- The US dollar quotes quite contained after more comments on tariffs of the US president, Donald Trump
- A 25% tariff will be applied to all imports of steel and aluminum from all countries.
- The dollar index (DXY) does not advance and quotes around 108.00.
The dollar (DXY) index, which tracks the performance of the US dollar compared to six main currencies, is in general or slightly weaker and quotes around 108.00 at the time of writing this article on Monday, after a weekend full of headlines. The president of the United States, Donald Trump, announced 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum for all countries that import the US USA to match taxes imposed by other commercial partners of the country.
Apart from the headlines on tariffs, it will be a very quiet beginning of the week in the economic calendar. The operators will want to focus on the semiannual testimony of the president of the Federal Reserve (FED), Jerome Powell, in Capitol Hill on Tuesday and Wednesday. The operators will seek new clues on the way to follow for the monetary policy of the US, while Powell will probably highlight the resilient economy as a key reason why central bankers are not in a hurry to further reduce indebted costs.
What moves the market today: without clear projections
- Apart from the headlines of the US president, Donald Trump, on reciprocal tariffs and tariffs on the import of steel and aluminum, no real deadlines or dates were given, reports Bloomberg.
- The US Treasury is auctioning a 3 months and another 6 months at 4:30 p.m.
- The actions are not impressed by President Trump’s announcement about more tariffs. All main indices are quoting green on Monday.
- The CME Fedwatch tool projects a 93.5% probability that the Fed maintain interest rates without changes in its next meeting on March 19.
- The 10 -year performance of the United States trades around 4.49%, recovering even more than its new annual minimum of 4.40% registered last week.
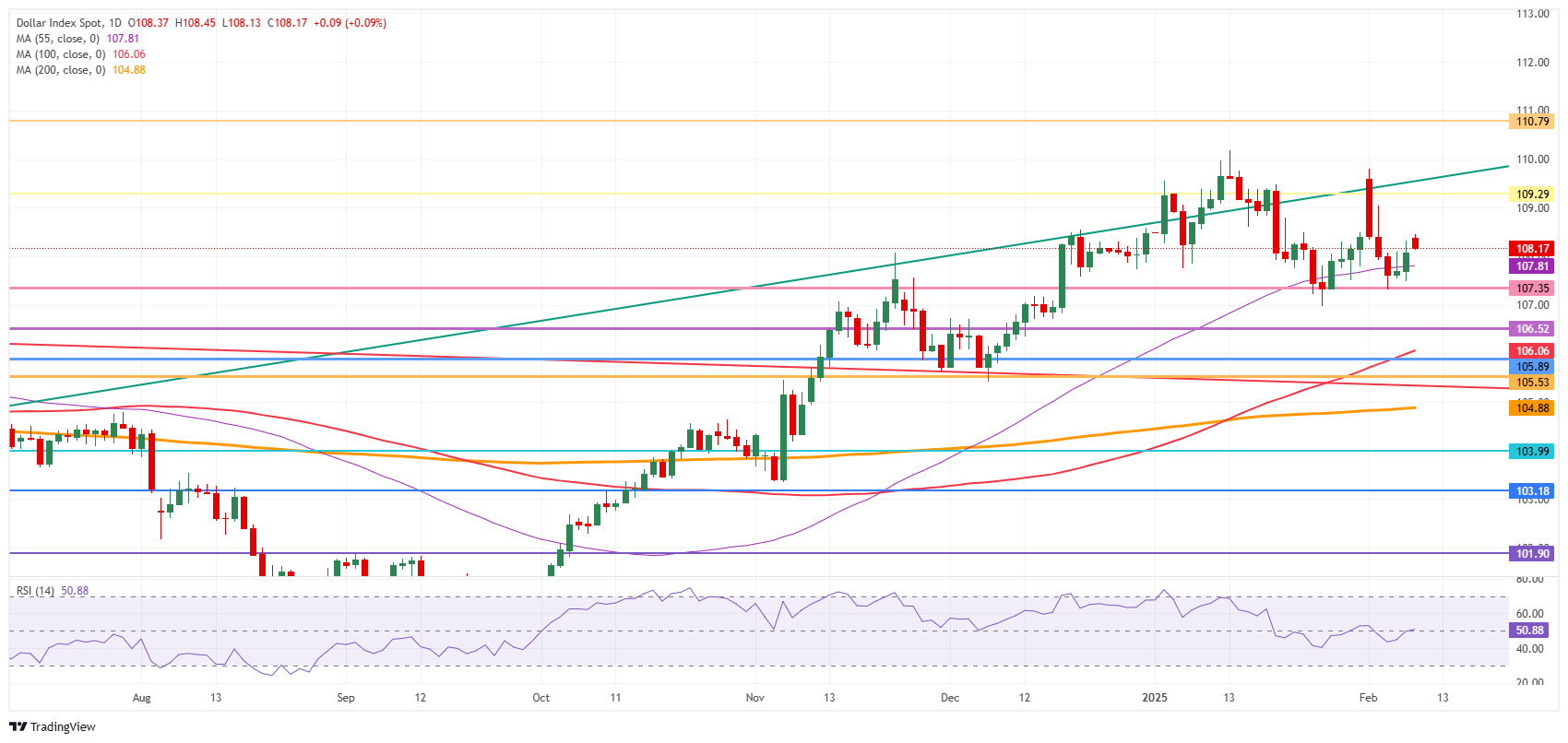
Technical analysis of the dollar index: without interest
The dollar index (DXY) is not breaking schemes this Monday and is not included in the flight to safe shelters against tariffs. Only gold seems to be the great winner in this case. Meanwhile, the yields in the US are slightly higher, although not enough to really boost a stronger US dollar, while operators evaluate what to do next with all these additional ads of tariffs.
Upwards, the first barrier in 109.30 (maximum of July 14, 2022 and a line of ascending trend) was briefly surpassed, but did not remain last week. Once that level is recovered, the next level to be reached before progress remains more at 110.79 (maximum of September 7, 2022).
