In July, Russian scientists came up with a new way to record and reproduce sound that creates real sound, deprived some types of bacteria of the ability to reproduce using infrared lasers, came up with an unusual thermal control system for small satellites, created a generator for obtaining drinking water from atmospheric air, and discovered a new effect for creation of new generation superconducting diodes.
💡 This is a material from the “Made in Russia 🇬🇺” cycle, which describes the main domestic inventions, as well as important events in various fields of science and industry in Russia.
The Future of Sound Recording: Holographic Recording and Sound Reproduction
💡 In simple words
At Moscow State University, they found a way to move away from existing stereo sound creation systems, which only create the illusion of surround sound, by inventing holographic sound recording. Thanks to a system of hundreds of microphones and speakers, sound waves will be recorded and reproduced as identical to reality as possible. In fact, people will hear the actual sound, not the effect. The author is sure that a new stage will begin in cinematography, on television and radio, when stereo sound will be replaced by holographic sound, as stereo sound replaced mono sound in its time.
👨🔬 Detail
The first sound recording device was invented by Thomas Edison in 1877. The phonograph recorded the mechanical vibrations of the microphone membrane by cutting grooves on the sound carrier (foil on the cylinder) with a special needle. During playback, the sound was not loud enough, and the sound carriers wore out quickly. However, technology has improved. Soon there were gramophones with records, tape cassettes, and then the digital age came. Modern sound recording and playback systems solve almost all problems (quality, loudness, durability), except for one – surround sound. Of course, stereo sound, quad sound, surround sound, sound dome, immersion, and the like use the binaural effect that occurs when sound is perceived with two ears, creating the illusion of real sound. In fact, this is a deception of human hearing, just as in the case of stereo glasses, which create a pseudo-three-dimensional image.
Aleksey Osokin, Ph.D. (Physics and Mathematics), an employee of the Moscow University Development Program, received a patent for a completely new sound recording system that allows you to restore the appearance of a sound wave in space exactly as it comes from a real source. The idea is to record hundreds of small microphones at the same time, tightly packed together. Each of them will fix the sum of sound waves coming to a specific point. The playback system should consist of the same number of small speakers. Neighboring speakers will also transmit vibrations corresponding to neighboring microphones, which are different because the sound reaches each of them at different times. The interference of waves created by the speakers will restore the front of the wave incident on the platform with microphones as accurately as possible, which is the Huygens principle. In this case, the sound will be perceived regardless of the characteristics of the listener.
Found a way to destroy pathogenic bacteria with a laser

💡 In simple words
Scientists have found that the light of infrared lasers is able to deprive bacteria of activity and the ability to reproduce (the experiment was carried out on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) no worse than existing disinfection methods, but without harming a person. This method can be used in medicine and industry for the treatment of instruments, surfaces and wounds. And in the future there is the prospect of creating a portable infrared disinfectant.
👨🔬 Detail
The widespread use of antibiotics has led to the fact that today the proportion of microorganisms resistant to them is growing in the world. Antibacterial agents are becoming less and less effective, so the search for other methods of disinfection becomes relevant. One of these is the use of chemical disinfectants that destroy the superstructure of proteins and other major components of the cell wall, disrupting cellular metabolism. However, they also affect human cells in the same way, so they can only be used in rare scenarios. Also, ultraviolet irradiation is used to solve the problem of microorganism resistance. It leads to photolytic or photochemical damage to cell molecules and destroys DNA. However, this can lead to mutations. Mammalian DNA is also susceptible to this effect (for example, melanoma can develop in humans due to UV exposure).
Scientists from the P.N. Lebedev RAS decided to use mid-infrared lasers to break hydrogen bonds in the molecules of proteins and nucleic acids of bacteria, from which they lose their activity and ability to reproduce. The researchers placed Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria on a 1-millimeter thick calcium fluoride substrate and irradiated them with 3 and 6 micron femtosecond mid-IR laser pulses. These wavelengths correspond to the vibration frequencies of the amide groups of proteins and nucleic acids (6 microns) and C-H vibrations of the carbon skeleton, the most common bond for all biopolymers (3 microns). The pulse duration was 130 femtoseconds, the pulse energy was up to 4 microjoules, and the frequency was 1 kilohertz. For both bacterial cultures, the spectra showed a blue spectral shift and clearing of the samples in the spectral range of characteristic vibrations of C-N bonds (comprised of proteins and nucleic acids) and CH (the most common bonds in all biopolymers), which means the breaking of hydrogen bonds. Thus, irradiation inactivates microorganisms, destroying the vital structural units of a bacterial cell: DNA, RNA, proteins and the cell wall.
Laser disinfection technology can be used in medicine to sterilize instruments and treat wounds, even deep wounds, as well as to treat malignant tumors, since mid-IR radiation can penetrate deep into the body and does not have mutagenic properties. It is also applicable in the food industry for non-contact disinfection of products through transparent packaging. And if it comes to the creation of portable infrared disinfectants, then everyone can treat rooms, tools and wounds at home.
