- The Dow Jones leaned to the downside, falling 300 points.
- Exhaustion plays are on the cards with indices deep in overbought territory.
- Despite a cut at the top, the Dow is on track for another record month.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) retreated on Wednesday, losing around 300 points and falling below the 42,000 area, as the main stock index takes a pause after a period of repeated breaks into record territory.
Treasury yields rose on Wednesday and most US indices are testing red, with the Dow Jones bearing the brunt of the damage, falling 0.8% during the US trading session. Market focus is now shifting back to the state of the US economy following the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) 50 basis point rate cut last week.
US consumer confidence indicators fell this week as the average US consumer does not share the stock market’s enthusiasm for the Fed’s rate cuts, with key sentiment readings falling to their lowest levels in three years and consumer inflation expectations for the next 12 months rising. Friday will see a further update of the US Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index inflation figures.
New home sales also fell in August, declining 4.7% to 716K from the previous month’s revised 751K. Meanwhile, investors will see another release of US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth for the second quarter, which is expected to hold steady at an annualized 3.0%. Thursday will also bring a series of speeches and public appearances from several Fed officials, including Fed Chair Jerome Powell.
Dow Jones News
The majority of the Dow Jones Industrial Average was tilted into the red on Wednesday, with about two-thirds of the stock board down on the day. Intel (INTC) still managed to extend a short-term rally, rising another 2.5% to $23.40 per share, but the chipmaker is still down more than 53% year-to-date.
Amgen (AMGN) fell nearly 5% on Wednesday, dragging the broader Dow lower and dropping below $315 a share for the second time since early August. The pharmaceutical company’s recent exploration into a new eczema drug called rocatinlimab yielded results that failed to meet efficacy expectations and also underperformed competitors’ products that already exist to treat atopic dermatitis.
Dow Jones Price Forecast
Wednesday’s bearish performance for the Dow Jones puts the index at risk of closing in the red for the week as overexerted buyers run out of gas and give short squeeze a chance to build back up. However, despite a short-term pullback, the index is still firmly planted on the long side of the trend, and a build-up of short positions could lead to a rally back into record territory on the chart.
If the bears win the short-term battle, the Dow Jones could retreat to the 50-day exponential moving average (EMA) near 40,800.
Dow Jones daily chart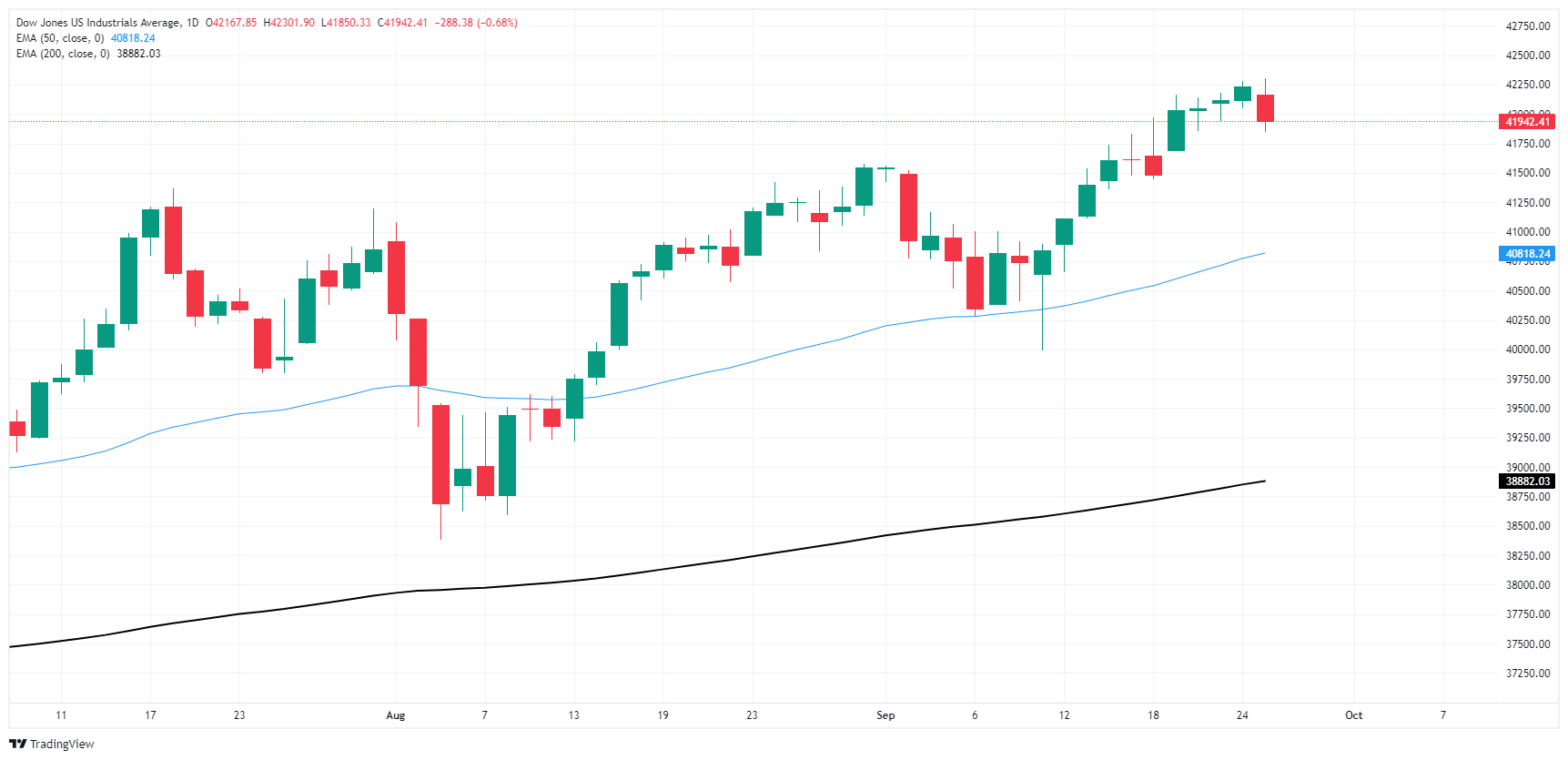
The Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the United States is directed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and to promote full employment. Its main tool for achieving these goals is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This translates into a strengthening of the US Dollar (USD), as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight meetings a year, at which the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC consists of twelve Federal Reserve officials: the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the eleven regional Reserve bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit into a jammed financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008. It involves the Fed printing more dollars and using them to buy high-quality bonds from financial institutions. QE typically weakens the US dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the capital of maturing bonds in its portfolio to buy new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.