Downward, the maximum of October 3, 2023 in 107.35 continues to act as a strong support after several tests last week. In case it occurs more drop, look for 106.52 (maximum of April 16, 2024) or even 105.98 (resistance in June 2024 and a half single mobile of 100 days) as better support levels.
Dollar index: daily graphic
US dollar FAQS
The US dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the “de facto” currency of a significant number of other countries where it is in circulation along with local tickets. According to data from 2022, it is the most negotiated currency in the world, with more than 88% of all global currency change operations, which is equivalent to an average of 6.6 billion dollars in daily transactions. After World War II, the USD took over the pound sterling as a world reserve currency.
The most important individual factor that influences the value of the US dollar is monetary policy, which is determined by the Federal Reserve (FED). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and promote full employment. Its main tool to achieve these two objectives is to adjust interest rates. When prices rise too quickly and inflation exceeds the 2% objective set by the Fed, it rises the types, which favors the price of the dollar. When inflation falls below 2% or the unemployment rate is too high, the Fed can lower interest rates, which weighs on the dollar.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more dollars and promulgate quantitative flexibility (QE). The QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is an unconventional policy measure that is used when the credit has been exhausted because banks do not lend each other (for fear of the default of the counterparts). It is the last resort when it is unlikely that a simple decrease in interest rates will achieve the necessary result. It was the weapon chosen by the Fed to combat the contraction of the credit that occurred during the great financial crisis of 2008. It is that the Fed prints more dollars and uses them to buy bonds of the US government, mainly of financial institutions. Which usually leads to a weakening of the US dollar.
The quantitative hardening (QT) is the reverse process for which the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvote the capital of the wallet values that overcome in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US dollar.
Source: Fx Street
I am Joshua Winder, a senior-level journalist and editor at World Stock Market. I specialize in covering news related to the stock market and economic trends. With more than 8 years of experience in this field, I have become an expert in financial reporting.