Specialists from QLU, which develops ultrasensitive magnetic sensors, together with scientists from the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology and a number of other universities, have successfully completed laboratory tests of a new type of sensor for the analysis of magnetic nanoparticles. During the tests, the researchers were able to visualize the signal in test tubes and in the tissues of living organisms. The work was published on the ResearchGate portal.
Imaging methods of living organisms are used to diagnose various diseases. They are divided into magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT) and others. The first two are the most informative and are widely used in medical institutions, but they have drawbacks. For example, the large dimensions of the equipment and the high cost, as well as the complexity of use.
As an alternative, devices based on ultrasensitive magnetometers are used. They register signals from contrast agents that are introduced into the circulatory system, distributed in the body and serve as markers. The advantage of this imaging method is that it allows you to quickly and efficiently assess the intensity of blood flow, detect tumor nodes on a scale of tens of thousands of cells, and areas of tissue ischemia.
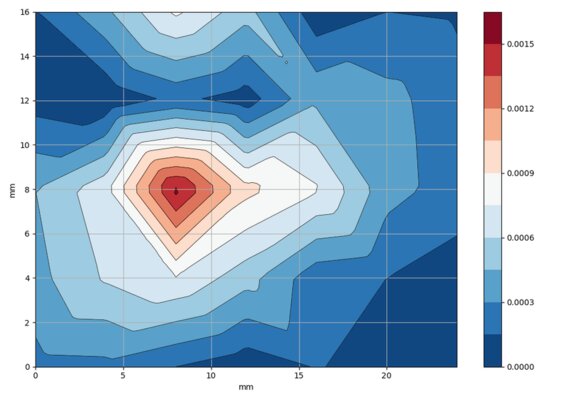
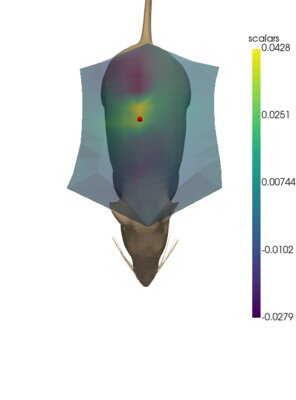
Russian scientists used this method to evaluate the distribution of nanoparticles in the body of laboratory mice after injection. They were the first to use a new yttrium iron garnet microfilm sensor with an optical signal detection system. The results of the study showed that the sensor effectively registers the magnetization of nanoparticles both in the test tube and introduced into the body of laboratory mice. Experts believe that in the future it will be possible to create an inexpensive system for diagnosing diseases, including oncology at earlier stages.
Source: Trash Box
Charles Grill is a tech-savvy writer with over 3 years of experience in the field. He writes on a variety of technology-related topics and has a strong focus on the latest advancements in the industry. He is connected with several online news websites and is currently contributing to a technology-focused platform.