Developed a thermal control system for small satellites
💡 In simple words
Roskosmos has come up with a thermoregulatory “scale” of mechanical action, which will protect the equipment of microsatellites in Earth orbit from overheating without the cost of electricity and external control. Tests of the first samples are planned to be carried out on the ISS.
👨🔬 Detail
At the moment, small spacecraft are mainly launched into low orbits with a short period of revolution around the Earth. This means that they are practically not subject to either hypothermia in the planet’s shadow or overheating on the sunny side. However, when moving to higher orbits or simply reducing the size of satellites in the future, the problem of insufficient heat capacity of vehicles is very acute. To solve it, the Russian Space Systems holding (part of Roscosmos) has developed an adaptive microsatellite thermal control system built on the principle of scales. It has small weight and size characteristics and does not require power supply. The mechanism of its operation is based on the technology of micromechanical systems with moving elements. The materials used are thermomechanical polyimide-silicon actuators (an active element that converts one type of energy into another), on which reflective elements are attached. Depending on the intensity of solar radiation, the reflective coating of the satellite automatically changes shape (the plates rotate), protecting the spacecraft equipment from overheating without the cost of electricity and external control.
Developed a generator to produce clean drinking water from the air

💡 In simple words
The hydropanel is an autonomous generator of clean drinking water from atmospheric air. In any place where there is sunlight, and the air humidity is more than 5% (that is, almost everywhere on Earth), you can get water, which is important not only for some regions of Russia, but also for countries in Africa, the Middle East, and so on. The device can operate both autonomously from solar panels and from a network for industrial production of drinking water.
👨🔬 Detail
A team of Russian scientists and engineers led by Candidate of Chemical Sciences Ilya Menshchikov from the Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry. A. N. Frumkin of the Russian Academy of Sciences, which became the winner of the fourth season of the presidential competition of managers “Leaders of Russia”, created a unique sorption generator of atmospheric water – a hydropanel. With its help, you can get the purest drinking water from atmospheric air. The device is completely self-contained, compact and suitable for domestic use with minimal air humidity (more than 5%). The principle of operation is quite simple: the adsorbent installed in the hydropanel absorbs moisture from the air at night. During the day, the device receives energy from the sun’s rays thanks to a special selective screen. The process of evaporation of moisture from the adsorbent begins, and then condensation into a liquid state occurs. Thus, from one square meter of the hydropanel, up to four liters of water of the highest quality can be obtained per day. The device fits perfectly into the concept of a smart eco-house, and can also be useful in places with problematic access to drinking water (for example, in Africa). The hydropanel surpasses the only analogue (produced in the USA) in key parameters (dimensions, performance, cost, air humidity threshold). Parts production and assembly are scheduled for 2023.
Discovered a new effect that will help in the development of energy-efficient electronics
💡 In simple words
In Vladivostok, scientists have discovered a fieldless superconducting diode effect (SDE) in thin-film multilayer systems. Thanks to this, it is already possible to produce energy-efficient electronics for spacecraft now, and in the future – non-volatile memory devices, logic elements, and so on.
👨🔬 Detail
Ordinary semiconductor diodes have electrical resistance. In addition, it grows with decreasing temperature, which leads to strong energy losses. One solution to this problem would be to use superconducting diodes, which have zero electrical resistance in a certain current direction. However, their operation requires an external magnetic field, which creates a new problem. Scientists from the Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU), together with foreign colleagues, have proposed using mirror symmetry breaking with respect to spatial inversion when creating a superconducting diode. They took a multilayer system in the form of a microwire of superconducting niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta) and vanadium (V) and cobalt (Co) ferromagnet. It turned out that by changing the direction of the magnetization of the Co layer and the polarity of the applied current, the scientists were able to control the current density.
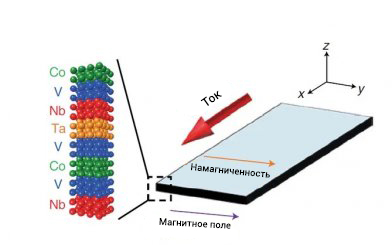
Thus, the superconducting diode effect manifested itself in the state when there were no external influences by a magnetic field, and the direction of the effect was controlled by changing the direction of the magnetization of the ferromagnet layer. The very mechanism of control of SDE magnetism for scientists has not yet been clear, but in practice the method can already be applied in electronics and electrical engineering. True, as FEFU Vice-Rector for Research Alexander Samardak noted, at the moment there is still a threshold for operating temperatures. Therefore, breakthroughs in consumer electronics should not be expected yet, but the method is suitable for electronic components of spacecraft. This research work was carried out as part of the Priority 2030 program.
Source: Trash Box
Donald-43Westbrook, a distinguished contributor at worldstockmarket, is celebrated for his exceptional prowess in article writing. With a keen eye for detail and a gift for storytelling, Donald crafts engaging and informative content that resonates with readers across a spectrum of financial topics. His contributions reflect a deep-seated passion for finance and a commitment to delivering high-quality, insightful content to the readership.







