirmed that Nadir was created by an asteroid impact, the researchers, as reported by the Athens News Agency, consider it possible that there was originally a larger parent asteroid, which upon falling to Earth it broke up in the atmosphere into smaller pieces large enough to cause cataclysmic disasters. Alternatively, there may have originally been two separate asteroids – or more whose craters have not yet been found – that fell within close proximity of each other.
Seismic analysis and subsequent modeling lead to an estimate that the asteroid had a diameter of about 400 meters and would have fallen – with a force equivalent to a 5,000 megaton TNT explosion – into a sea that would have been 800 meters deep, successively causing a huge tsunami up to a kilometer high, an earthquake of 6.5 to 7 degrees and possibly releasing significant amounts of greenhouse gases from seabed carbon deposits.
Source: News Beast
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.